Pandemic Learning Loss Statistics 2025-2026: Education Impacts
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on December 31, 2025
The COVID-19 pandemic is behind us, but unfortunately, the pandemic learning loss is still impacting education in the U.S. and globally. In this article, we’ll explore key statistics on this learning loss with exact numbers by state and global regions, talk about 5 negative effects of COVID-19 on education, and more.
Key points
- As of January 2022, over 25% of schools were not fully open all over the world (McKinsey report) and remained closed for an average of 5.5 months (≈22 weeks) (UNESCO)
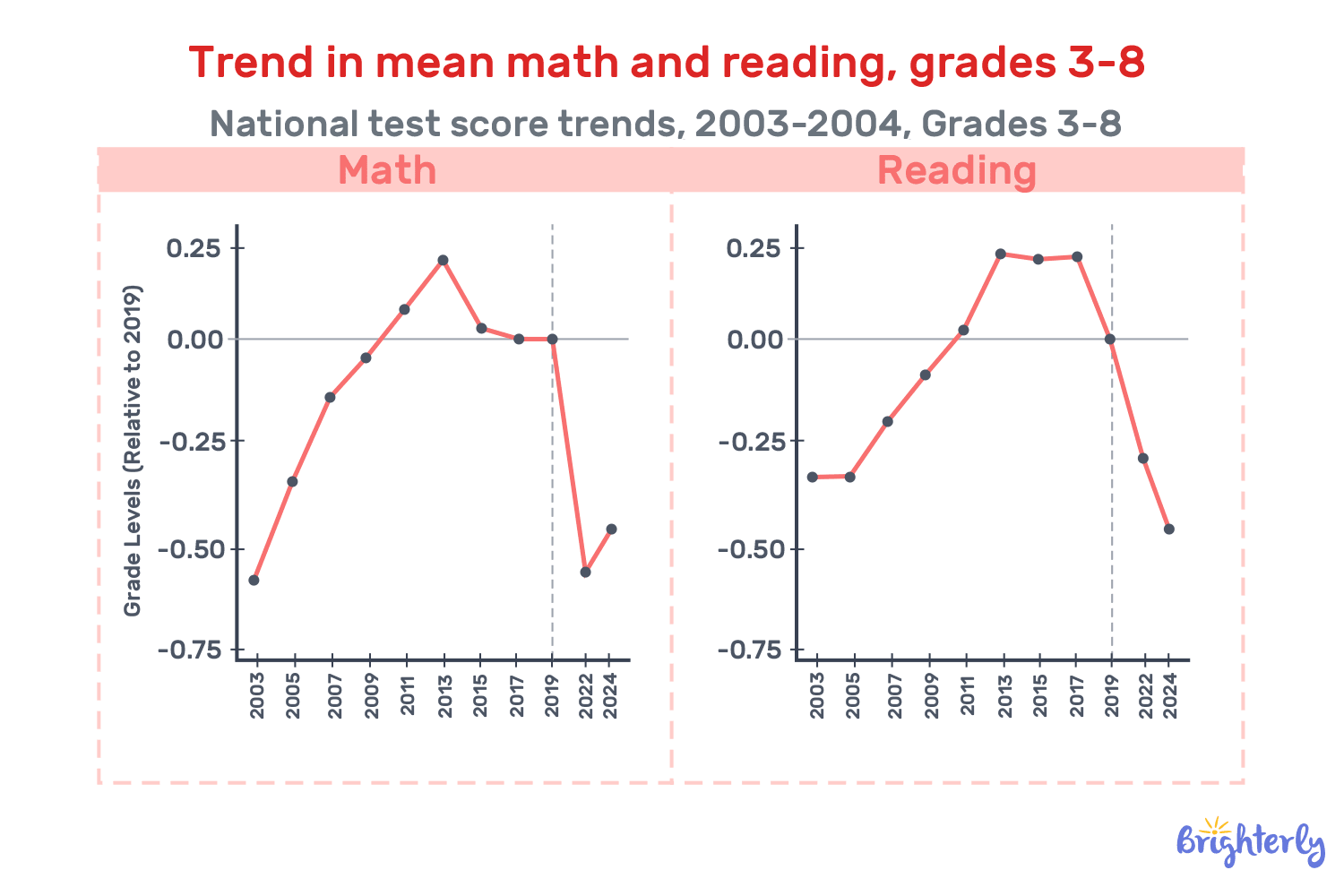
- As of spring 2024, the average US student in grades 3–8 remained nearly half a grade level behind 2019 achievement in math (Education Recovery Scorecard Report) due to the COVID impact on education.
- Post-COVID learning loss can reduce global GDP by $17 trillion by 2050.
What impact did COVID-19 have on the American education system?
COVID-19 changed the American education system to the core, making the schools stop for an average of 22 weeks and shift to online learning during the pandemic (and after it). This transformation accelerated technological innovation yet widened educational inequalities at schools, causing political and mental problems for students.
