Base Ten Numerals – Definition with Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on January 8, 2026
Imagine a world where numbers lacked structure, and 1 and 10 looked completely different. In this world, to count above 10, we would need to learn what seems like an entirely new language. Luckily, we don’t have to do it, and the reason is the base 10 system.
Base 10, also known as the decimal system, is the foundation of every number we use daily, bringing simplicity and order both to mathematics and to our lives.
So, in this article, we will be looking at what is base 10 in math, how to find the value of a digit, the decimal number system, place value, and more.
What is base ten?
The answer to what are base 10 numerals is straightforward. It’s simply referring to the fact that in this system, we use exactly 10 unique symbols to represent every number, no matter how big or small that number is. This system, which is also known as the decimal system, is the foundation of mathematics.
What are base ten numerals?
The base 10 numerals are the symbols we use every day to express numbers in math and in life. Those symbols are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
They are also called the Hindu-Arabic numerals, so if you come across this term, don’t be surprised!
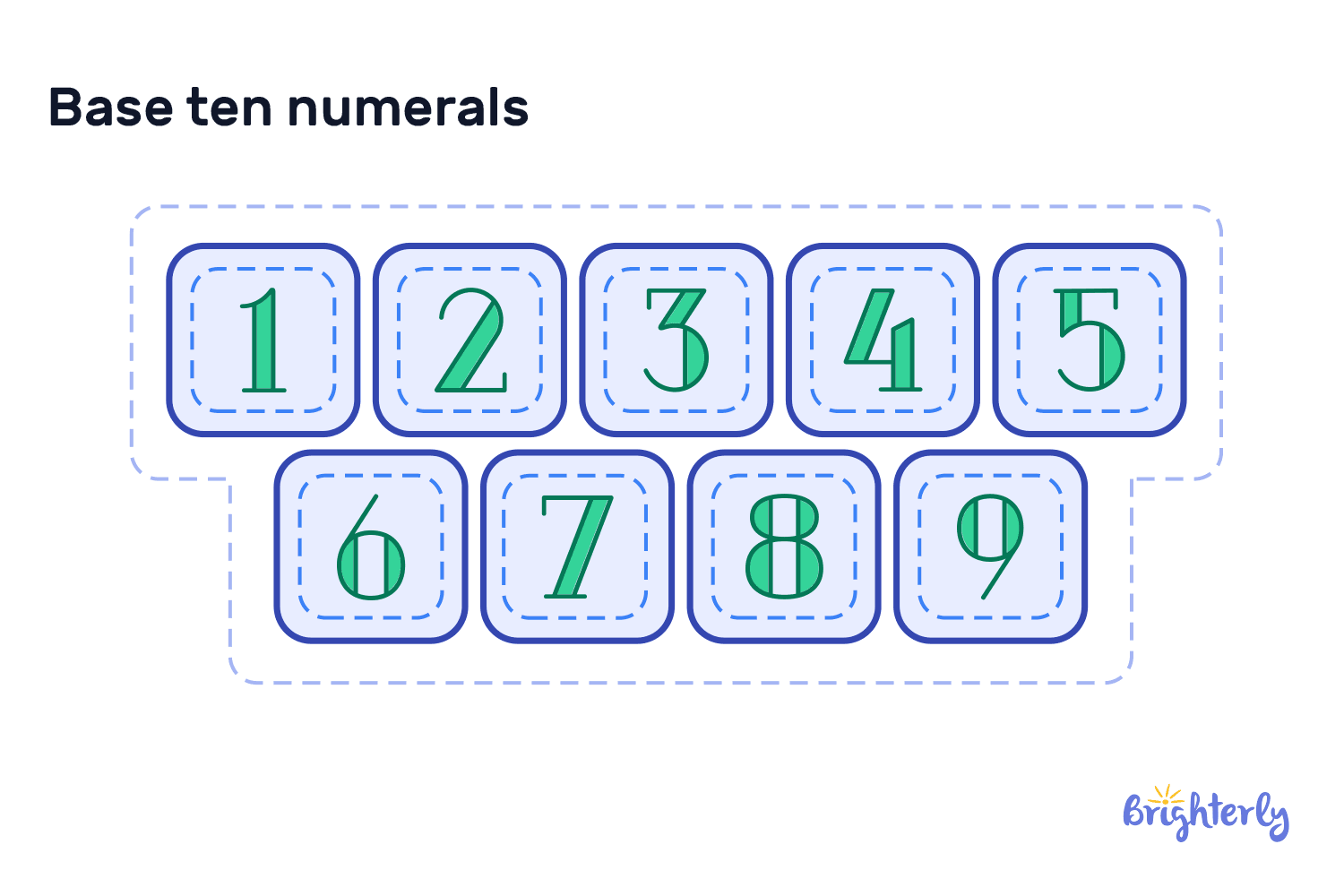
Base ten numerals definition
The definition of base ten numerals captures the structure of the everyday numbering system we use. We can separate the base ten number system based on three characteristics:
- Ten symbols are the ten distinct numerals we discussed, 1-9 and 0. No matter what number you want to write, it will be an arrangement of these symbols.
