Brackets in Math – Definition with Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on January 13, 2026
In the world of mathematics, clarity is everything. So, to ensure everyone solves the equations the same way, we use brackets to specify the order of operations. Without them, the string of operations in any equation would be open to interpretation, and we all would get different answers to any problem, unable to understand which one is right.
In this article, we will explain what are brackets in math, talk about the types of brackets in math, how to use each, look at some examples, and solve problems.
What are brackets?
Brackets are the symbols we use to pair group numbers, variables, or operations together within math expressions. There are different types of brackets, but their primary job is typically to dictate the order of operations.
When your child sees brackets, it’s a signal to look there first. By grouping with brackets, they can override the standard order of operations, such as putting multiplication before addition.
What does a bracket look like?
When you think of brackets, you probably think of the () symbols. These are also called parentheses or round brackets.
However, the round brackets are not the only ones in math. We will look at other types later in the article. But for now, it’s important to mention that all math brackets always come in matching sets. Visually, they act like a container, with one bracket opening the group and another one closing it.
What are the different types of brackets?
In math, we use the term “brackets” as an umbrella term for a family of symbols that create a hierarchy within an expression. While these brackets all function as grouping tools, we typically use them in a specific order to keep complex equations from becoming a visual and logical mess.
The three kinds of brackets in math are:
- The parentheses, also known as round brackets, and represented by the brackets symbol ()
- The square brackets, which are also known as braces []
- The curly brackets are written using the symbol {}
Each bracket in math has a different purpose, and your child will need to use them correctly.
We will look at each bracket type’s meaning in detail later in the article.
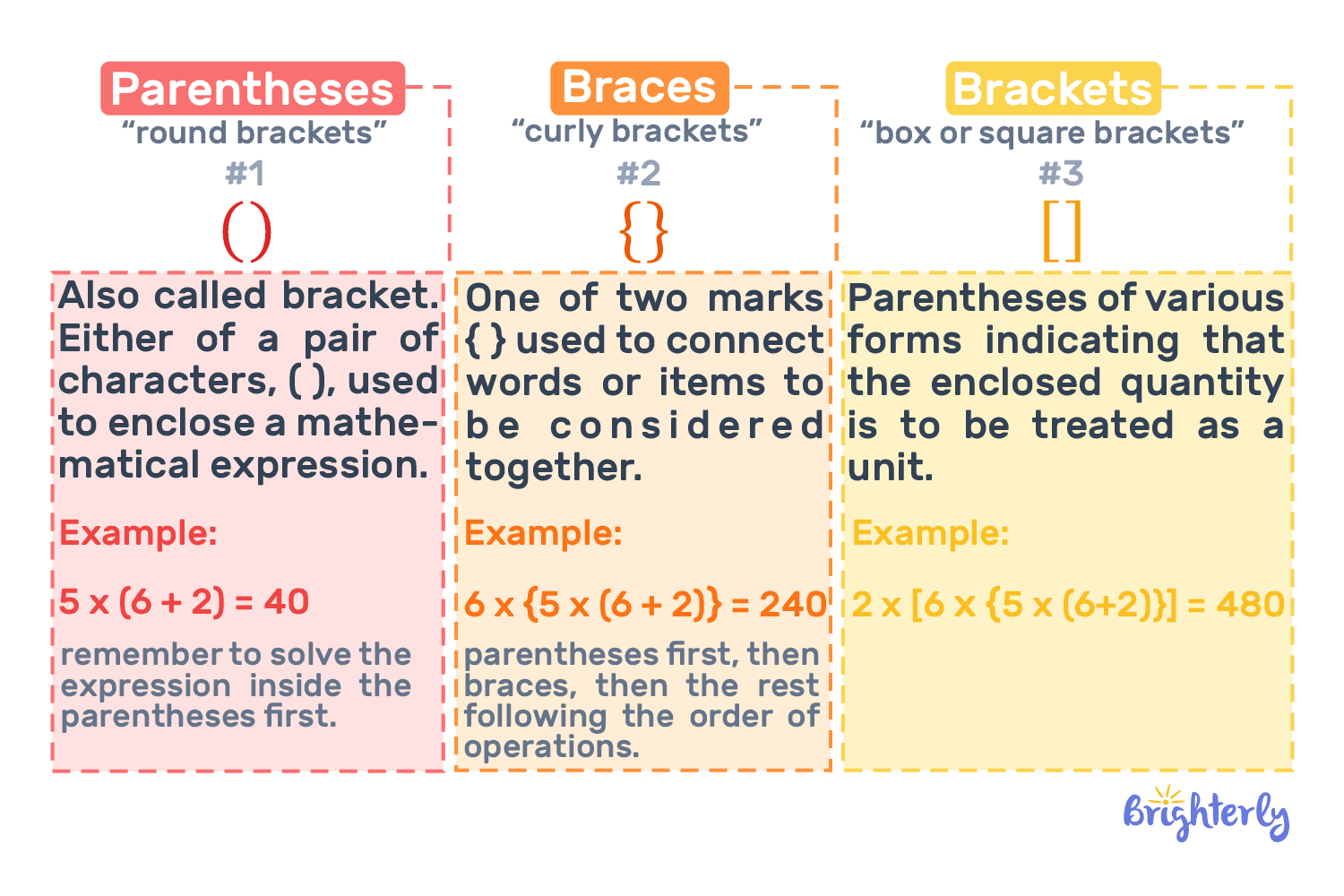
What are parentheses?
Parentheses, represented by the rounded symbols (), are the most common grouping symbol in mathematics. You have definitely come across those, if not in math, then in English, because of how often they are used.
In the standard order of operations in math (also often referred to as PEMDAS), the parentheses meaning is that they represent the very first step of any calculation. Your kid can think of them as a priority pass, telling students to solve the operations inside them before moving to the other operations in the equation.
Parentheses are very versatile; that’s why we use them everywhere in math, from very basic calculations to complex calculus. It’s one symbol in math that your child will interact with over and over again.
Parentheses in math example
