Geometric Shapes – Definition With Examples
Updated on January 7, 2026
Look around you right now, and you’ll likely notice that you’re surrounded by shapes of every kind! When it comes to learning the names of all geometric shapes, it can sometimes be a little tricky, particularly when you need to figure out if a shape is two-dimensional or three-dimensional. Our Brighterly guide goes through the geometric shapes definition, the most popular geometric shapes, answers the question of what is a geometric shape, and helps make shape learning easier (and more fun!)
Geometric shapes definition
Geometric shapes are mathematical figures defined by points, lines, curves, or surfaces. They are fundamental to understanding geometry around us. That’s what the geometric shape definition says!
Types of geometric shapes
Different shapes in geometry can be classified into two main types according to their dimensions:
Two-dimensional geometric shapes
Unlike three-dimensional geometric shapes, two-dimensional geometric shapes do not have any depth. There is no volume to them, as they lie entirely on a plane. The boundaries of these shapes are defined by points, lines, and curves.
2D shapes have the following key features:
- Surfaces that are flat.
- There are only two dimensions – length and width.
- Perimeters and areas can be measured.
The following are common 2D shapes:
A circle, triangle, square, rectangle, pentagon, hexagon, etc.
Three-dimensional geometric shapes
Three-dimensional geometrical shapes have length, width, and height (depth). It is physically possible to touch and hold these math shapes because they occupy space and have volume.
Key features of 3D shapes:
- Exist in the real world with three dimensions.
- Have faces, edges, and vertices (depending on the shape).
- Can be measured with surface area and volume.
Common 3D shapes in geometry include:
Cube, sphere, cylinder, cone, pyramid, prism, etc.
List of geometric shapes & their properties
Triangle
Triangles are formed by connecting three line segments. Due to its variable angles and measurements, it is a complex geometric figure. Triangular objects include pizza slices, nachos, birthday caps, etc. The name of a triangle varies depending on its angles and sides. Right triangles, for instance, are formed when two line segments of a triangle form a right angle.
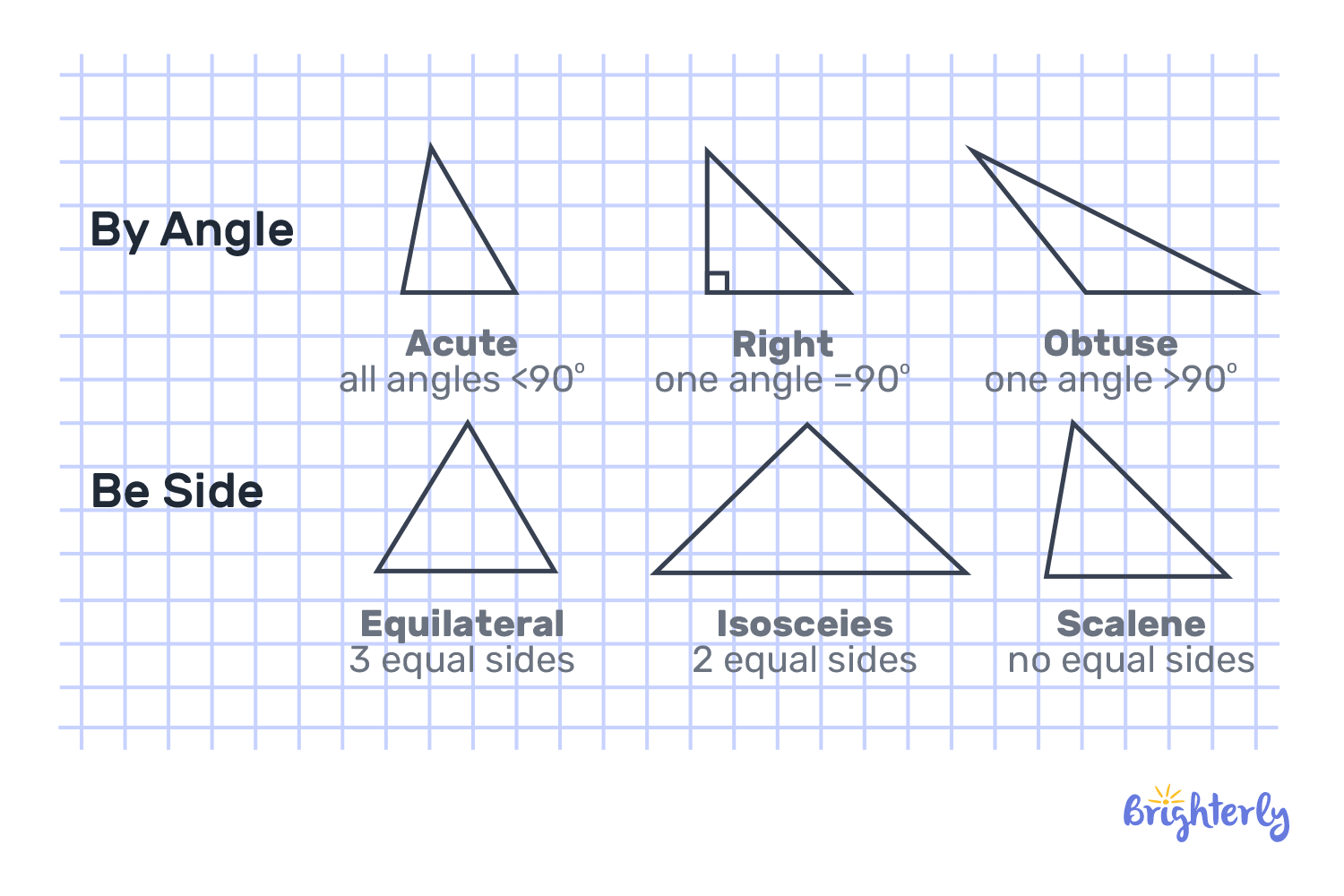
Triangles with acute angles are referred to as acute-angled triangles. As well as obtuse-angled triangles, triangles with one angle exceeding 90 degrees are called obtuse-angled triangles. Equiangular triangles have all of their interior angles equal to 60 degrees, and their sides are all the same length.