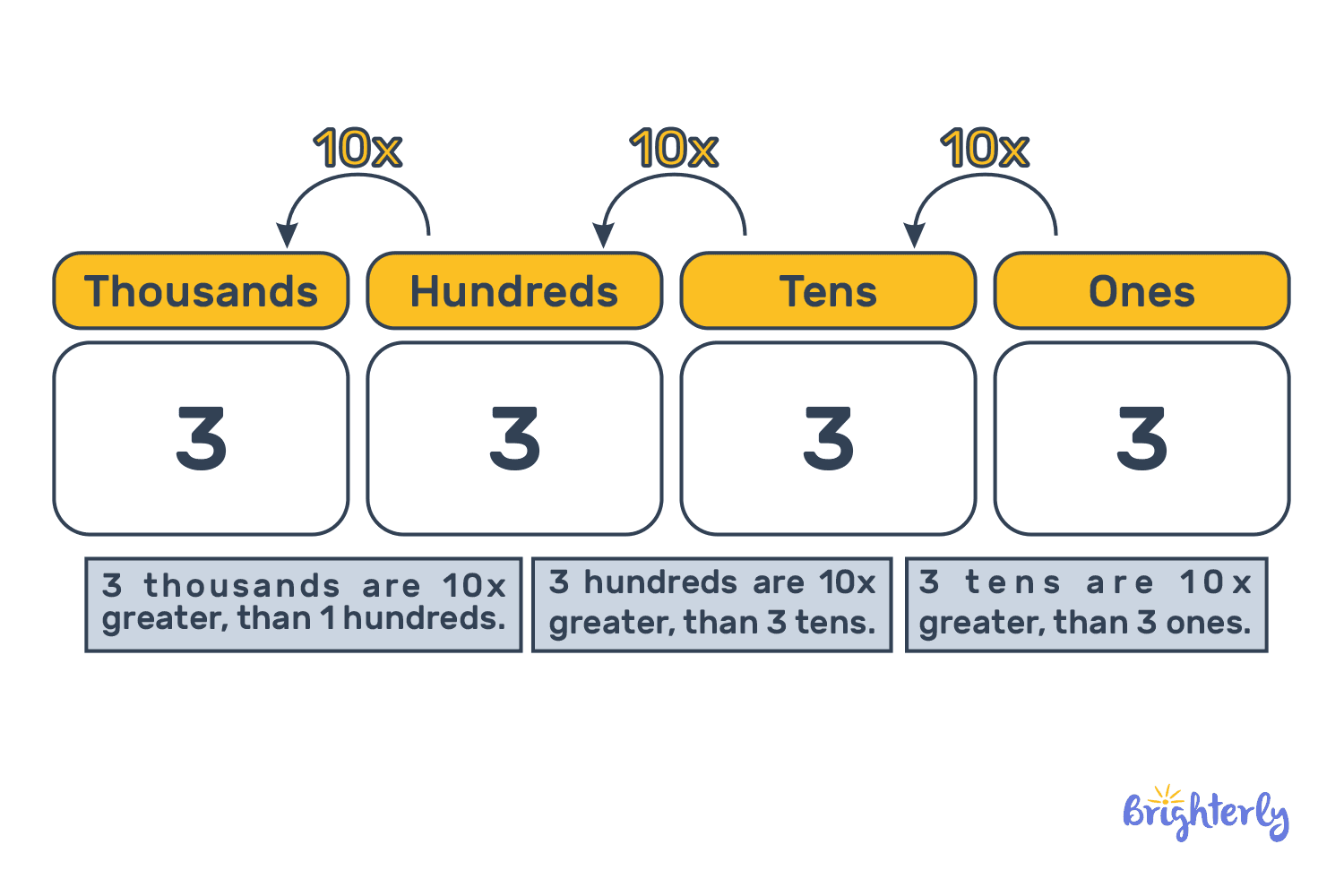
- Positional notation is another key characteristic, as the base 10 system is a positional system. To put it simply, the position of the digit in the sequence determines its value. For example, in the number 458, 8 means 8, 5 means 5 tens, and 4 means 4 hundreds.