We think the best way to show why parentheses are so important in math is to look at how they can change a result.
Let’s take the example of expression 4 + 6 x 2. If we followed the standard order of operations according to PEMDAS bracket rules in math (parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, subtraction), we would first multiply 6 and 2 to get 12, then add 4 to get 16 as the final answer, right?
However, when we put parentheses around the addition, the equation looks like this: (4 + 6) x 2, and the instructions change completely. In this case, parentheses force us to add 4 and 6 first, and this is what we get:
- Step 1: 4 +6 = 10
- Step 2: 10 x 2 = 20
As you can see, using parentheses changed the final answer.
What is the difference between brackets and parentheses in math?
Brackets vs parentheses in math are two different types of symbols we use to group numbers together so that operations are performed in a specific order.
When it comes to terminology, in the US, we use parentheses () exclusively to define round brackets. These are the symbols, the operations inside which your child will need to calculate first.
Brackets, on the other hand, specifically refer to the [ ] square symbols, which are used as a second-layer grouping in an expression that is already in parentheses. Square parentheses are another name for the brackets you may come across. We’ll discuss them in detail shortly.
How to use parentheses in math?
In math, we use parentheses not just for one function, but for several. Primarily, they indicate multiplication, isolate numbers to prevent sign confusion, and group numbers to change the order of operations.
Multiplication
Multiplication is one of the most frequent uses of parentheses in math that your child will come across. If your child is wondering what is a bracket, it is a symbol used to group numbers or operations together, and parentheses are the most common type. In this case, we use parentheses to specifically indicate multiplication without confusion. This is especially important in algebra, because there, your child will deal with the variable x a lot, and since multiplication is often indicated by the symbol x, it can become a source of confusion.
In the case of multiplication, when a number sits next to parentheses without any other symbol in between them, you need to multiply. For example, 5(4) is the same as 5 x 4, both equal to 20. In the case of algebra, 3(x + 2) tells you to multiply 3 by every element in the group, giving 3x + 6 as an answer.
Isolating numbers
The next common use of parentheses is to isolate a specific number. This is often the case when dealing with negative values, as parentheses prevent symbols from running together, making the equation much easier to read and understand. For example, writing 10 +- 5 can be visually confusing, while 10 + (-5) clearly shows that you are adding a negative five to ten. This also works when subtracting, for example, 8 – (-3) indicates that you are extracting a negative 3 from 8, giving 11 as the answer.