Circle
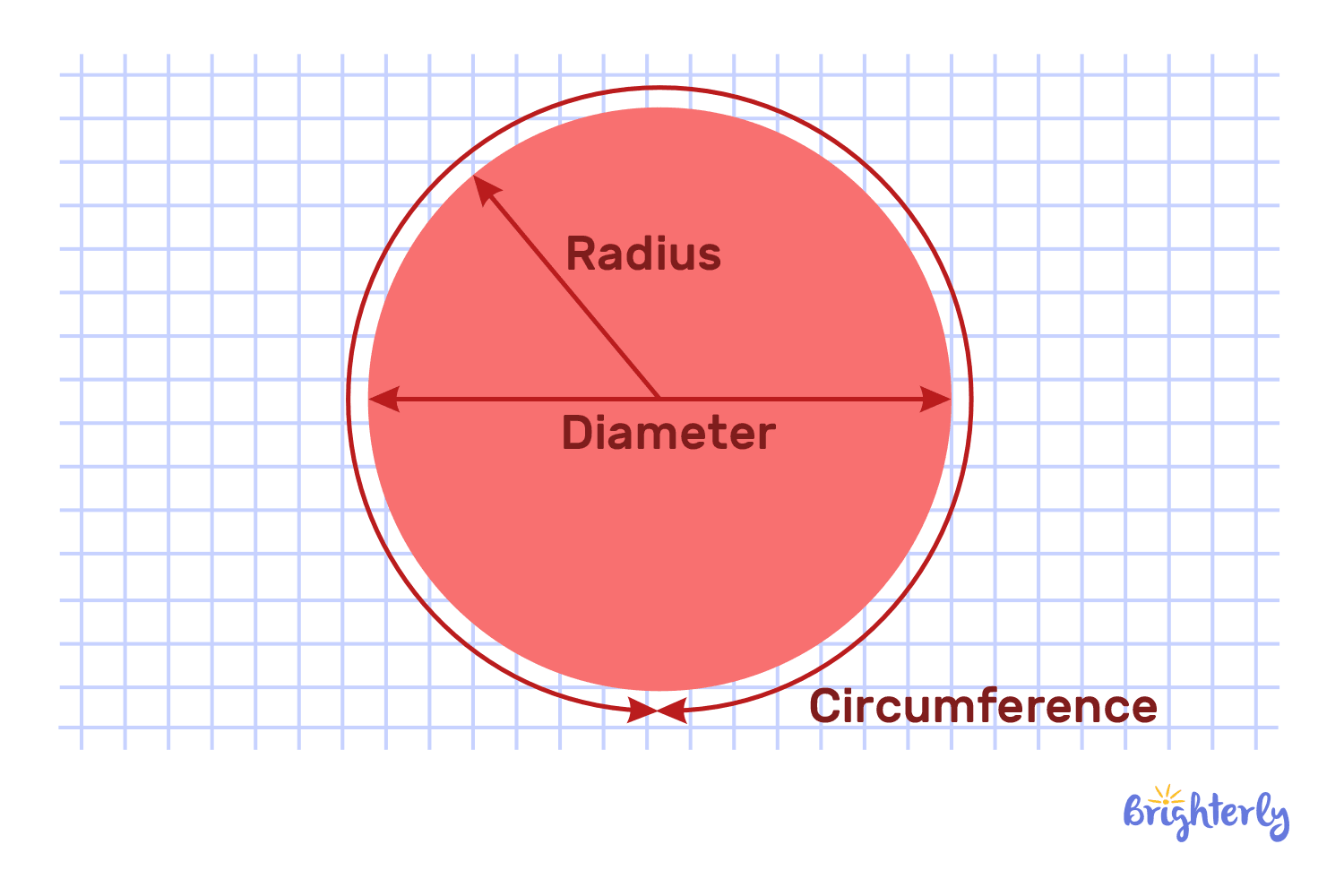
Among simple geometric shapes in geometry, a circle is a shape without straight lines. The points in a circle are all equally far from the center, so we can assume they are uncountable.
A pizza or a wheel is an example of a circular object. A circle always has a radius — a line from its center to any point on its edge. Radius is essentially half the length of the diameter (the whole line from one edge of the circle to another).
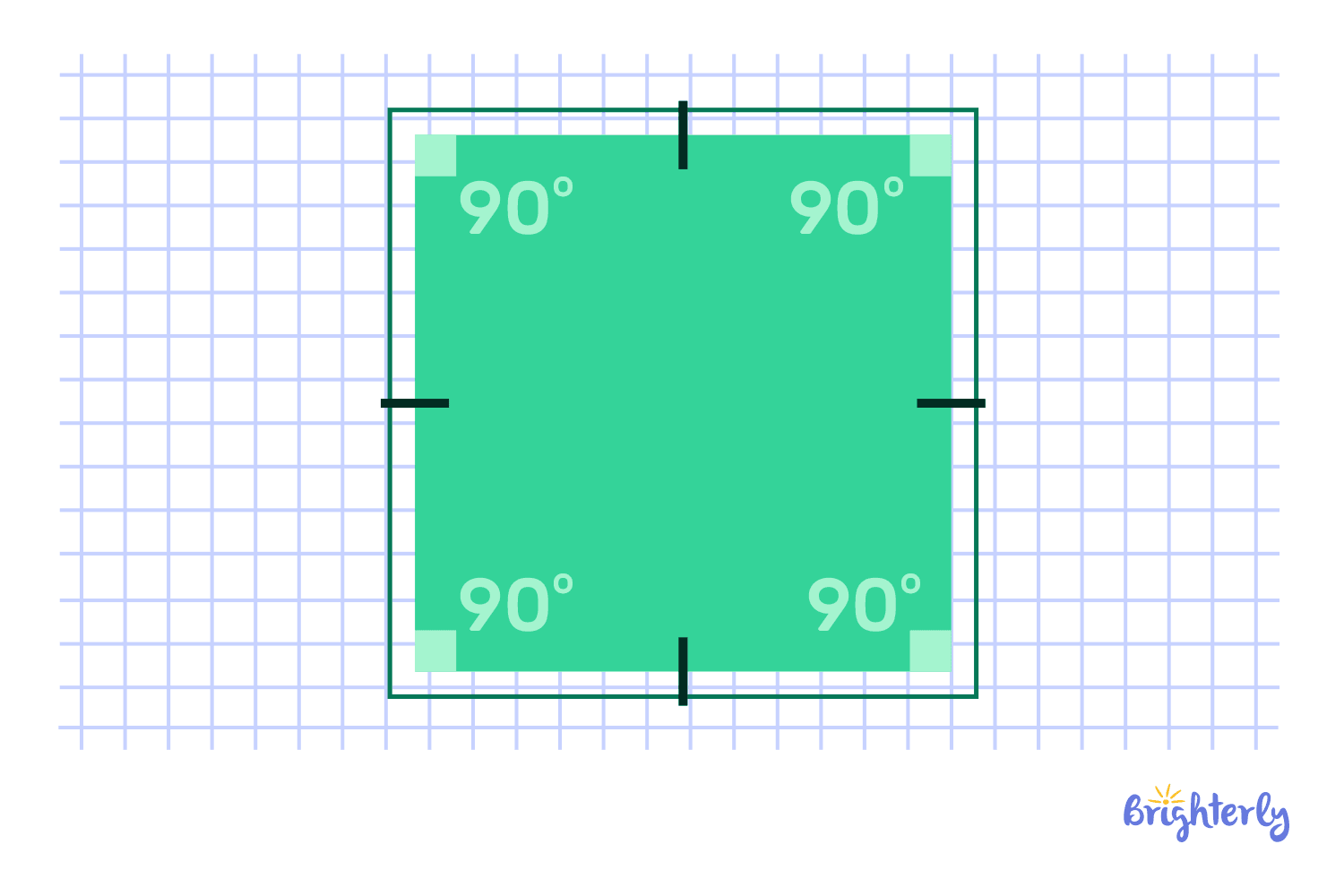
Square
An equal-length line segment creates a four-sided geometric figures known as a square. In the same way as rectangles, squares have right-angled lines. Square objects include Rubik’s Cubes, dice, chessboards, and so on.
