Compensation in Math – Definition With Examples
Updated on November 3, 2025
When it comes to mastering math, it’s also important to learn a range of methods to make solving equations easier. Today, we’ll explore the method of compensation in math. It allows us to make complex operations easier to solve by changing number values.
We’ll cover the compensation math definition, its properties and share examples. We’ll also give you practice problems so you can hone your skills in using this method.
What is compensation in math?
Compensation in math is a method of solving equations by changing the value of one or both numbers to make them easier to work with. It’s a great way to improve mental math skills and deal with complex numbers.
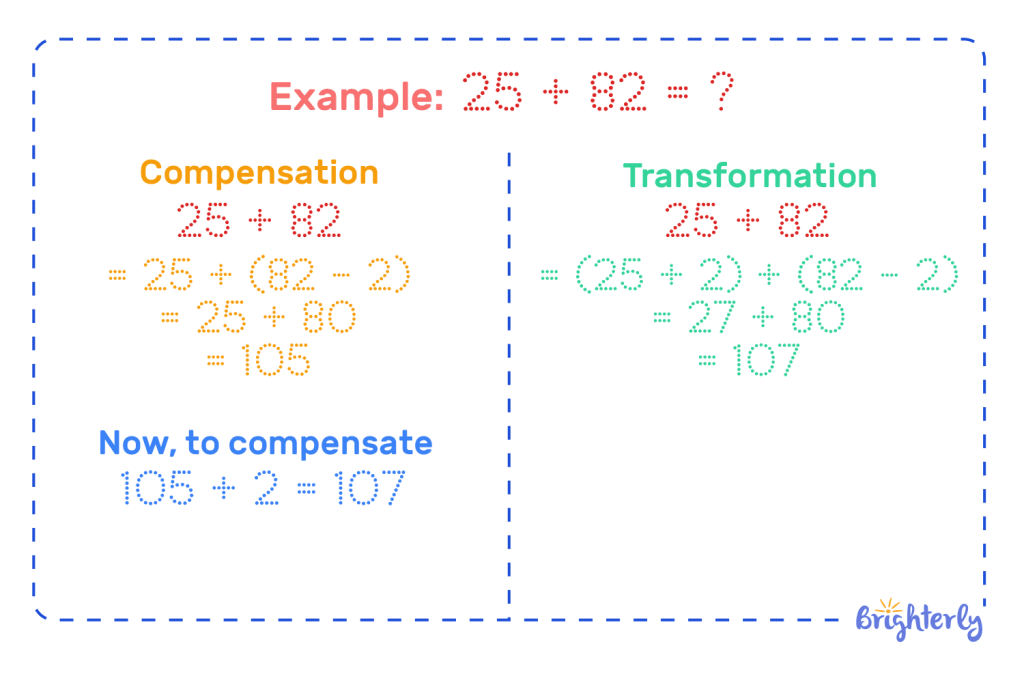
Definition of compensation in math
The definition of compensation in math is making a math problem easier to solve by adjusting one or both numbers in an equation. You turn one or both of your numbers into a number that’s easier to work with, like a multiple of 10, to solve it faster.
Understanding compensation in math with examples
Let’s look at some examples of compensation in math.
If we have the equation 47 + 56, we could add 4 to the 56 to give us the round number of 60. 47 + 60 = 107. Then, subtract the 4 from your answer: 107 – 4 = 103.
With 92 – 23, we could take 2 from both numbers, giving us the nice round number of 90 and 21, which equals 69. This is the same result as 92 – 23.
Properties of compensation in math
There are some properties of compensation in math that dictate how you use it in addition and subtraction.
- In addition, if you add to one of your addends, you can subtract the same number from your simplified sum or from your other addend to keep the same result
- In subtraction, if you add or subtract the same number to your minuend and subtrahend, the result will be the same as your original sum. You can also add or subtract from one number, then subtract or add that number at the end
When is compensation used in math?
Compensation is used in math when you have an addition or subtraction problem with two complex numbers — i.e. not rounded numbers. Using compensation means we can make one or both numbers a rounder, or ‘friendlier’ number, which is easier to solve mentally.
How does compensation work in math?
Compensation works through equally modifying numbers, or simplifying one number by adding to it or taking away from it, then subtracting or adding that number back to your result. It makes math problems feel more balanced and less daunting.
Compensation formula
There is no specific compensation math formula — instead, you’ll modify one or both of the numbers in an addition or subtraction sum.
If you’re simplifying a subtraction sum, you could use the formula of (n + x) – (n + x) to remember that adding the same number to your minuend and subtrahend gets the same result as your original sum.
In addition, the comp formula (n + x) + (n – x) reminds you that if you add to one number, you can use compensation to subtract the same number from your other addend.