- The last characteristic is the power of tens. When you move in the sequence from left to right, the value of the place is multiplied by 10. For example, 10s are 101, 100s are 102, and so on. This is also why the system is called base 10.
So essentially, we can define base 10 in math as building blocks, which, when you place them in the correct position, can help you represent any number and quantity accurately and easily using just a few symbols.
How to write a number in base 10 form?
You already do it every day! Writing a number in base 10 form just means writing it in the standard numerical form we do for everything. For example, the number “four hundred sixty-five” is written in the base 10 number system as 465. This form is efficient because the position of each numeral (4, 6, and 5) automatically tells us its place value.
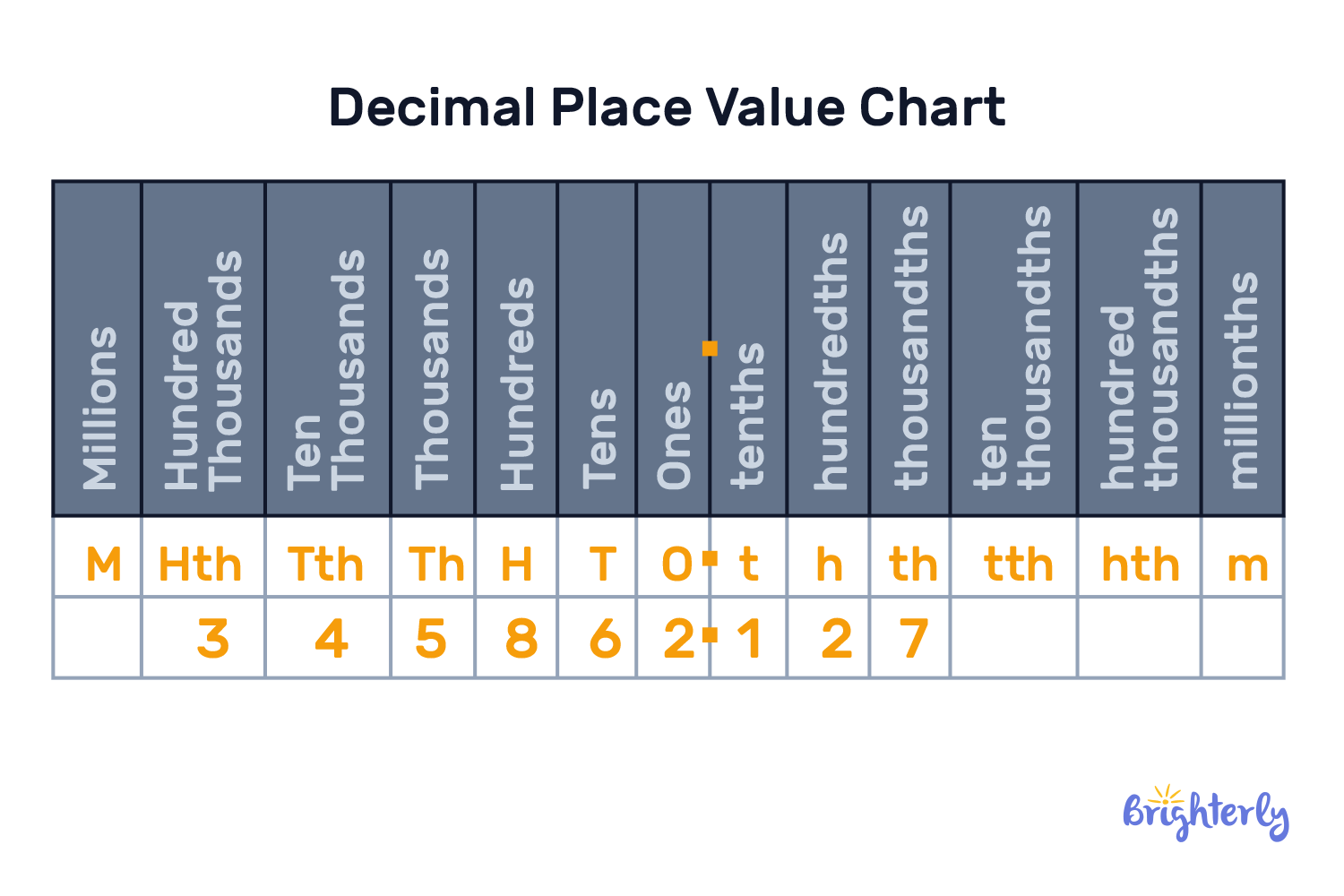
Base ten place value chart
The easiest way to visualize how the base ten number system works is through a chart. Below, you can see how the position of each digit determines its value.