The key properties:
- Four equal sides.
- Four 90° (right) angles.
- An opposing side is parallel to the other.
Rectangle
In geometry shapes names, a rectangle is formed by joining four points with four lines. Rectangles have parallel and equal sides. An angle in a rectangle is a right angle. Unlike a square, a rectangle has two parallel line segments that are longer than the others, while all line segments in a square are the same length.
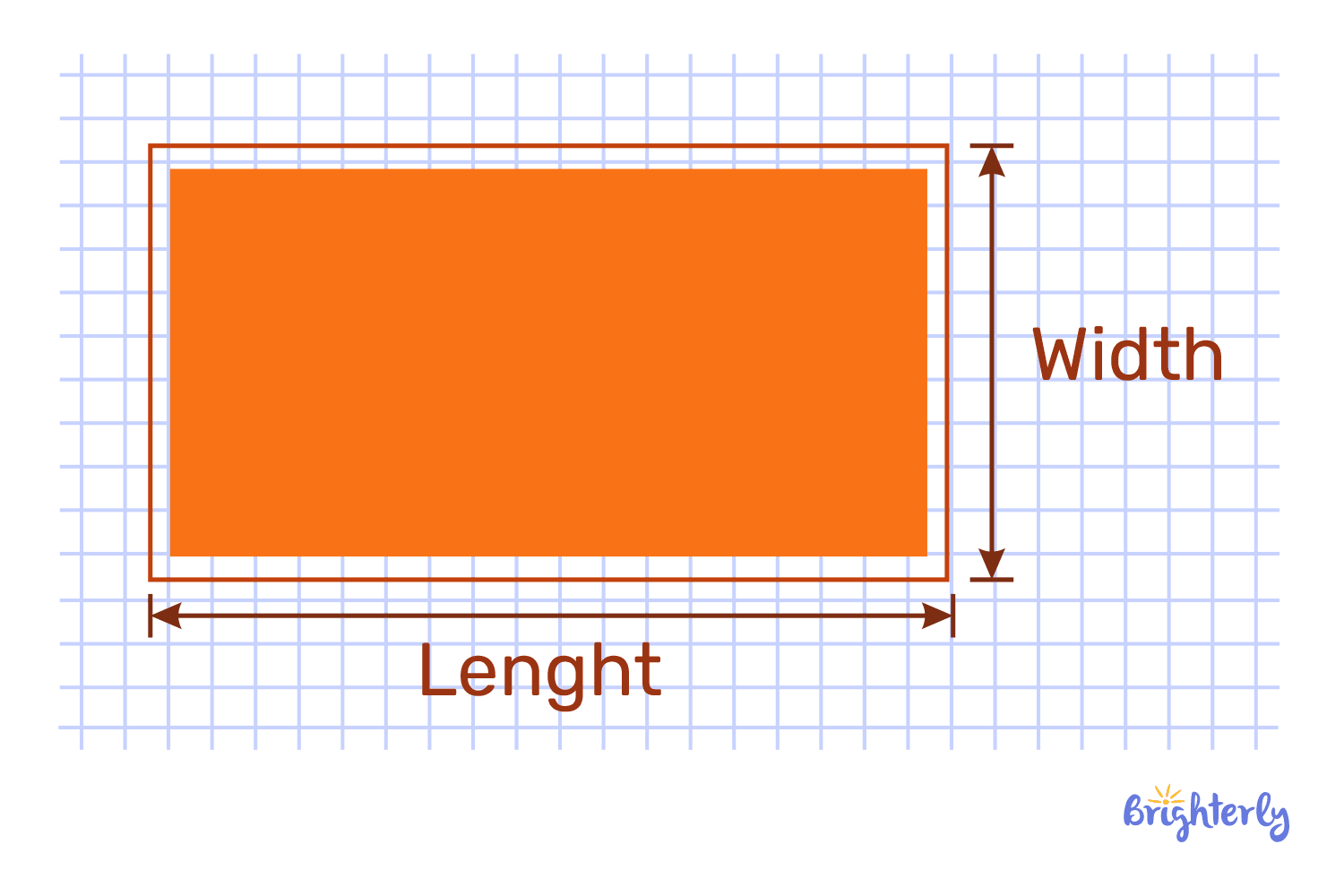
A laptop screen, a mobile screen, or any rectangular object can be described as a rectangular object.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four-sided shape formed by joining four points with four straight lines. In a parallelogram, opposite sides are equal in length and parallel to each other, while opposite angles are also equal. Unlike rectangles or squares, its angles are not necessarily right angles.