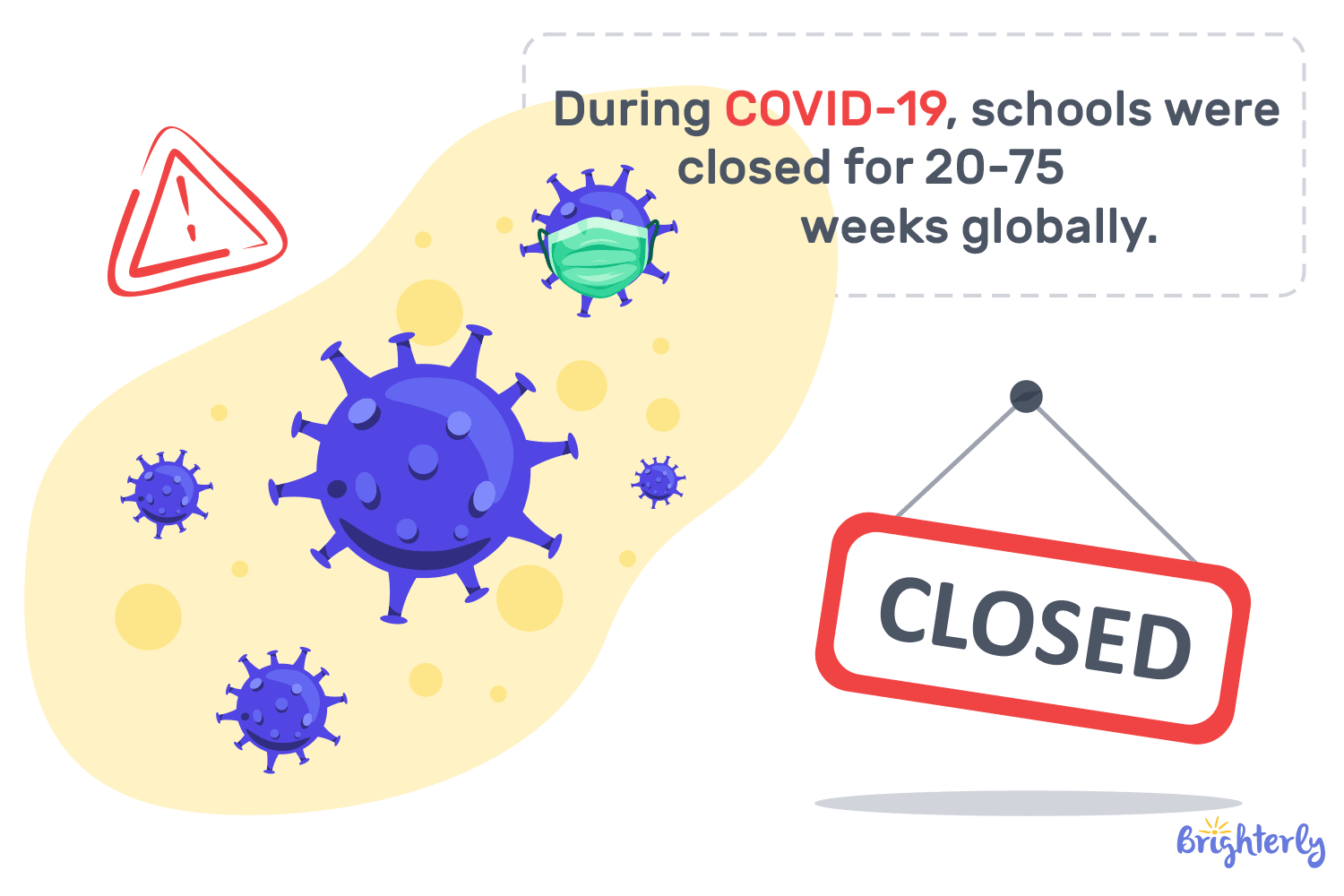
Outcomes of learning loss due to the pandemic by 2021-2022
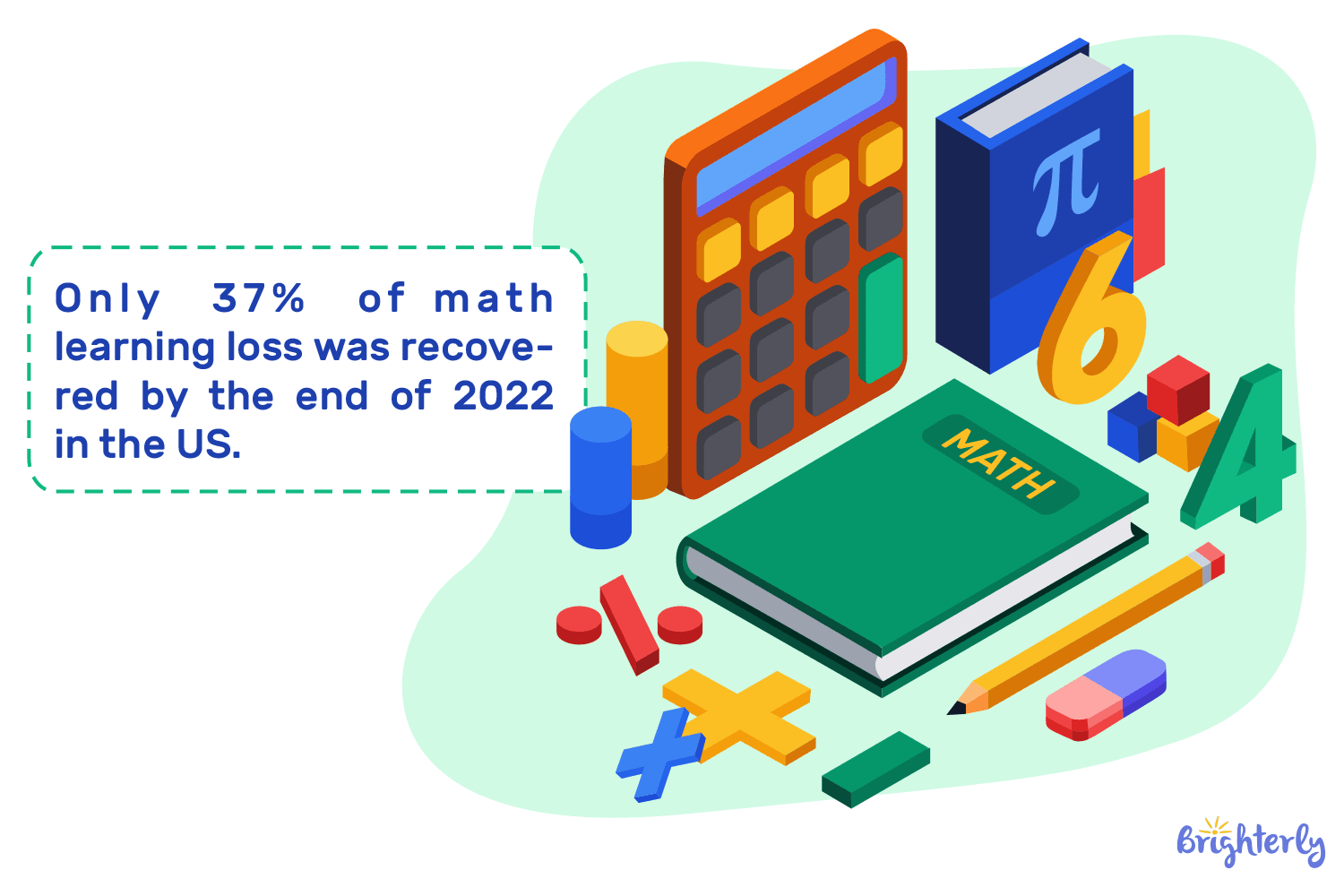
According to the study results of the National Bureau of Economic Research, isolated students during the pandemic lost an average of 0.4 years of math education by the end of 2021, and only 37% of math losses were recovered by the end of 2022.
How have students been affected by the pandemic by 2023-2025?
In 2025, the learning loss due to school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic still affected children. Education Recovery Scorecard reports that in Spring 2024, students in the U.S. were left half a grade behind pre-pandemic achievement in reading and math. To make matters worse, students even further behind in reading compared to 2022, yet there are evident patterns of recovery by race and income level.
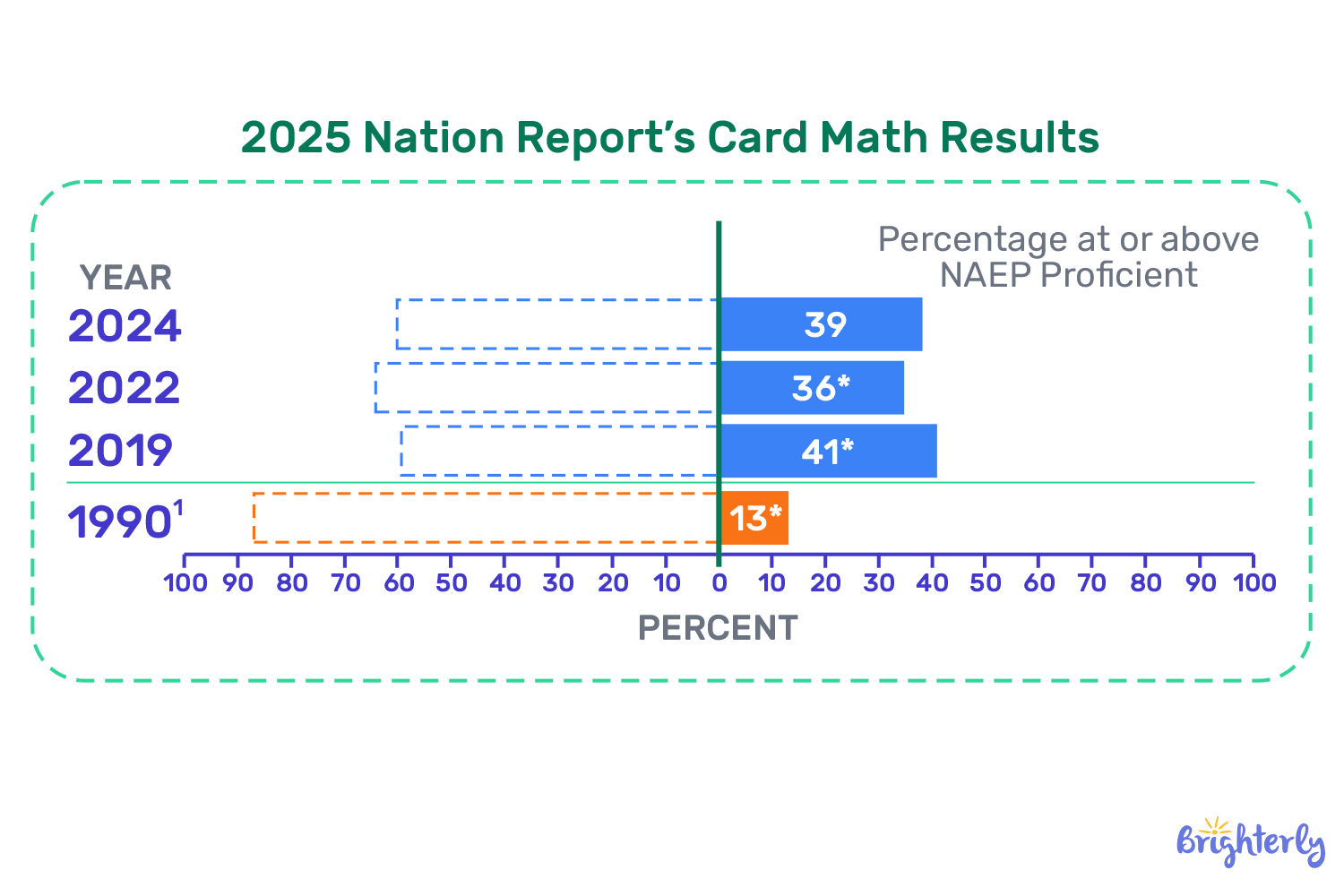
In 2024, the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) under the National Center of Educational Statistics (NCES) showed that 39% of middle school students (4th grade) performed at or above the NAEP Proficient level in math, which was 3% better than in 2022 but still 2% lower than in 2019. 24% of 4th graders performed below the NAEP Basic level, which is 1% less than in 2022 but still 5% more than in 2019.