Difference between compensation math strategy and other strategies
Compensation is one strategy that can make math problems easier to solve. There are many other math methods, like carrying and borrowing or decomposing numbers, that can simplify equations.
The difference is that there are set rules with compensation strategy math that allow you to work with it, and there is no set number you need to modify your numbers with.
Applications of compensation in math problems
Compensation in math has many applications, from simplifying complex sums in math class to adding up items when you’re grocery shopping. Its real-world applications mean its importance goes beyond math class!
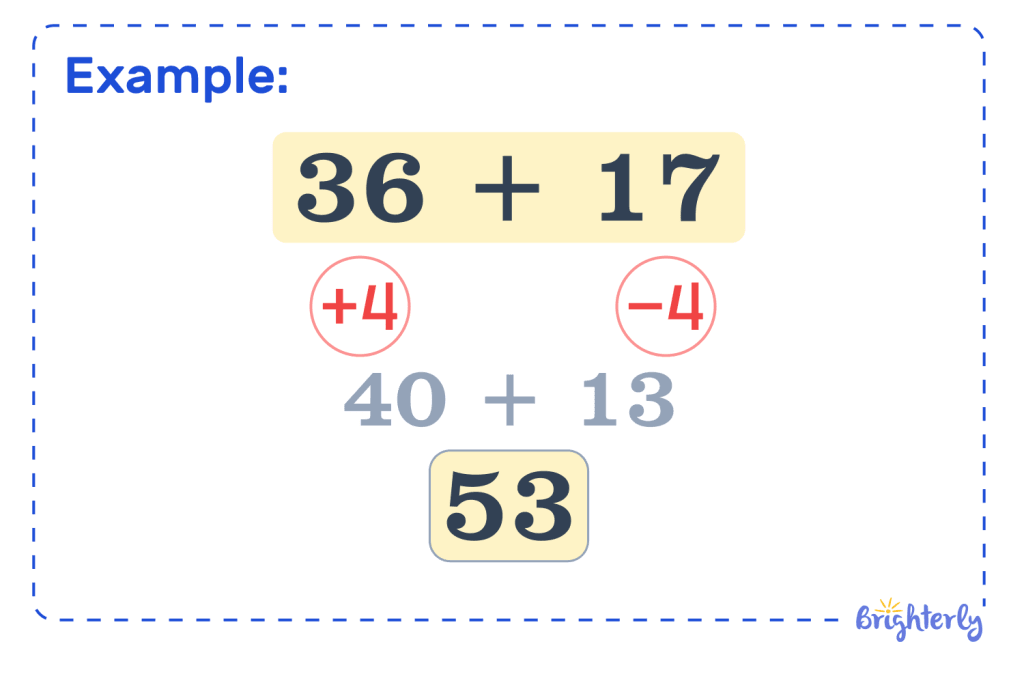
Writing equations using compensation in math
To write equations using compensation, you need to adjust one or both of your numbers.
Let’s use the example of 68 + 71. We can take 1 away from 71 to make 70, then either add 1 to 68 or add it at the end of our equation.
- 69 + 70 = 139
- 68 + 70 = 138 + 1 = 139
Now, for a subtraction example: 46 – 32. We can either add 8 to both numbers, giving us the same result, or add 8 to 32 and add it to our final number.
- 54 – 40 = 14
- 46 – 40 = 6 + 8 = 14
Compensation in math: Practice problems
Now that you’ve learnt all about the compensation in math method, it’s time to try it out! Use mental math or a pen and paper to solve the following math problems. You’ll see how much easier they are with compensation!
- Using compensation, solve the sum 406 + 399.
- Solve the following equation using the compensation method: 850 – 629.
- Using compensation, solve the sum 58 + 79.
Conclusion
Math compensation is one of many methods to simplify sums and make them easier to calculate in your head. Now, you have another tool in your toolkit to make math much less daunting!
Compensation in math: Frequently asked questions
What does compensation mean in math?
Compensation means modifying one or both numbers in an addition or subtraction equation to make it easier to solve. As a compensation math example, in 63 + 24, you can take 4 from 24 and add it to 63, making the simpler equation of 67 + 20 = 87.
How to use compensation in math?
You can use compensation in math in different ways:
- In addition, add to one of your numbers and take the same amount away from your other number, or take it away from your result
- In subtraction, add or take away the same number from both numbers to get the same result
What is an example of compensation in math?
An example of compensation in math is the sum 47 – 23. You can take 3 away from both numbers to get 44 – 20 = 24, which is the same result. However, you can also just take 3 away from 20, giving you 47 – 20 = 27, then take away 3 from that number. 27 – 3 = 24.
How does compensation differ from other math strategies?
Compensation differs from other math strategies because there are no set numbers that you modify your equation numbers with. You make one or both numbers simpler to work with. The compensation math 4th grade method will support your learning.