If you think of each number as a column, then the value of each number is 10 times larger than the value of the number to its right.
This is true both for whole numbers and decimals. One important thing to note, however, is that, in the case of decimals, while the number keeps decreasing as you move to the right, the naming flips. While in the case of whole numbers hundredth was larger than the tenth, in the case of decimals, the tenth (or the numeral closer to the decimal point) is bigger than the hundredth, and so on.
Base 10 form example
Let’s take the number 5862.12 as a base tens example and see how it is read using the place value chart:
- 5 is in the thousands place, so its value is 5000.
- 8 stands in the hundreds and is valued as 800
- 6 is in the tenth place and has a value of 60
- 2 is in the ones place, and is valued at 2
- 1 (after the decimal point) is in the tenths place, so it’s valued at 0.1
- 2 (after the decimal point) is in the hundreds place, so it’s valued at 0.02.
How to find the place value of a digit?
Finding the place value of a number is relatively simple and depends mainly on its position relative to the decimal point. The decimal point is located right after the ones place of a whole number, so it comes right after the whole number ends and the fraction starts.
To determine the value of a whole number, count from right to left, starting with ones and moving to tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands, and so on.
To find the value of decimals, start counting from the first digit to the right of the decimal point: the first place is the tenths, the second is the hundredths, the third is the thousandths, and so on, with each place representing a negative power of ten.
Then, to find the value of the digit, simply multiply it by the value of the column it is in. For example, the 4 in 3452 is in the hundreds place, so its value is 400.
Base 10 decimal number system
The base ten number system is often called the decimal number system, mainly because of its strong connection to decimals. The decimal point extends the system of whole numbers to also include fractions of one.
In this base ten numbers system, anything left of the decimal point is a whole number, and anything right of the decimal point represents numbers smaller than one, such as tenths, hundredths, and so on.
Numbers in the decimal number system
As we’ve mentioned earlier, you can write any number in the decimal number system using the 10 unique numerals (1-9 and 0). This is the base ten numeral form. While whole numbers consist of a single part, decimal numbers consist of two parts separated by a decimal point. The whole part of the number is to the left, and the fractional part is to the right.
Base of a number system
When referring to the base of a number system, we mean how many unique digits it uses. It also refers to how much the place value changes for each digit. In the base ten system, as the name suggests, we use ten unique numerals. The value of each digit also grows and shrinks by the power of ten as you move left or right, respectively.
How to show the base-ten?