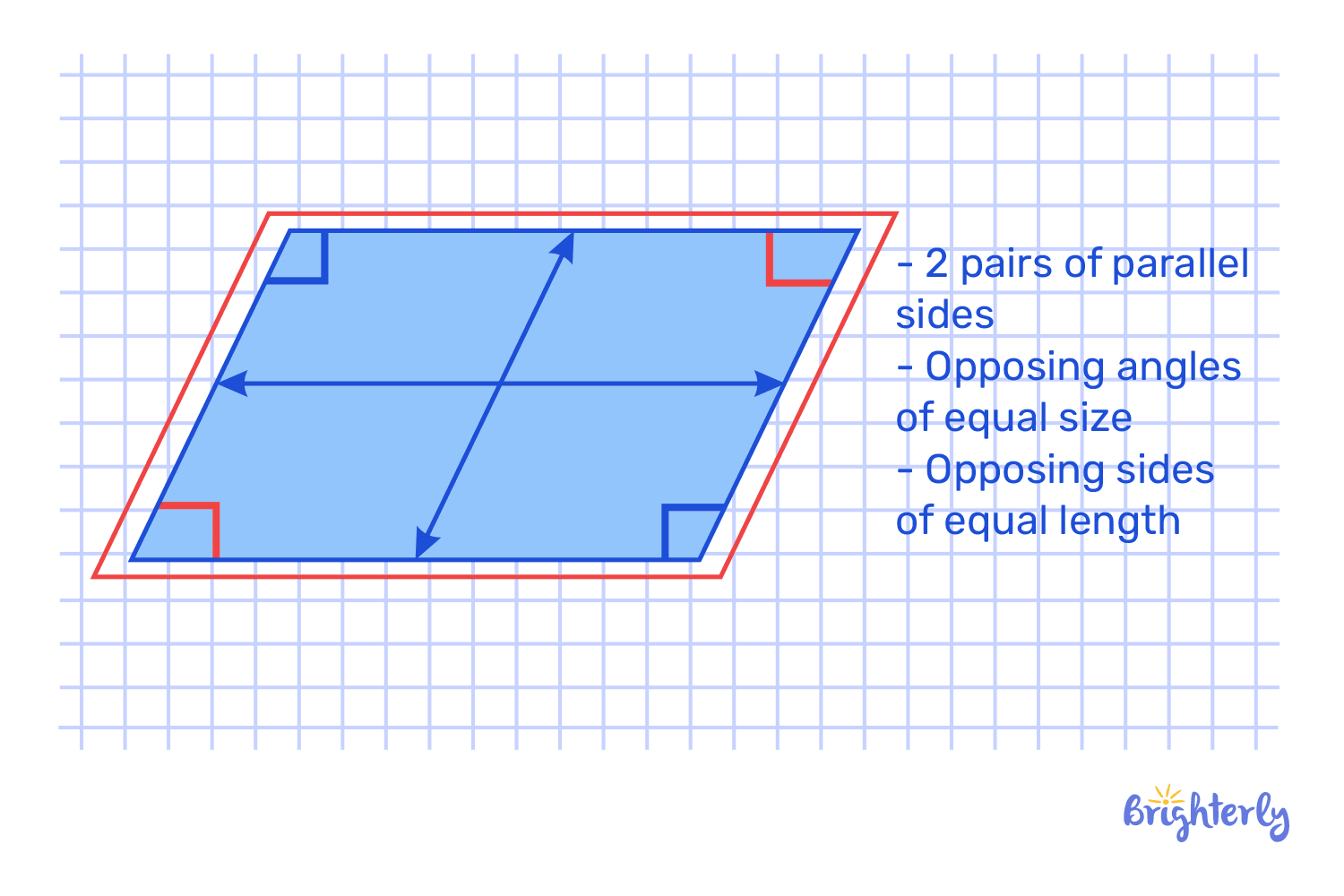
Examples of parallelogram-shaped objects include slanted tiles, patterned floor designs, and some book covers viewed at an angle.
Polygons
The polygons are one of the interesting names of geometric shapes, among other figures. It is a closed shape formed by joining straight line segments. The sides of each polygon do not cross over each other, and each polygon has vertices and angles. An example of a polygon is a triangle. A polygon is also a square, a pentagon, and a hexagon.
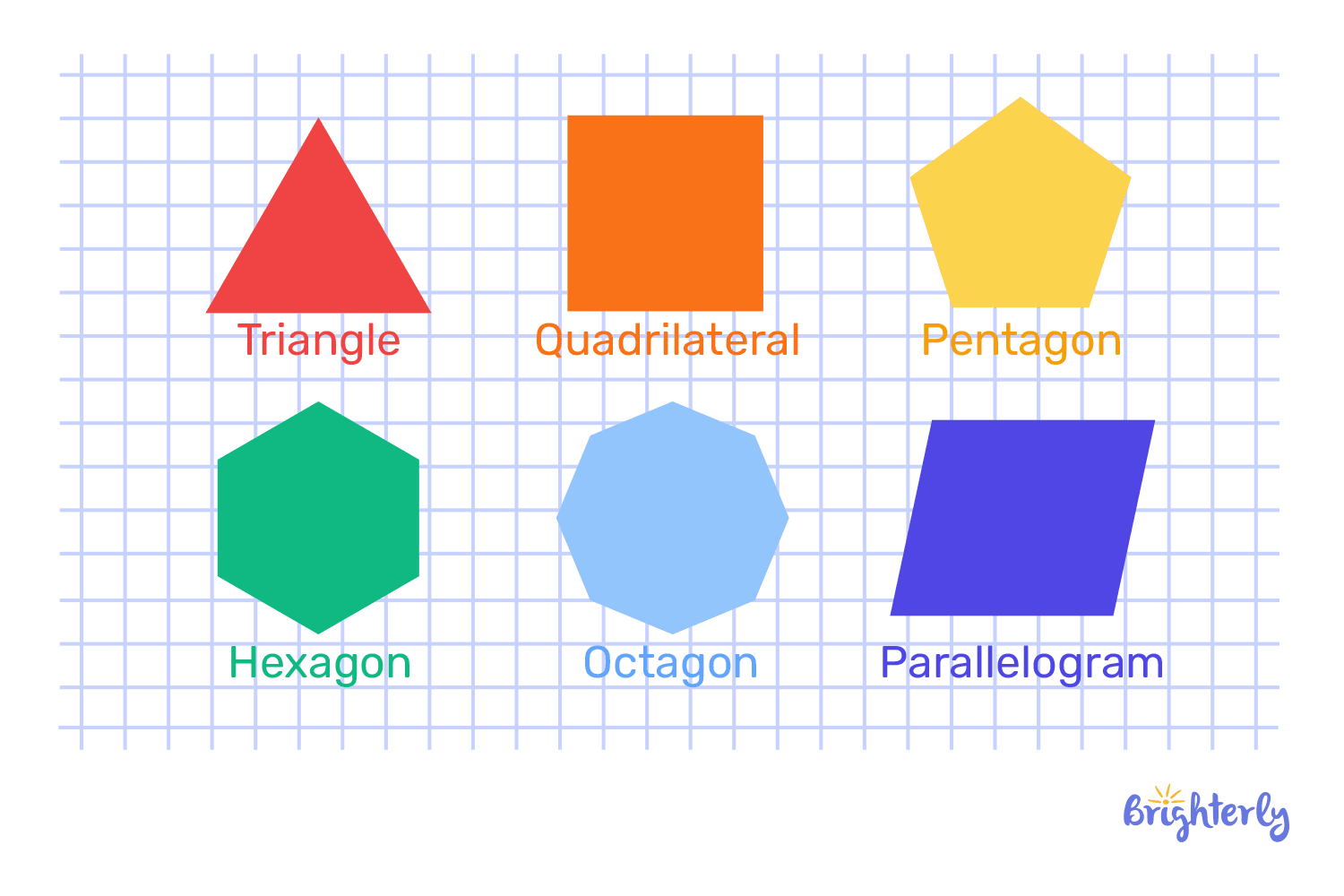
Three-dimensional shapes
Cube
Сubes are three-dimensional geometric shapes names made of six identical square faces. All edges are equal in length, and every angle is a right angle. The key properties
- There are 6 square faces.