For 8th graders, the harsh effects of pandemic on students seem even harder to overcome. 28% performed at or above the NAEP Proficient math level, which is almost the same as in 2022 but 6% lower than in 2019. 39% of 8th grade students performed the NAEP Basic level — again, almost the same as in 2022 but 8% more than in 2019.
Negative impact of COVID-19 on education in reading
Students during pandemic have also experienced learning loss in reading. As of 2024-2025, the U.S. educational system is dealing with literacy decline among schoolers. The latest National Literacy Institute data shows that approximately 64% of fourth-grade students nationwide are not reading proficiently.
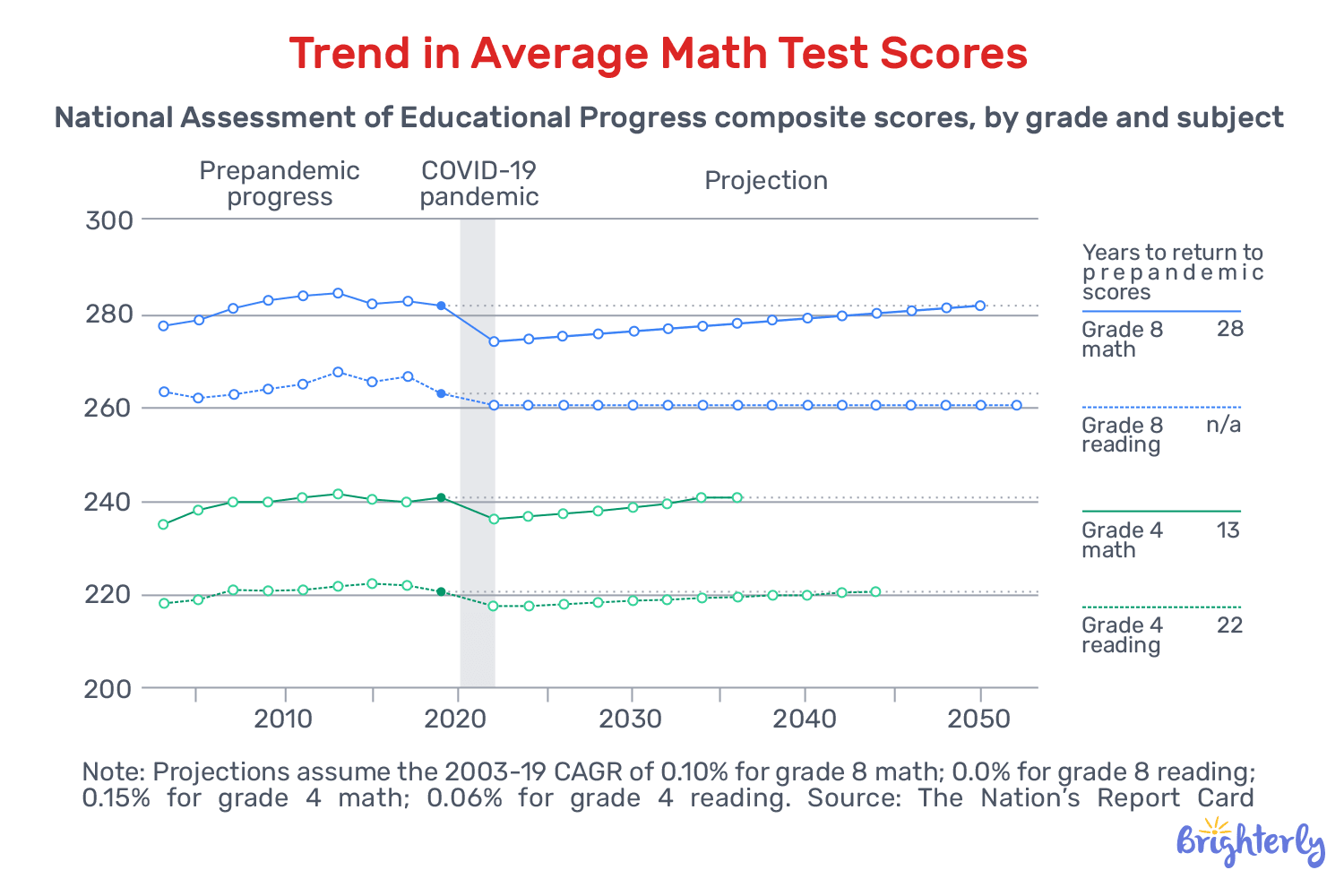
According to the NAEP research, literacy outcomes continue to decline in 2024 due to the coronavirus and schools. The average score fell to 215, down 2 points from 2022 and 5 points from 2019. This means that children’s reading proficiency returns to early 1990s levels, erasing decades of progress.
What are the key problems connected with pandemic learning loss?
The pandemic caused massive learning losses due to COVID in the U.S. and globally, with significant long-term consequences evident to each household. According to the National Report Card, the impact on education from the pandemic has caused more than 20 years of progress loss on NAEP assessments. In essence, fourth-grade students will not catch up to 2019 math levels until 2036, and reading levels until 2044.
To explore more on how has COVID affected education statistics in the U.S. in reading, these articles – Child Literacy Statistics United States and Reading Scores Statistics – go into more detail.
What can be done with post-pandemic learning loss in 2026?
In 2025-2026, it’s hard to determine whether closing schools during COVID-19 may have had any effect in stopping the pandemic from spreading. But it’s evident that this decision harmed children’s academic performance globally, and the pandemic effects on students are hard to overcome even in a couple of years.
Here’s what Geillan Aly, Founder & CEO at Compassionate Math, has to say about math COVID 19 learning loss:
“Now we have a generation of math learners who have nuances in their misunderstandings and are trying to fit new math concepts into their understanding, and seeing contradictions that they can't figure out. ”
If you feel that your child is still struggling with math or reading because of the learning loss during the pandemic, one thing that can be done today is to use the expert help of reading and math tutors. For example, the Brighterly math and reading platform is designed with the idea to make math understandable, fun, and affordable to any parent. You can check the reading and math program and see how it works.
Over 200,000 parents trusted Brighterly (4.4 satisfaction score on Trustpilot). They found it helpful based on lesson experience, tutor rating, platform score, service rating, and customer service. The personalized approach is what makes math tutoring a working tool while overcoming the loss of learning during the pandemic.
You can check the detailed program of each math class to make an informed decision!
Note: If you don’t know how to start working on your child’s education gaps, no worries! Let them pass one of these free diagnostic math tests and reading tests so Brighterly experts can comprehensively assess your child’s knowledge and adjust the program to your needs.
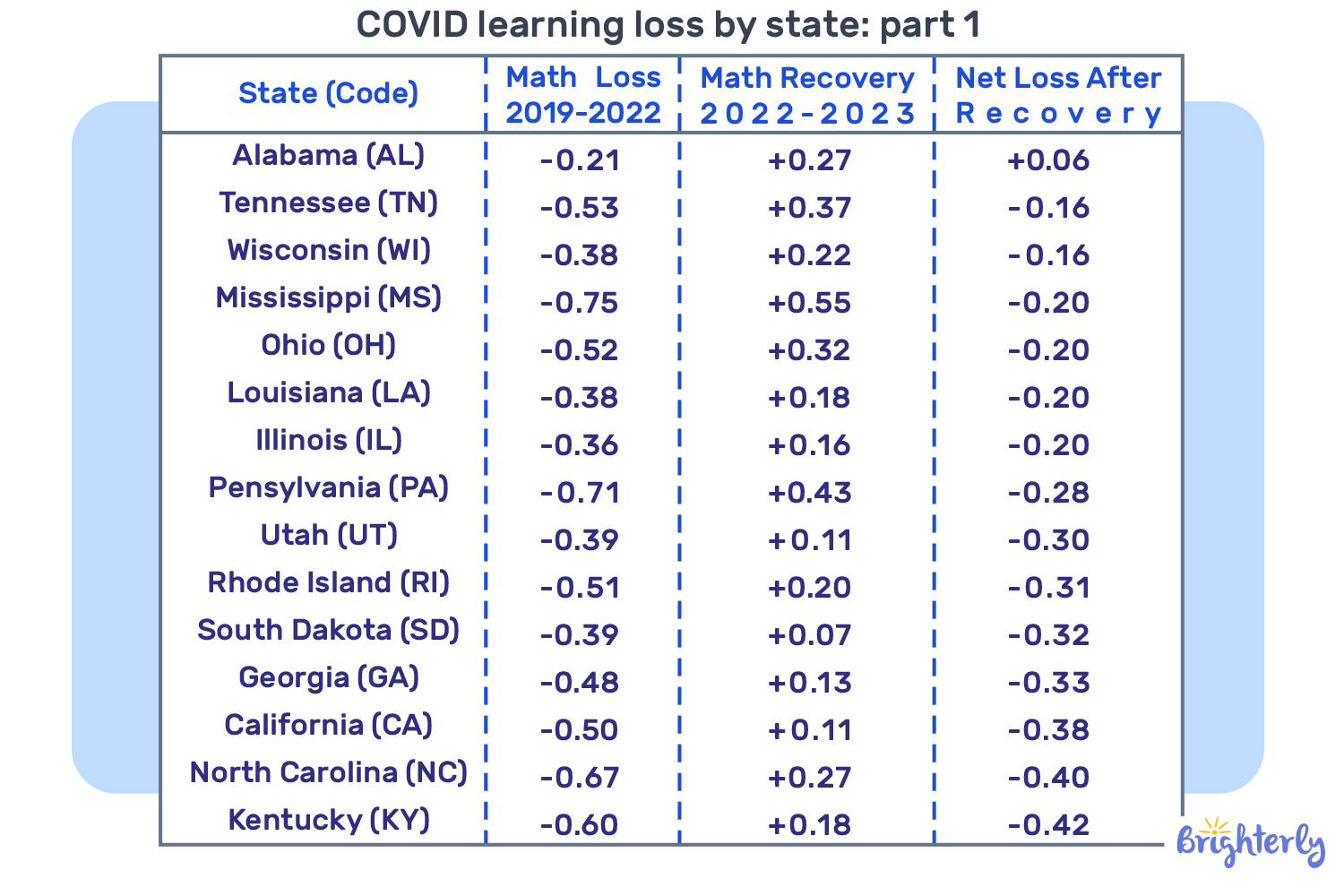
COVID learning loss by state
The table below shows how the learning loss during pandemic affected students state by state. The data is taken from the Education Recovery Scorecard (ERS) report and demonstrates the dynamic in test score results from 8,000 school districts across 30 states. The researchers annually measure pandemic learning loss by analyzing the results of state-administered standardized math tests for grade 3-8 students.