Group numbers
The most fundamental job of parentheses is to group numbers and operations together to signal priority. The PEMDAS order indicates that, with P (for parenthesis) being the first action, your child needs to take. So, if you want a specific part of an equation solved before anything else, you must wrap it in parentheses. For example, in 2 + 5 x 10, you would do 5 x 10 first, then add 2, getting 52. With grouping (2 + 5) x 10, you do the addition first, then the multiplication, getting 7 x 10 = 70.
What are curly brackets?
In the math grouping hierarchy, we consider curly brackets (also known as braces) represented by the {} symbol as the “outermost” layer. What this means is, when we use braces in math, we indicate the final stage of grouping.
These braces wrap around square parentheses, which in turn wrap around regular round parentheses. Through this visual distinction, your child will be able to follow the problem without getting confused by multiple sets of the same symbol.
We also use these brackets to indicate sets. For example, if your child needs to express numbers 1-5 in a set, they’d need to write it as {1,2,3,4,5}.
What are square brackets?
Square brackets in math, also known as square brackets, are the secondary grouping symbol, used between round parentheses and braces. Their main purpose is visual organization, as it would be very easy for your child to lose track of which opening curve matches which closing curve if they have been working with something like ((())).
In more complex math, we also use square brackets to indicate interval notation. For example, [1,5] indicates that all numbers between 1-5, including 1 and 5, are included in the array.
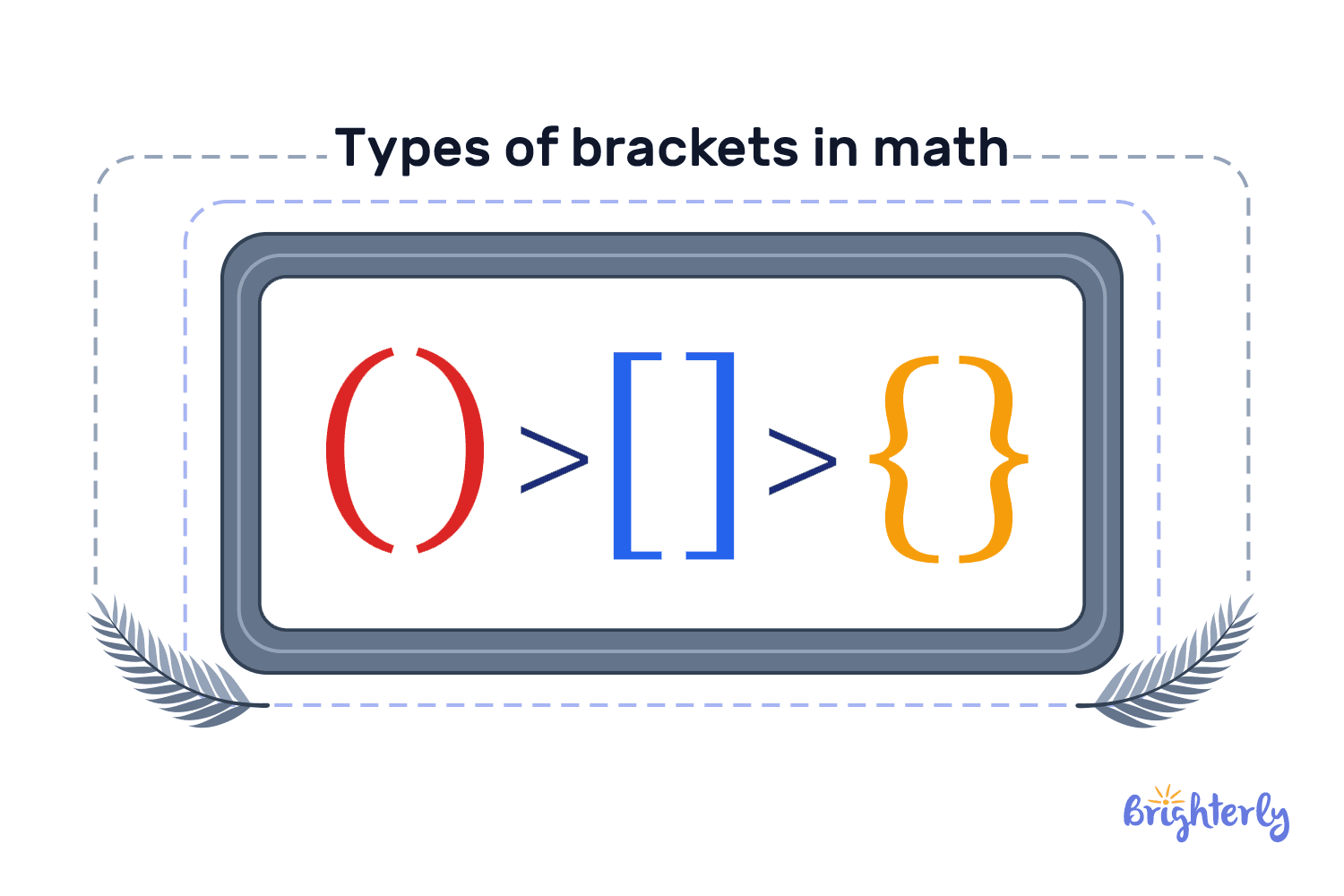