- There are 12 equal edges.
- A total of 8 vertices (corners) are present.
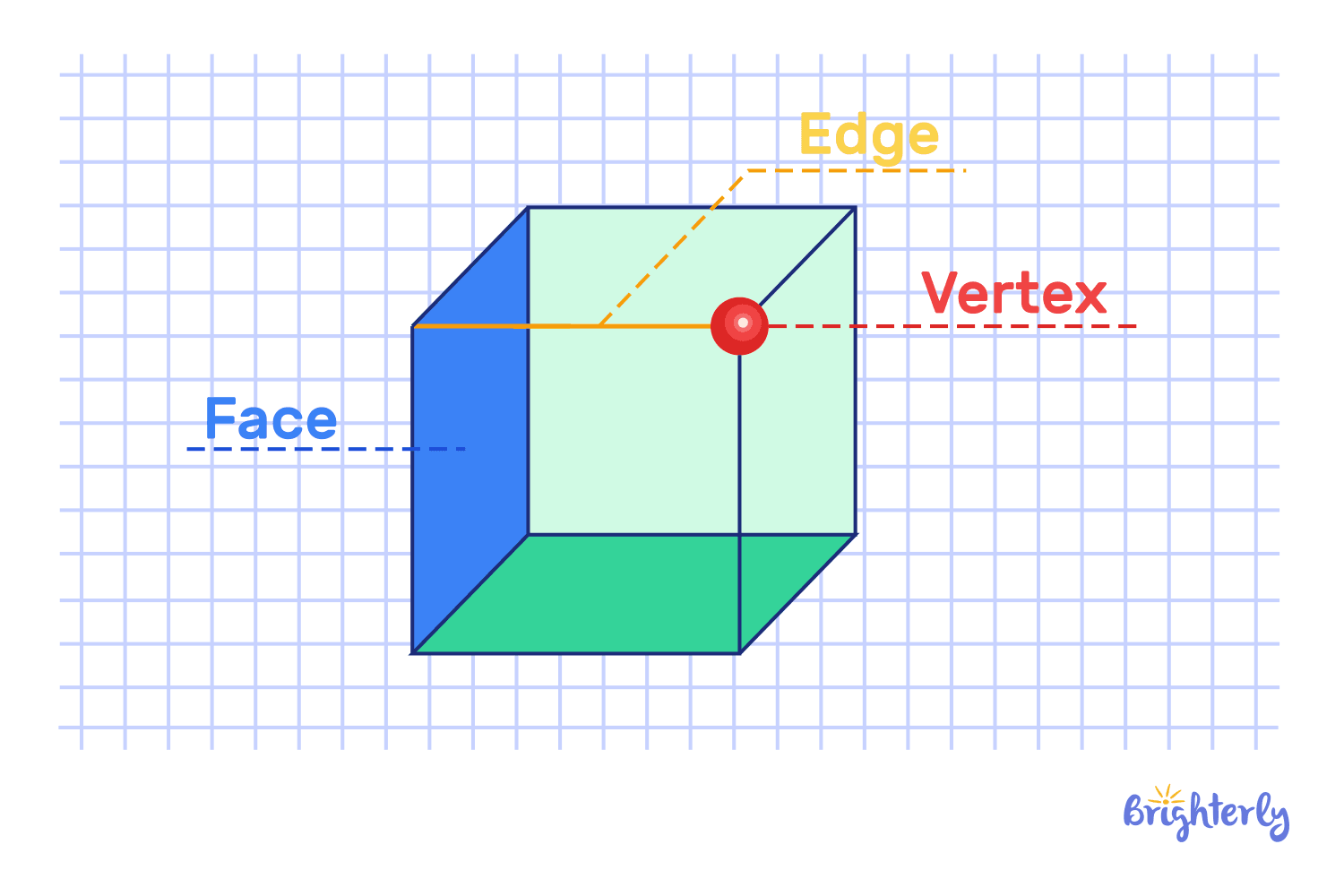
A dice or a Rubik’s Cube is a common example.