How did the pandemic affect students education in the US states?
- Alabama is the only state that managed to cover the loss of learning during pandemic and even outperformed it with an average achievement above 2019 levels in 4th grade math.
- Oregon is the only state that worsened its learning loss in pandemic.
- Tennessee, Pennsylvania, and Mississippi showed remarkable improvements in 2022-2023, enhancing by more than a third of a grade level in a single year.
COVID learning loss by state: part 1
COVID learning loss by state: part 2
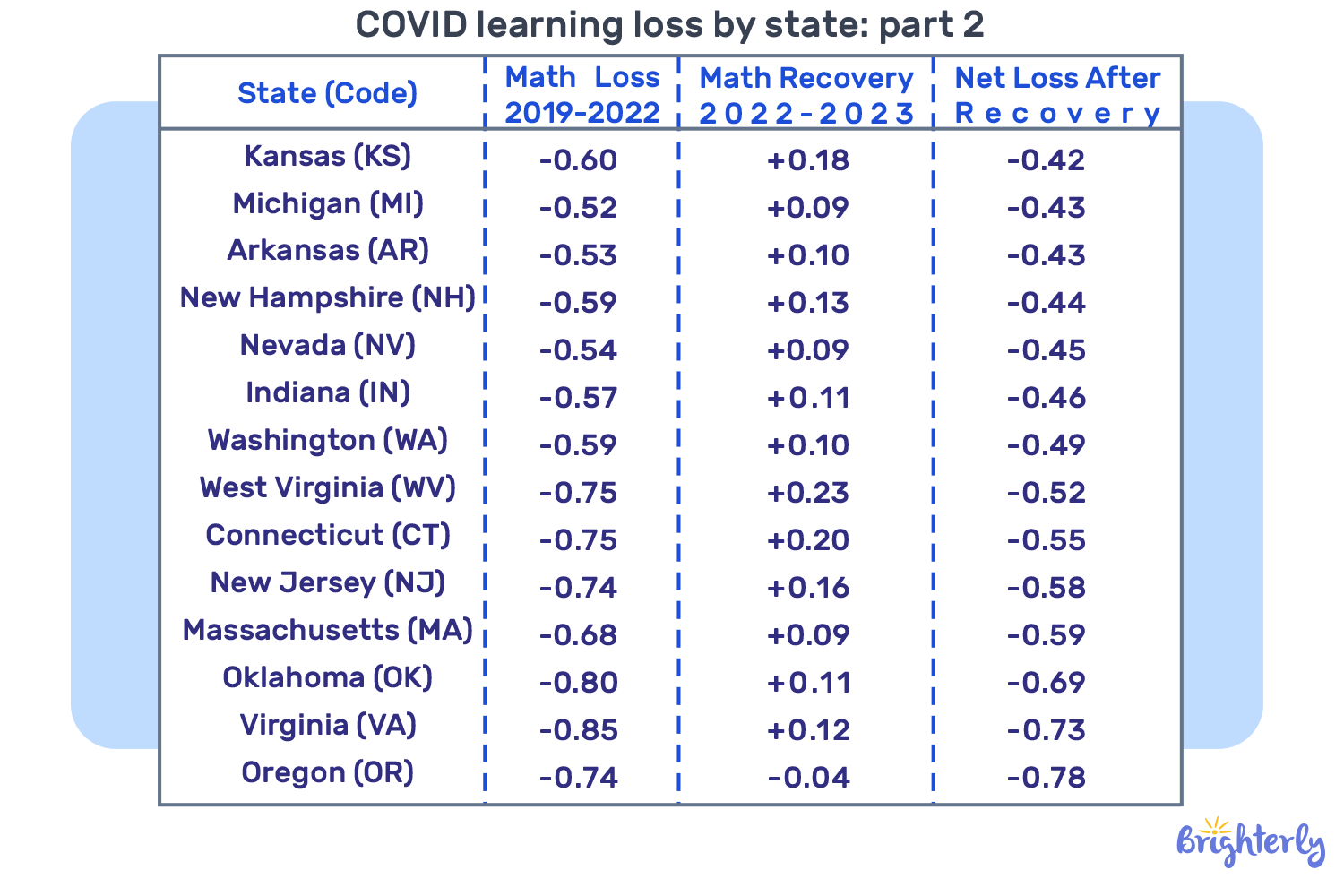
The COVID learning loss by state shows that American schools are slowly recovering from the pandemic. In terms of students’ academic performance, some states are showing success, but most are still struggling to cover the math gaps.
To explore more on standardized testing statistics, check out this comprehensive overview – Standardized Testing Statistics.
How did COVID affect students’ learning worldwide?
COVID-19 learning loss is a global problem, especially harsh on vulnerable groups in low-income, rural and marginalized areas. Similar to the US situation, where Black, Hispanic, and poor populations recover more slowly than others, the United States and Europe are better at post COVID learning loss recovery than Latin America and Africa globally.