Although very rarely, sometimes your kid needs to specify that they are using a base 10 system. For this, they can identify it using the ten as a subscript, like so 9765. However, the base ten numeral system is so prevalent, simply writing the number correctly will convey the value you intended.
Expanded form
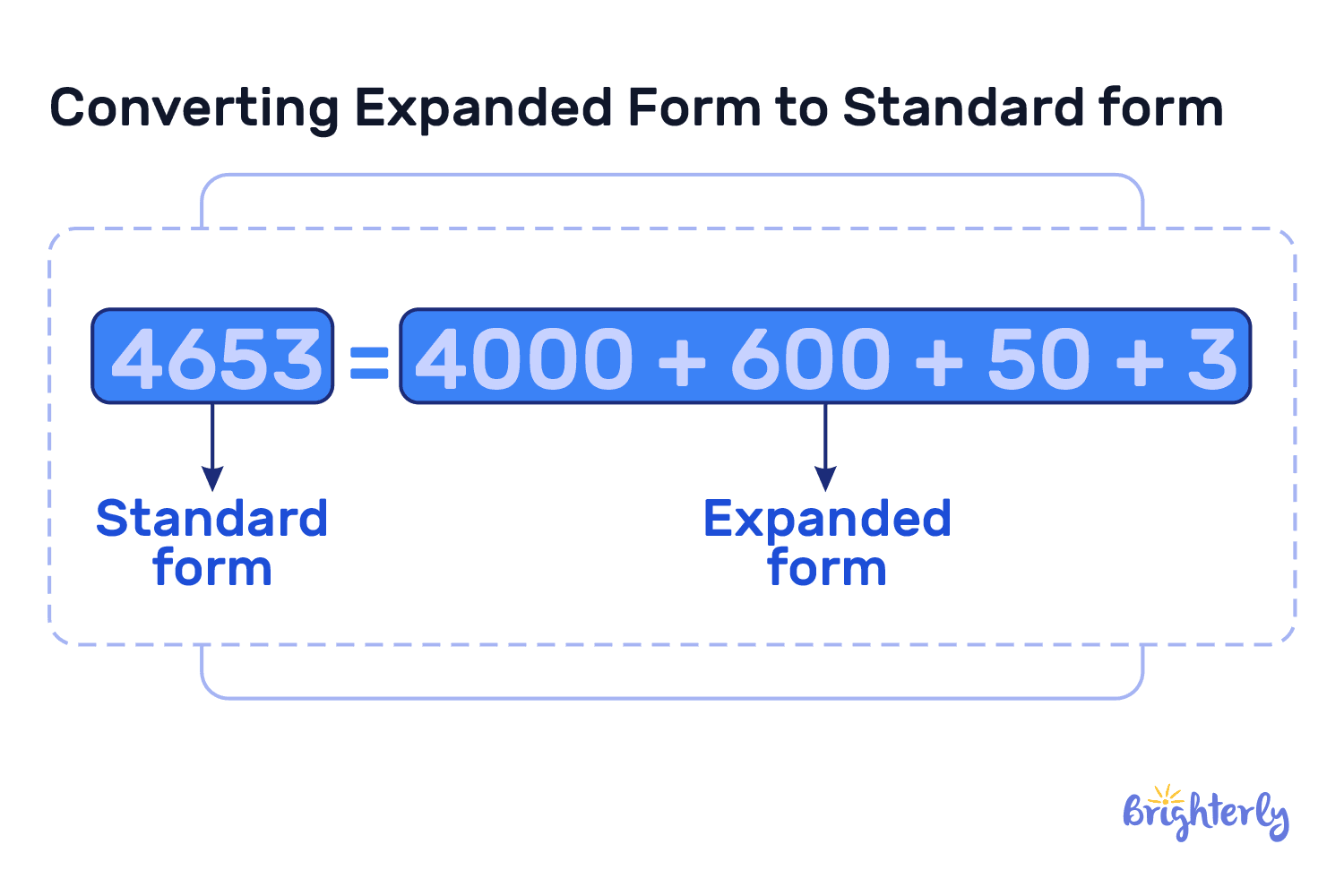
One of the easiest and most understandable ways to show the structure of the base 10 system is the extended form. Explained simply, to get an extended form of a number, we need to break it down to the sum of the values of each of the digits. So, the extended form of 12673 would be:
10000 + 2000 + 600 + 70 + 3.
You can break it down further, like so:
(1 x 10000) + (2 x 1000) + (6 x 100) + (7 x 10) + (3 x 1) = 12673
Place values in decimals
The place value of decimals works the same way as whole numbers, but, as mentioned earlier, the powers of 10 are negative.
The first position after the decimal point is the tenths (not ones, like in the case of whole numbers), followed by hundredths (1/100), and so on. So, 0.29 would be (2 x 1/10) + (9 x 1/100).
Solved examples on base ten
1. What is the value of the digit 6 in the number 46091?
Solution: Digit has the 4th position relative to the decimal point (ones, tens, hundreds, thousands)
Answer:
| 6000 |
2. Write the following number in standard base ten form: (5 x 1,000) + (8 x 100) + (1 x 10) + (4 x 1)
Solution: 5000 + 800 + 10 + 4
Answer:
| 5814 |
3. What is the place value of the digit 5 in the decimal number 0.305?
Solution: Digit has the 3rd position in the decimal space (tens, hundredths, thousandths)
Answer:
| 0.005, thousandths |
Base-ten numeral: practice math problems
Frequently asked questions on base-ten
Why do we use base ten?
We use the base ten system because it is an efficient positional system. This means that you can use only ten digits (0-9) to represent any number. All you need to do is simply change their positions relative to the decimal points.
How do you write in base-ten numerals?
Base ten numerals are the standard numerals we know. We write each numeral in a position that determines its value. For example, if you write 4 as the second number after the decimal point, it will be valued at 0.04.
What is the significance of base ten in real life?
The main significance of this system is that it is the foundation of all daily calculations, measurements, and operations everywhere. Knowing the base 10 system is essential for finance, engineering, and even timekeeping, and its consistent structure makes it very versatile.
How is base ten related to place value?
The base 10 system is directly dependent on place value. Each position in the system is a power of ten, and the position of every digit is what determines its value.
What’s the difference between base ten and other number systems?
The main difference is the base the systems use for grouping. In the base 10 system, the base is naturally 10. In the binary system (used by computers), for example, the base is 2, as it only uses 0s and 1s.
Base ten numeral: Worksheets
Now that you know what is base ten numerals system is, you understand it is important. After all, it’s the foundation of not only math, but everything involving numbers. The free worksheets below, which come with detailed puzzles and exercises, are a great place to practice the topic further.