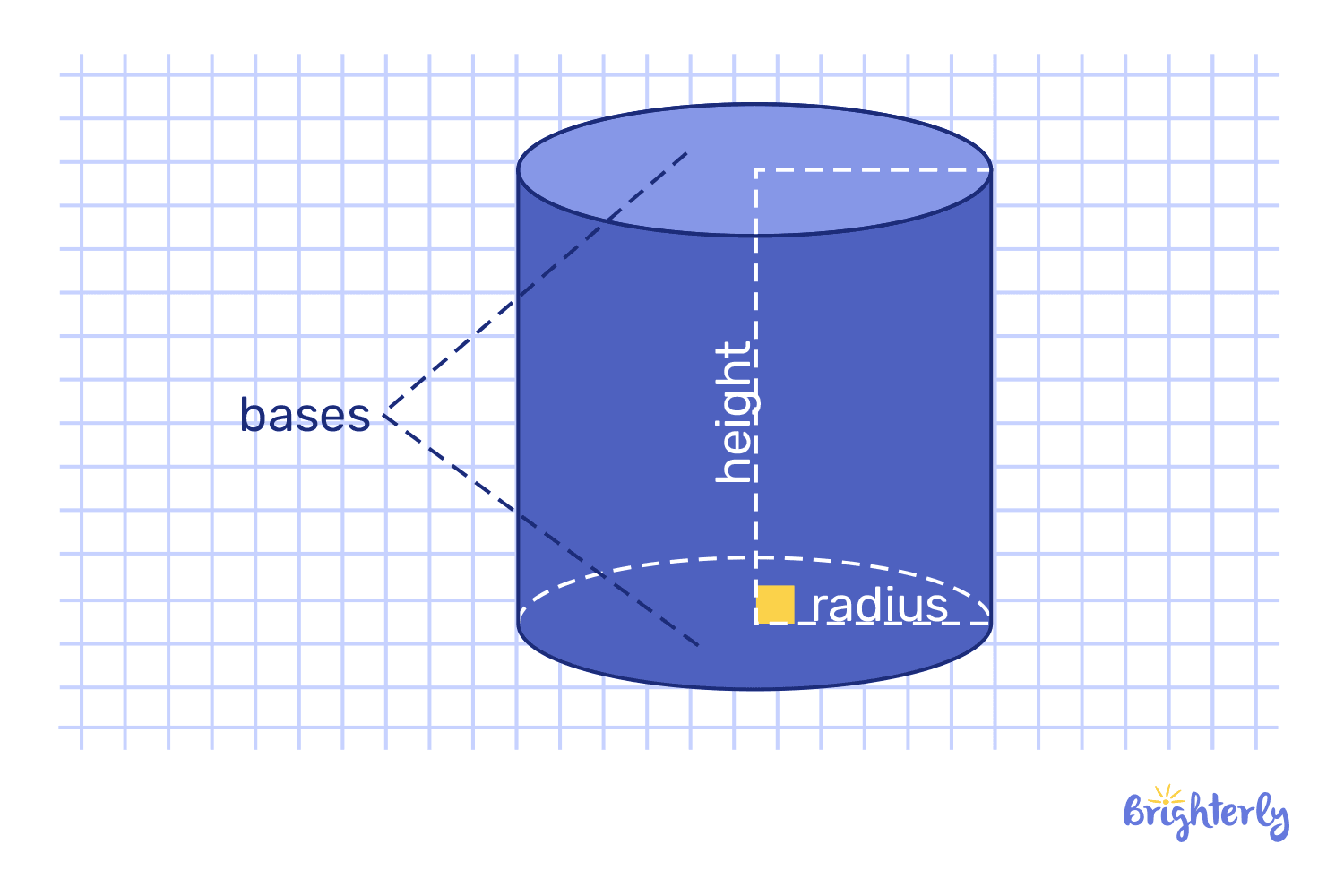
Cylinder
A cylinder consists of two circular bases connected by a curved surface. In terms of size, the bases are equal and parallel. Circular shapes are found in soda cans and paper towel rolls. The geometric properties of space
- A base consists of two congruent (identical) and parallel circles or ellipses.
- A curved surface connects the bases.
- There are two elements in this equation: the line segment (generator) and the direction in which it moves.
- The axis of a right cylinder is perpendicular to its base; an oblique cylinder is not.
- As a cylinder is unfolded, its curved surface creates a rectangle (height x circumference).
Sphere
Unlike shapes with edges or corners, a sphere is perfectly round. Every point on its surface is the same distance from the center. Bubbles, such as soap bubble,s take on a spherical shape when they are in equilibrium. Geometry often approximates the Earth as a sphere, and astronomy often considers the celestial sphere.
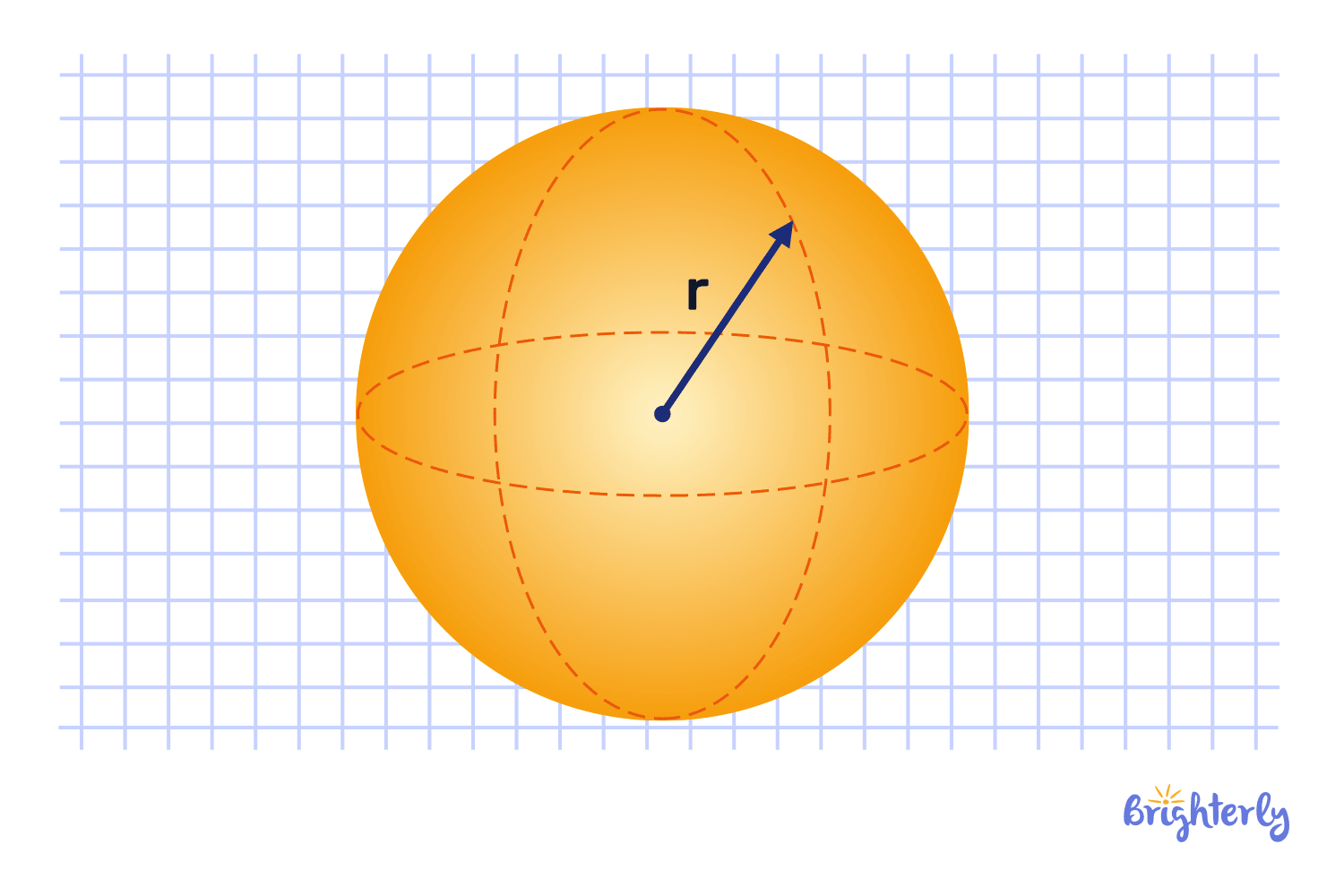
Balls and oranges are examples of spheres.