Parentheses vs brackets in math
In math, brackets vs braces are not interchangeable, despite the fact that we use both as grouping tools. The difference is mainly their hierarchy (square brackets being the second layer, while the braces are the last layer). In many cases, like in the case of interval notation, the type of a bracket can fully change the mathematical meaning of the expression. For example, the array {1,5] indicates that 1 is not included, leaving only the numbers 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the array.
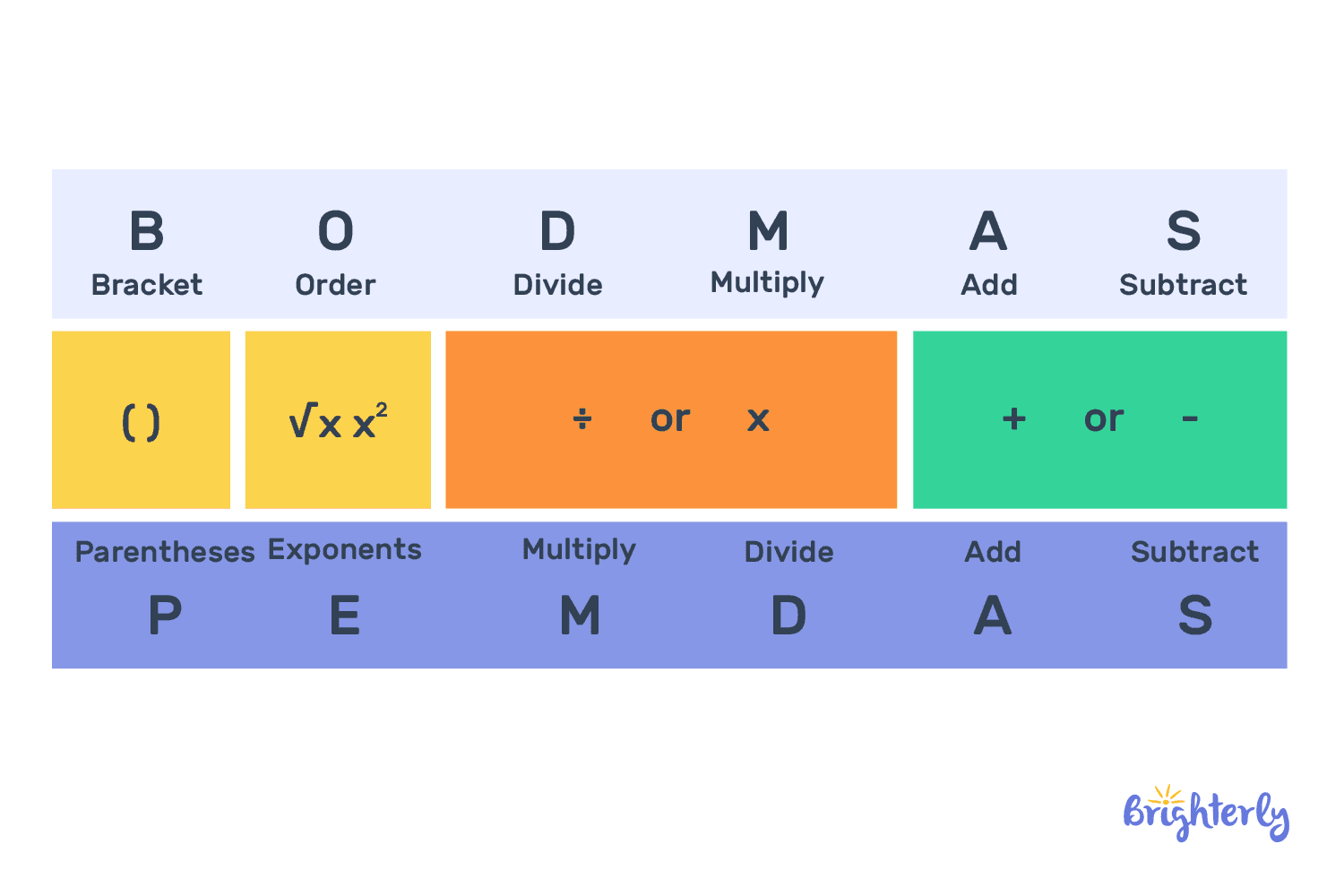
What is the order of operations for brackets?
The order of operations is a set of guidelines your kid needs to learn and remember. This is quite simple to do using the PEMDAS or BODMAS formulas.
So, we know that the expressions in brackets come first. But what if there are several types of brackets in one equation?
As mentioned below, the correct order is inside out:
- First come the round parentheses ()
- Next come the square brackets []
- Last are the braces {}
So, the braces in your equation should look like [{()}].
Let’s take the equation 5 {7 + [–3 + 4(6 + 1)]} as an example.
5 {7 + [–3 + 4(6 + 1)]}
= 5 {7 + [–3 + 4(7)]}
= 5 {7 + [–3 + 28]}
= 5 {7 + [ 25]}
= 5 x 32
= 160
In the example, we solved the expression inside the round parentheses first, then moved to the addition in round brackets, then added 7 + 25 in the curly braces before multiplying it by the number outside the braces.
Solved examples on brackets
1. What is the answer to the equation 60/[2(10-7)] +5?
Solution: We use the PEMDAS rule and start with the innermost operation: 10-7 = 3. Then, perform the operation in the square bracket: 2 x 3 = 6. Now that the brackets are cleared, we divide 60/6 = 10, then add the remaining 5.