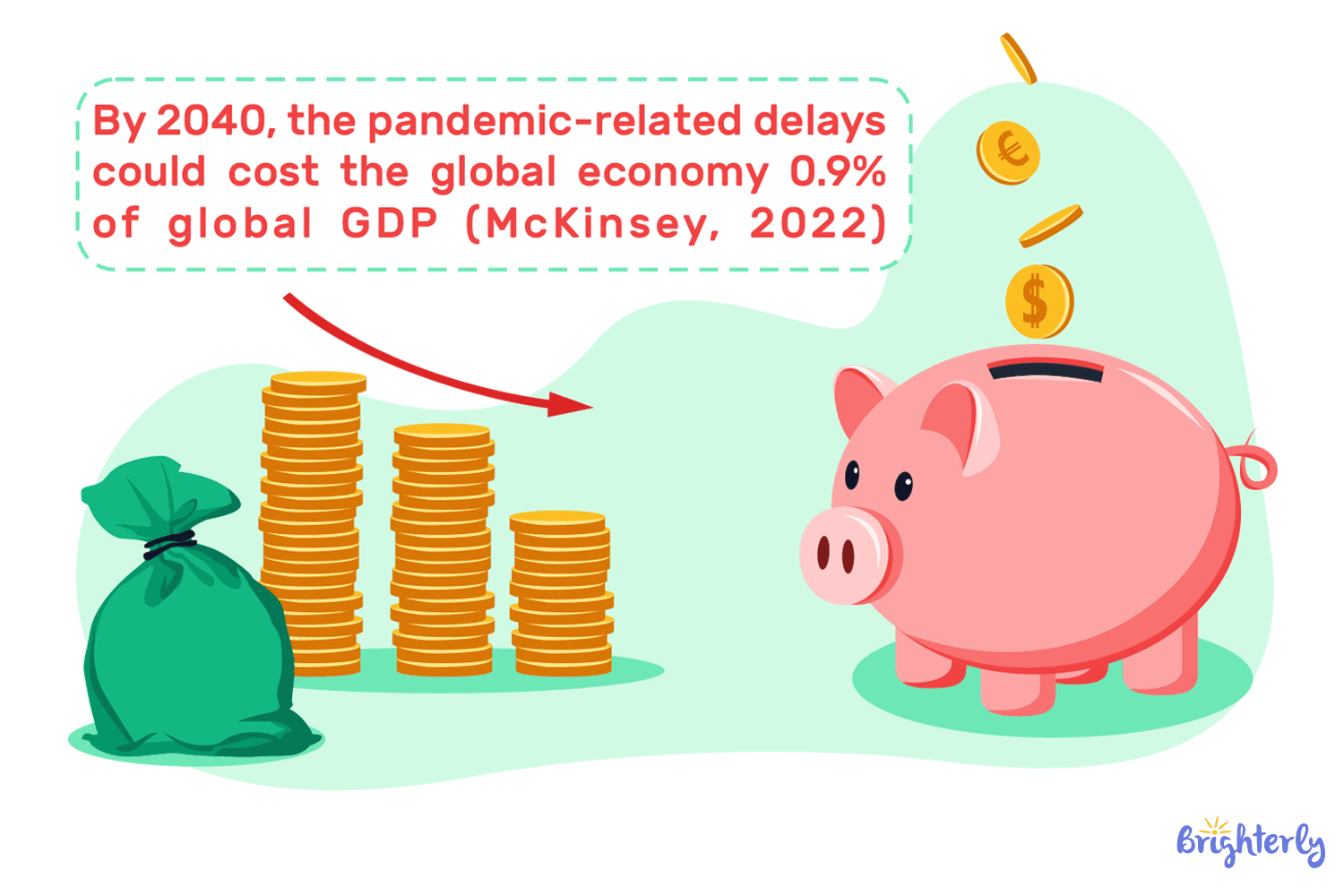
Source: McKinsey, 2022
The table below shows the average learning loss by global reach (raw estimate from UNESCO) along with key drivers that deepen the problem and prevent the region from full recovery.
Region |
Average learning loss |
Key drivers |
| USA | 7-8 months (0.36 SD) | Socioeconomic gaps, gender/performance disparities |
| Europe | 4-6 months (0.12-0.18 SD) |
Socioeconomic gaps, uneven policy responses |
| Asia | 6-12 months (0.18-0.24 SD) |
Digital divides, gender/income disparities |
| Latin America | 9-15 months (0.32-0.55 SD) |
Enrollment declines, overcrowded public schools |
| Africa | 12-18 months (0.78 SD) |
Minimal remote-learning infrastructure, economic shocks |
Pandemic learning loss statistics in Europe
The European Union demonstrates the smallest average learning loss in the world. But a closer look at the data shows dramatic differences in the performance of each EU country.
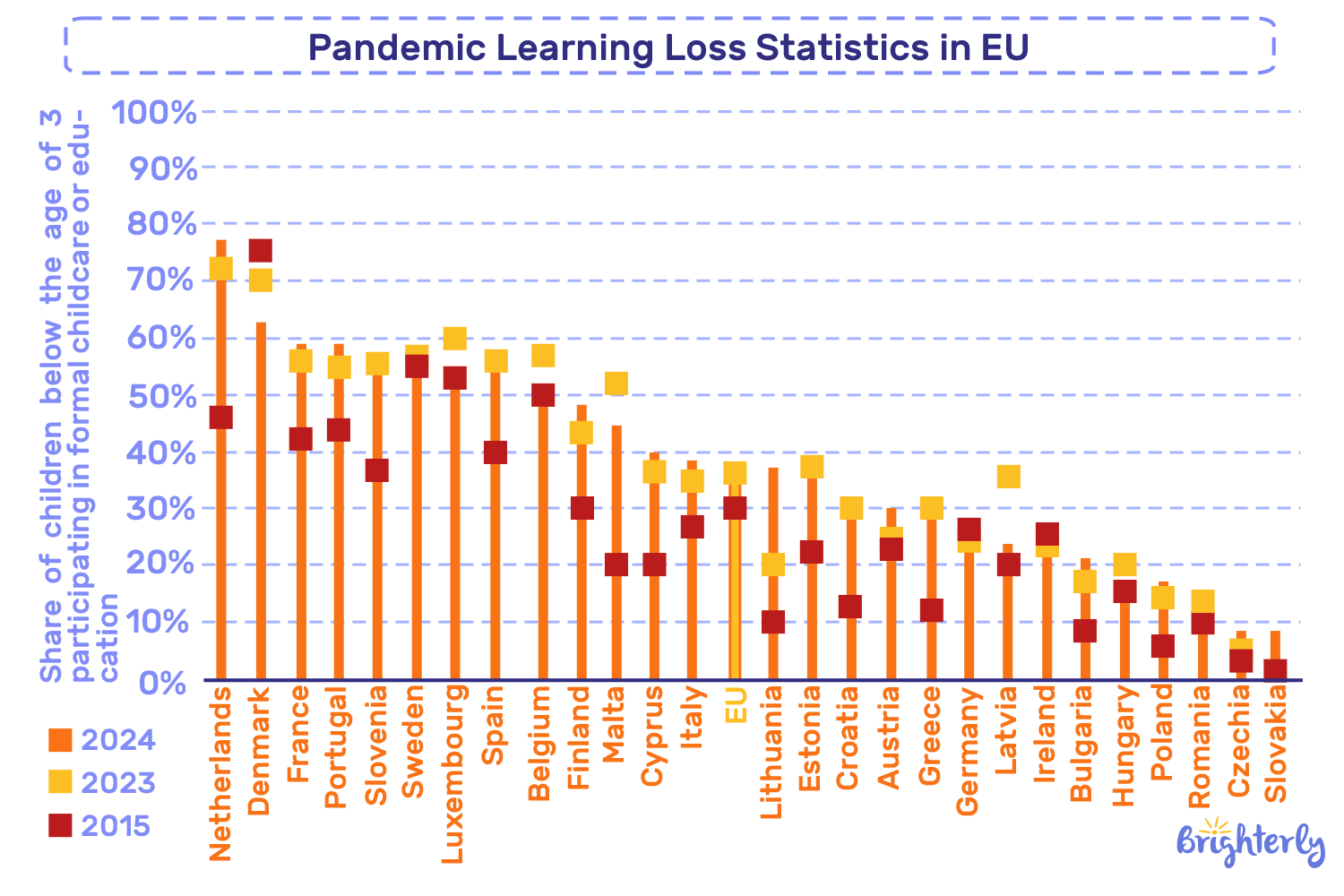
Source: European Commission Education and Training Monitor, 2025
TL;DR: Overall, the EU has made significant progress towards its 2030 educational goal. But, the COVID 19 impact on education shows uneven outcomes across countries. For instance, Croatia reduced early leaving by 9%, while Romania increased the share of early leavers from education and training even more (from over 15% to over 16%).
Note: The European Union pays special attention to early leavers from education and training because most of them become unemployed and experience difficulties in well-being, income, and social integration.
Pandemic learning loss statistics in Asia
Asian Development Bank surveyed 2,200 households and found out that multimodal learning delivery implemented by the government in all Southeast Asia countries was not working effectively in practice. Simply put, many children couldn’t access remote learning at all.