Cone
A cone combines one circular base with a single pointed vertex at the top. Its curved surface narrows smoothly toward the vertex. Cone properties:
- It has one Circular face
- It has one vertex
- Circular base and continuous curve
- A point above a base is called an apex
- Cone-shaped funnels
- Ice cream is shaped in cones
- The birthday hat is shaped like a cone
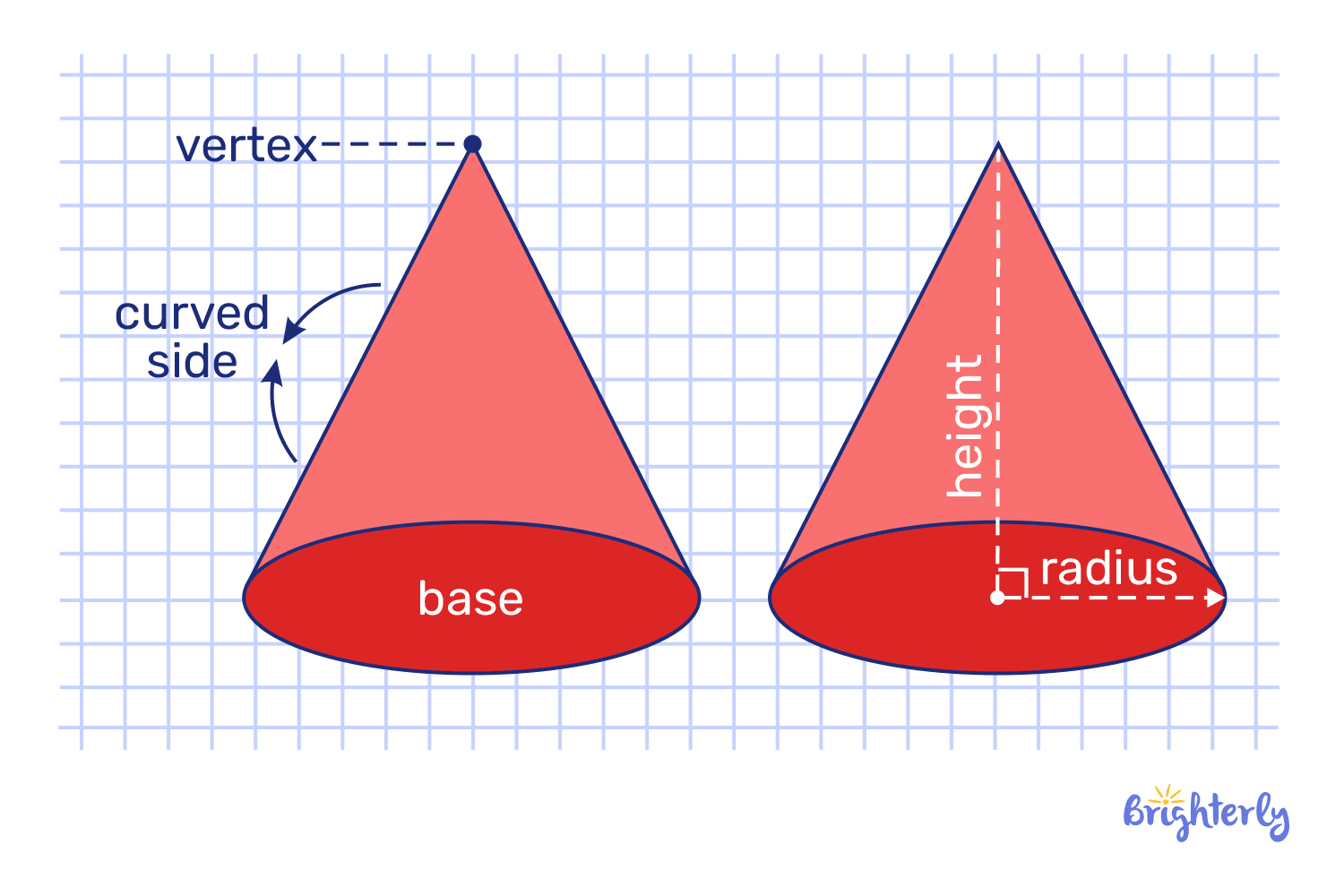
An ice-cream cone or a party hat shows this shape.
Open and closed shapes
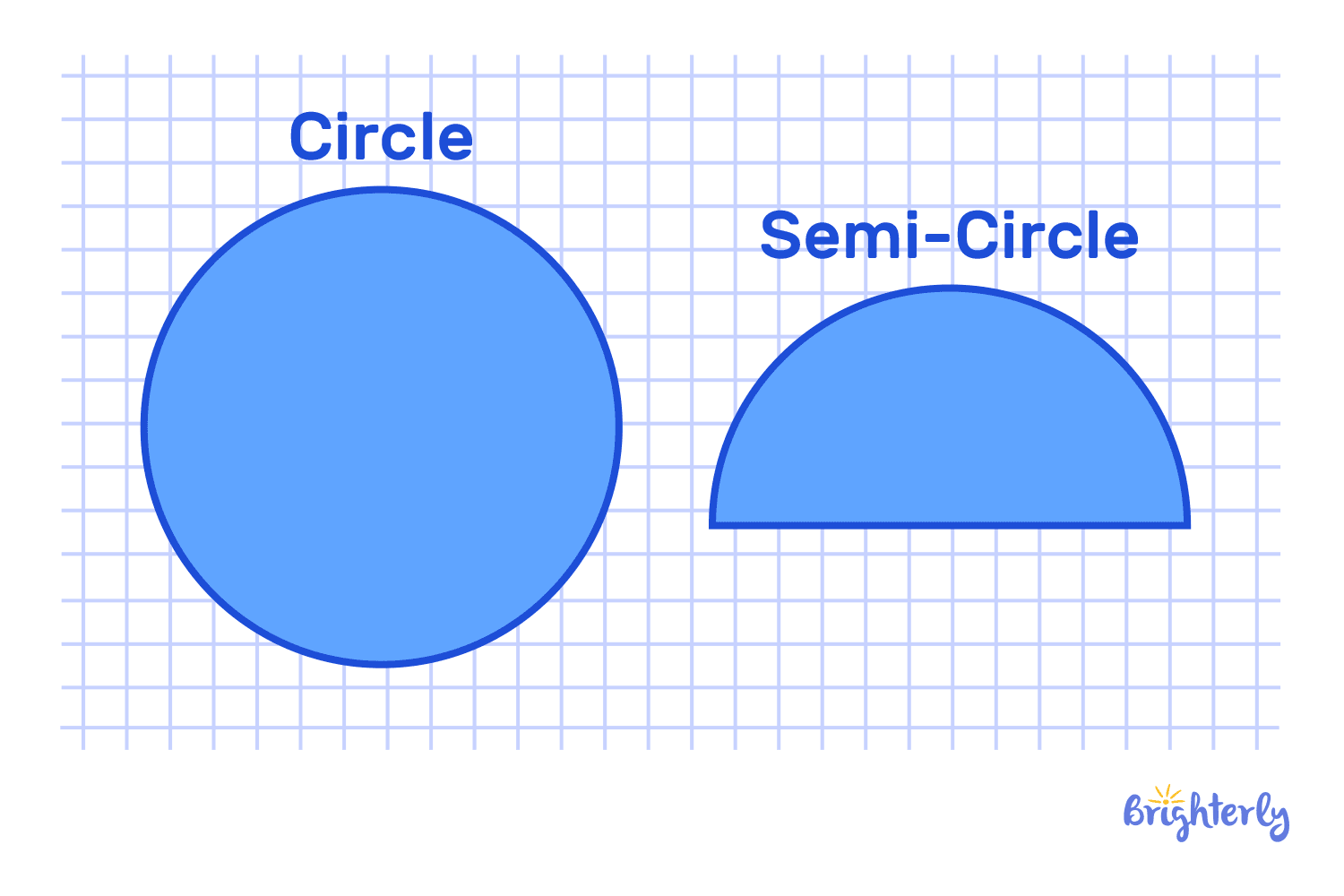
Kinds of shapes in two dimensions can be either open or closed.