Answer:
| 15 |
2. How to solve the expression 4 + {20 – [5 + (-3 x 2)]}?
Solution: Start with the innermost parentheses to multiply the negative number, so -3 x 2 = -6. Next, solve the square bracket 5 + (-6) = -1. Then, solve the curly braces 20 – (-1) = 21. Finally, we need to add the remaining 4.
Answer:
| 25 |
3. What is the answer to equation 2 x [18 – (3 x 4)]?
Solution: Again, we start with the innermost parentheses by multiplying 3 x 4 = 12. Then, we perform the operation in the square brackets: 18 – 12 = 6. Lastly, we multiply the result by 2 outside the brackets, getting 2 x 6 = 12.
Answer:
| 12 |
Practice Problems on Brackets
Frequently asked questions on brackets
What do brackets mean in math?
In math, brackets meaning are symbols we use to group numbers and operations together. They act as indicators to solve the equations inside them first. Brackets let us override the standard order of operations we know.
What does parentheses mean in math?
Parentheses () are the most common grouping symbol. They are always solved first. We use them to group addition or subtraction that must happen before multiplication, to indicate multiplication, and to isolate negative numbers.
What is the order of operations with brackets?
You need to solve the brackets in an inside-out hierarchy. First solve parentheses (), then solve square brackets [], and finally solve curly braces {}. Once this is done, you simply proceed with the standard PEMDAS rules.
Brackets in math: Worksheets
Help your child put what they’ve learned about brackets into practice with free worksheets covering relevant topics and many practice questions.