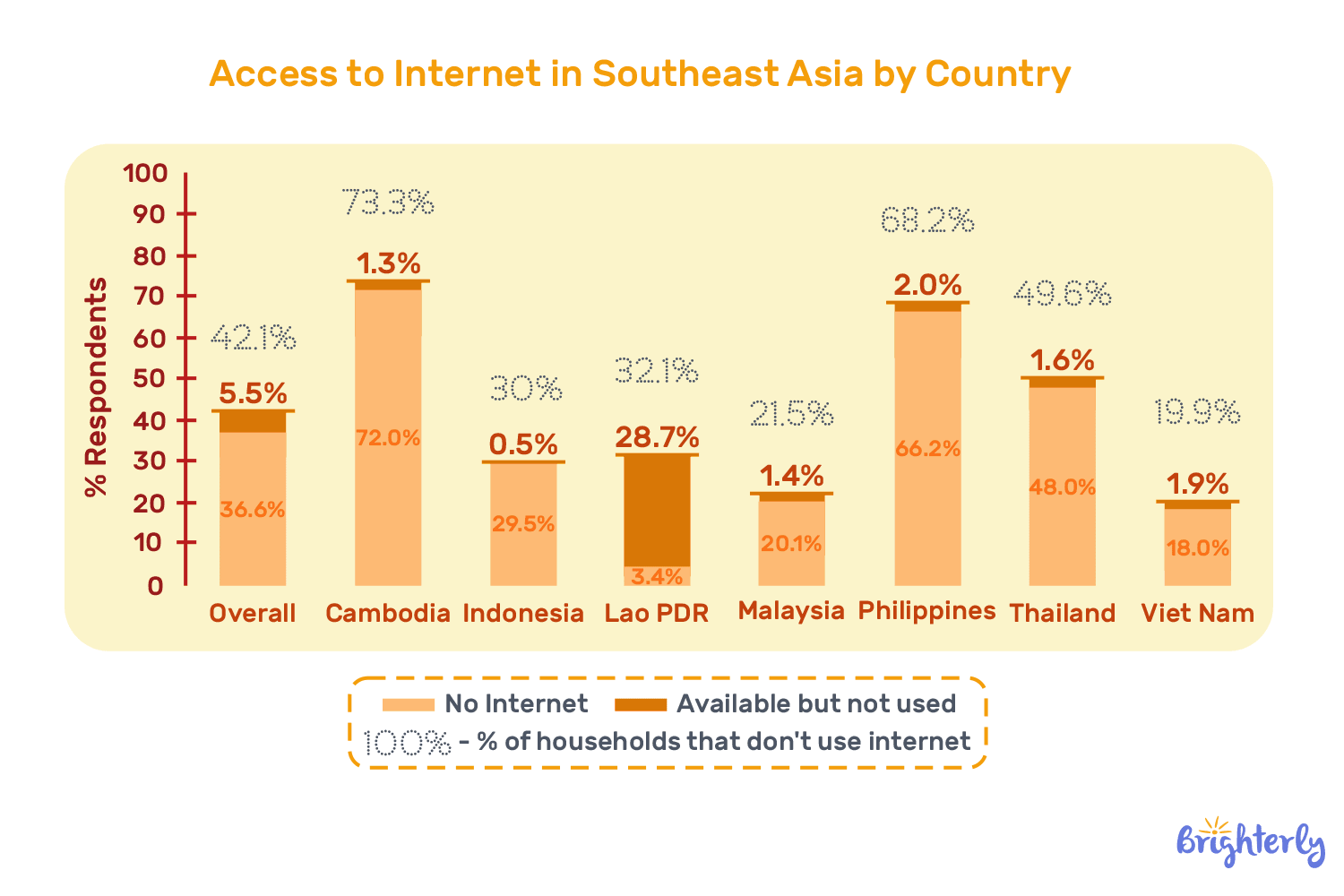
Given this situation, 80% of parents responded that they feel their children are suffering learning loss, and this percentage is lower in the countries that had access to remote learning (Vietnam) compared to no-Internet areas (Thailand, Philippines). Household income also played a difference in the responses.
Geillan Aly warns:
“Parents and teachers should take into consideration what content areas the student covered when they were doing remote learning with COVID because those content areas will likely need major reinforcements or extra support.”
The data highlights how learning gap in digital access and household income intensifies educational disparities during the pandemic.
Note: Students who had less access to remote learning models and weaker parent support suffered from the pandemic learning loss the most.
TL;DR: In Asia, the overall percentage of families that have no Internet connection and are unable to access multimodal learning is 36.6%. Given that, many of the families face significant learning loss in their children, with the Philippines and Cambodia being among the top.
Pandemic learning loss statistics in Latin America
The UNICEF report on the Latin America and Caribbean region states that 159 million children spent an average of 156 days out of the classroom since the pandemic, deepening the existing problem of 10 million children out of school already.
Like in Southeast Asia, the governmental initiative to digitalize learning didn’t meet the reality where around 40% of students don’t have access to digital or broadcast distance learning. Thus, the learning loss deepened the gap between low-income students and their high-income peers with Internet connections.
Note: 67% of educational platforms in Latin America provide only static content (no videos, textbook PDF files, or interactive math worksheets), which deepens the problem of low school enrollment in the region even further.
Pandemic learning loss statistics in Africa
The UNICEF report on Sub-Saharan Africa states that 300 million children were out of school with limited learning access to radio, TV, and the Internet.
In the region, the pandemic made already existing challenges for African schools in 2019 even more severe:
- Absenteeism and low competition: 20% of primary school age children, 33% of secondary school age adolescents and over 50% of upper secondary school age adolescents were out of school.
- Poor learning quality: Nearly 90% of 10-year-old students could not read and understand a simple text.
- Lack of qualified teachers: The continent needed 17 million additional teachers by 2030, as projected in 2019.
After COVID-19, the African situation is defined by the UNICEF report as a ‘learning catastrophe’, with learning loss, learning poverty, absenteeism, and lack of proper school attendance combined.
What are the negative effects of online learning during COVID?
Notwithstanding positive effects of online learning, pandemic learning loss and COVID-19 education impacts caused chronic absenteeism, low performance in math and reading, widening inequalities, mental health problems, and accelerated teacher shortages worldwide.
#1 Chronic absenteeism as a key pandemic’s impact on student learning
The U.S. Department of Education defines chronic absenteeism as “students missing 10% or more of school” and a severe post-pandemic challenge.
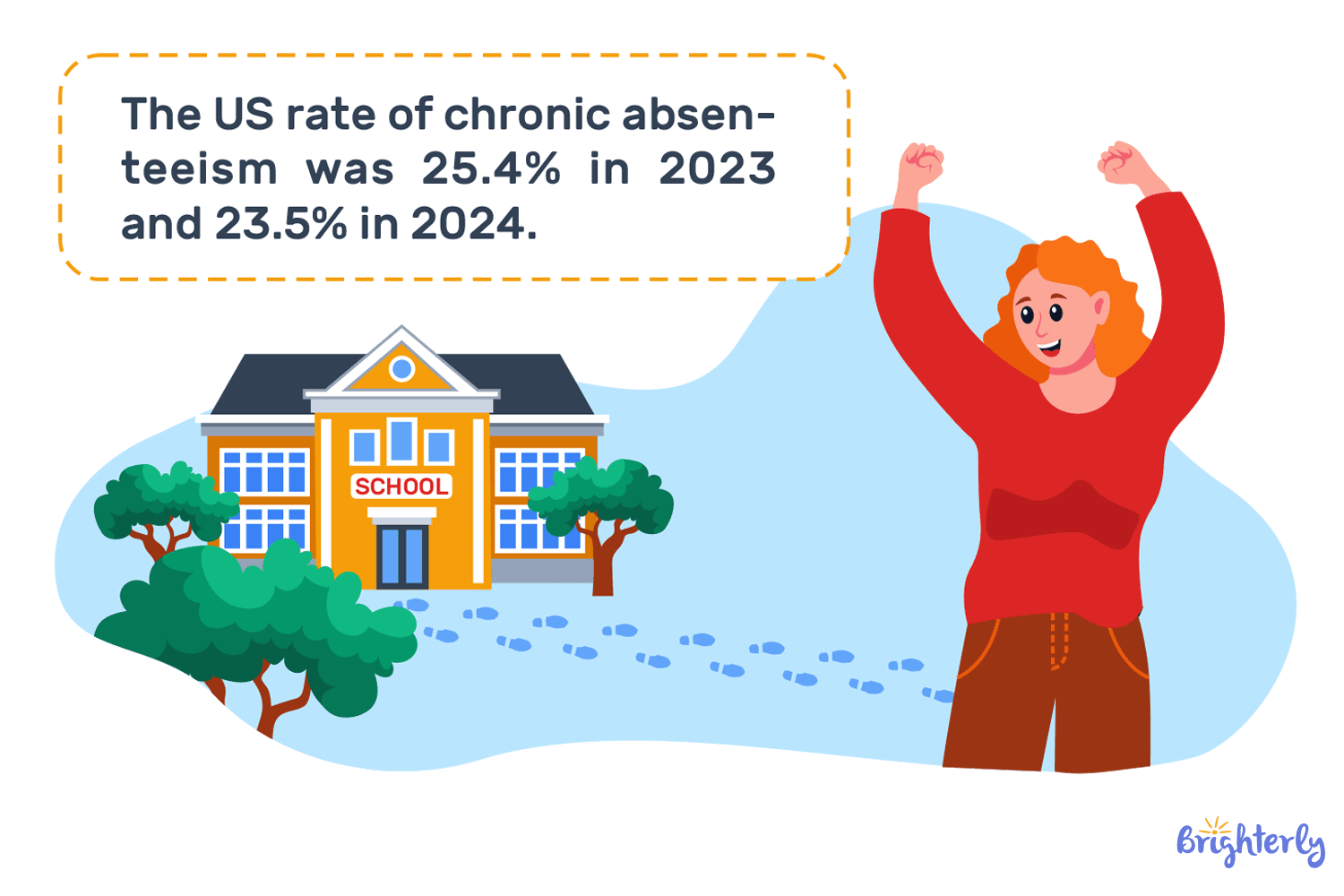
Key points
- In 2022-2023, 20 states reported over 30% of their students missing at least 3 weeks of school.
- According to the American Enterprise Institute, the absence in public schools decreased to 25.4% in 2023 and 23.5% in 2024, respectively.
- American Indians (46.1%), Pacific Islanders (45.1%), Black (37%), and Hispanic (33.2%) students showed the highest chronic absenteeism rates.
- Students with disabilities are about 36% more likely to experience chronic absenteeism.
The key complications caused by chronic absenteeism include poor academic performance and student disengagement from their peers and caring adults.
#2 Low performance in both math and reading as key negative effects of pandemic
In terms of academic performance, reading and math are the biggest challenges for learners in post-COVID times. As Axios reports, 8th graders showed the lowest reading competence (meaning the score below the “basic” metric) in the assessment’s history. Till now, both math and reading competence lag significantly and have become a complex issue for the American schooling system.
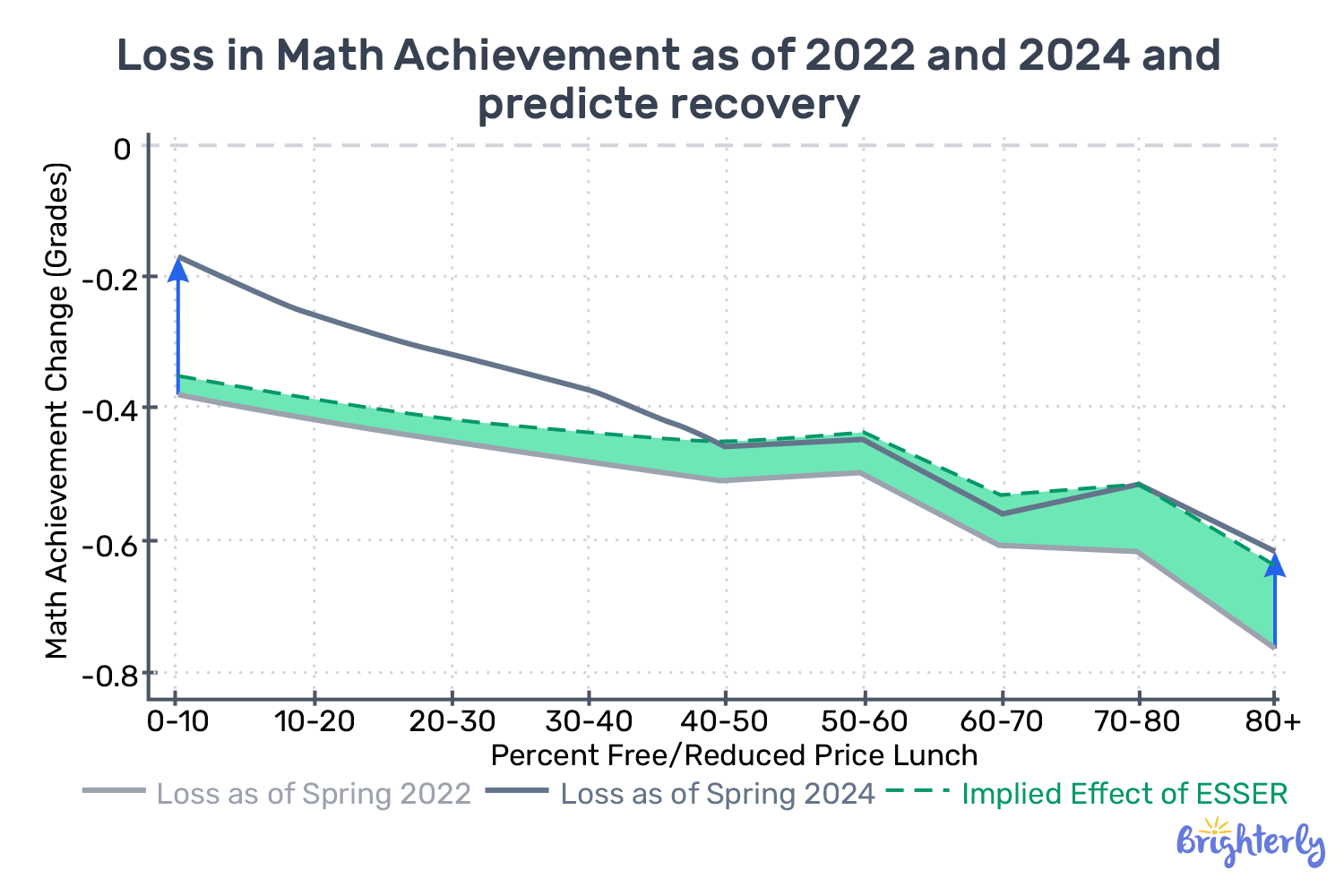
#3 Impact of COVID on students resulting in inequalities
All over the world, marginalized students (low-income, Black, Hispanic, and disabled) face the steepest barriers to recovery, with achievement gaps widening since the pandemic.
In the United States, district poverty analysis shows clear disproportions in learning loss between high-poverty and low-poverty districts (ERS, 2022).
Note: Even in Alabama, the only state that covered its pandemic learning loss by 2023, students in poorer Montgomery, Mobile and Birmingham lost more than half of grade level, while students in higher-income districts like Hoover and Shelby Counties lost little or improved significantly.
In the EU, the differences between high-income countries like Germany and Croatia and lower-income countries like Romania are also evident.
In other parts of the world, the severity of pandemic learning loss is directly linked to the income level and access to remote learning.
#4 Mental health problems
How did COVID affect mental health of students? As the Los Angeles Times reports, mental health issues and slow academic recovery are two key compound negative effects of COVID learning loss these days.
In many ways, society has moved on from the pandemic, but its impact on our kids’ learning is still very much with us, – said Stanford University professor Thomas S. Dee.
Social isolation, increased anxiety, and concentration problems are the key challenges for students, causing them to disengage from school activities, suffer from constant stress, and demonstrate academic unachievement.
#5 Teacher shortages as a severe short-term risk
The Economic Policy Institute lists teacher shortages as a negative pandemic effect that worsened an already existing crisis.
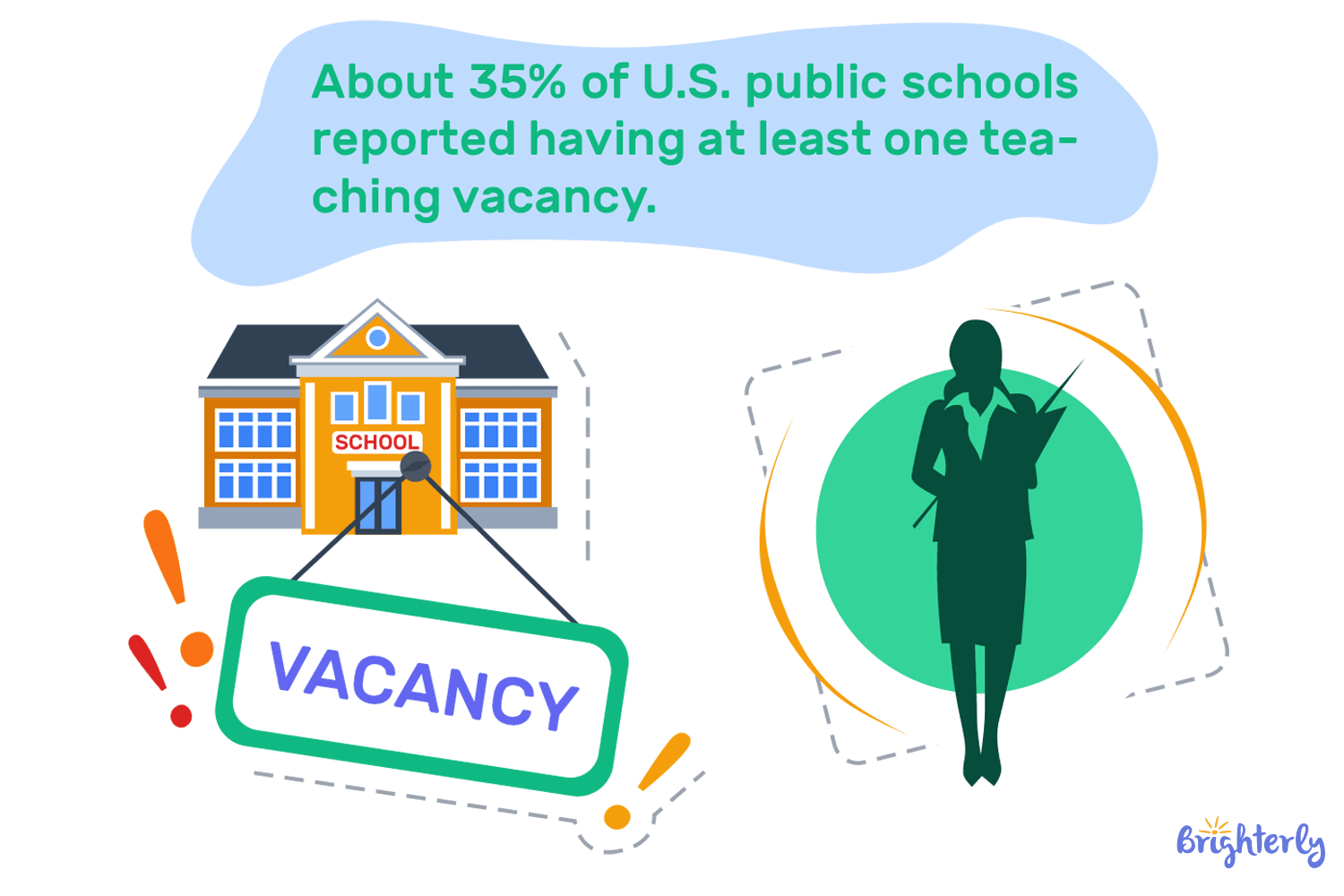
How the pandemic affected education – key numbers:
- In 2021, nearly 42% of teachers said they considered leaving their jobs during the 2020-2021 academic year.
- In 2022, all 50 states reported teacher shortages in the math subject.
- In 2024, the world needed 44 million more teachers (with 15 million in sub-Saharan Africa alone)
- According to the Houston Chronicle, in 2025, high teacher turnover continues with several hundred teachers leaving in a single year due to the enormous workload and systemic changes.
- By 2030, the world will need 69 million more teachers to achieve the universal basic education goal.
Have American schools done enough to combat pandemic learning loss?
Most research on learning loss due to COVID states that American schools are not systematic enough in fixing the existing problems. The federal funding is not allocated effectively, while some effective local initiatives are not big enough to bring stable results on a federal level.
Federal funding
The Biden-Harris Administration created the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) fund that allocated $190 billion in 3 tranches to deal with the impact of COVID 19 on education.
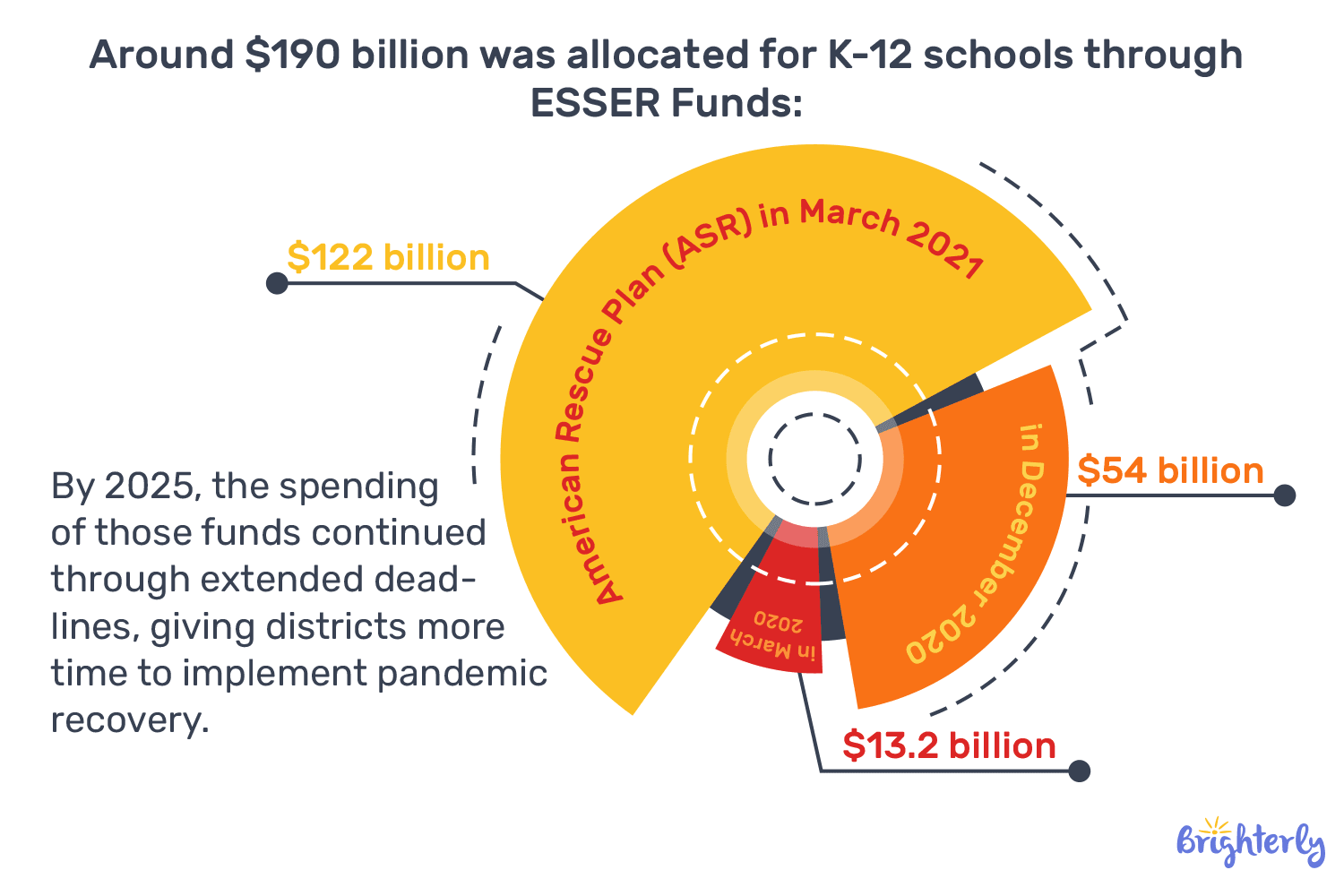
Although the funding covered some education-related problems and introduced tutoring, expanded learning times and summer schools, the majority of students are still suffering from the pandemic learning loss.
Note: In early 2025, the Trump administration froze federal education grants and pandemic relief funds, including $106 billion in K-12 education funding for Massachusetts.
Local incentives
Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Tennessee are among the states that managed to achieve positive changes in learning loss in pandemic recovery recently.
How did COVID affect education in Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Tennessee?
- High-dosage tutoring, or intensive groups and 1:1 sessions aligned with the curriculum
- Summer learning programs from federal funding
- Teacher professional development, including training in math instruction
- Buying high-quality materialsfor studying
- Personalized approaches to address specific student problems
Although these measures have brought positive results, they haven’t fixed the situation nationwide, yet provide good examples on how to combat pandemic learning loss on a community level.
Note: While the American education system is still figuring things out nationwide, you can start working systematically with Brighterly math and reading tutors for an affordable price from 17.3/lesson.
Pandemic learning loss and COVID-19 education impacts: Conclusion
The impact of post-pandemic learning loss on the future of the world is hard to underestimate. Targeting the most disadvantaged, low-income, and no-Internet minorities all over the world, the crisis is still unfolding.
So how did the pandemic affect students?
- On average, U.S. students are 5.5 months behind pre-pandemic levels in a month.
- Only a couple of states managed to achieve full or substantial recovery from pandemic learning loss.
- The disparities between income and racial groups are evident all over the world.
- Chronic absenteeism, teacher shortages, and a high percentage of early leavers from education and training are the key short-term risks connected with pandemic learning loss in the world.
Without urgent, targeted action, the world in general and the United States in particular risk cementing a generational crisis with cascading economic and social consequences. But since no systematic change is happening today, each parent faces the need to act. The best way to help the kids combat the learning loss is to provide them with extra materials, remote tools, learning opportunities, and emotional support.
If you’re looking for free resources to quickly fix some math-related problems for your child, give a try to Brighterly’s reading worksheets & math worksheets. These PDF materials are grouped by grades and math problems to help parents study with their kids.
Based on the experience of Mississippi, Louisiana, and Tennessee, high-dosage tutoring is a proven way to stop pandemic learning loss in individual students. If your goal is to find a qualified teacher ready to study with your kid systematically, book free lesson with Brighterly