You can compare the shape of a circle to the shape of a semicircle.
Closed shapes
Closed geometric shapes don’t have open ends and can be traced back without breaking.
Below are some examples of closed shapes:
- Triangles are closed figures with three sides and three vertices.
- Having only one face and no vertices, a circle is a closed shape.
- Having four sides and four vertices, a quadrilateral is a closed shape. Examples of a quadrilateral are a square, a rectangle, a rhombus, a parallelogram, a trapezium, etc.
- With five sides and five vertices, a pentagon is a closed shape.
- Hexagons are closed shapes that have 6 sides and 6 vertices.
Besides the closed shapes mentioned above, there are many others, including the heptagon, the octagon, the decagon, and the oval. Polygons are closed shapes made up of straight lines.
Open shapes
A shape with a different start point and endpoint is called an open shape. Open shapes are not continuous and cannot be traced without any breaks. The letter C is an example of an open shape.
Weird shape names
After exploring geometric shapes definition with examples, we also want to share some interesting types of shapes that you may not have heard of or seen before:
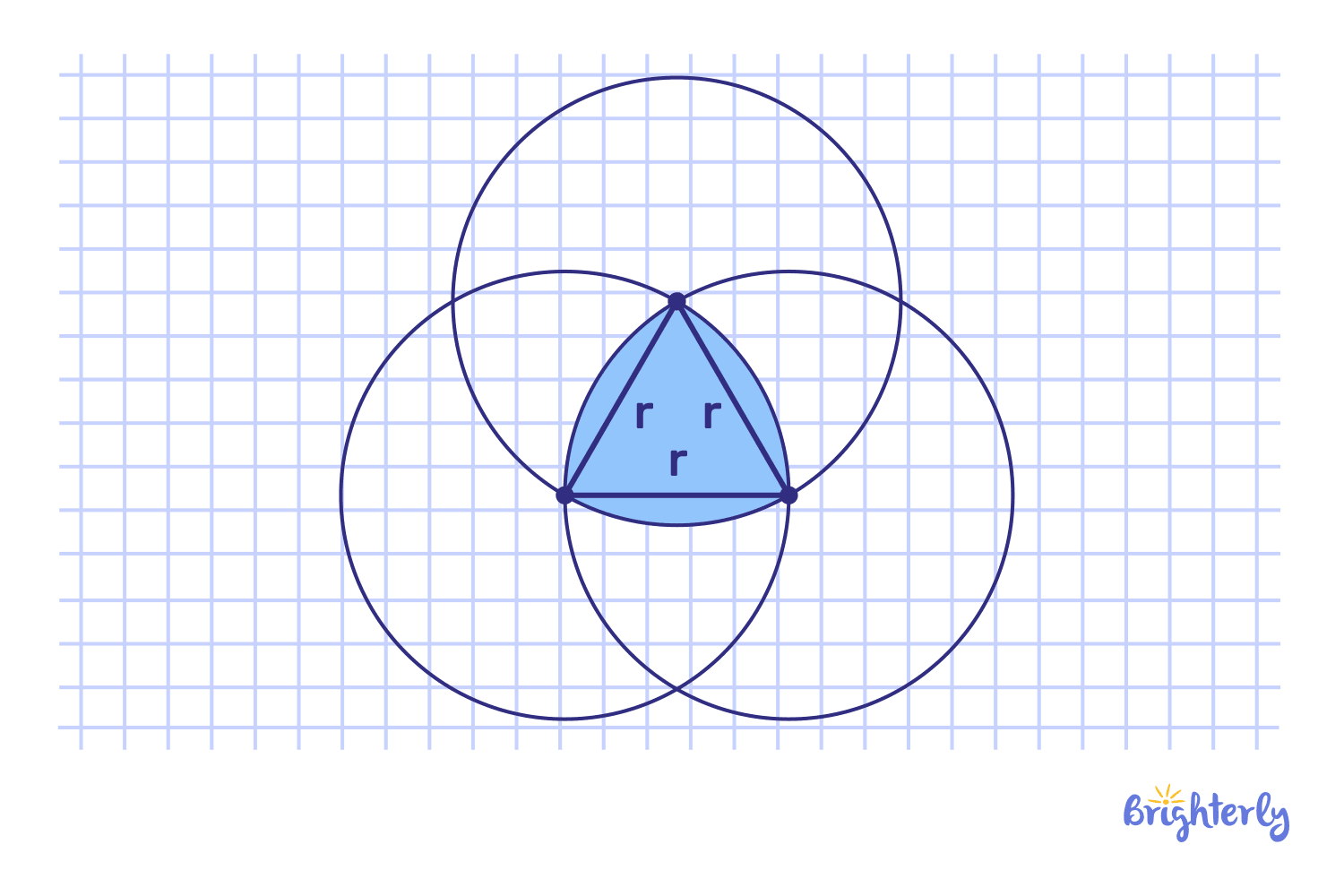
Reuleaux triangle
Reuleaux triangles are curved triangles with rounded sides so that the distance across the shape is constant regardless of direction. Since it can rotate inside a square and always touch all four corners, it is valuable in geometry.
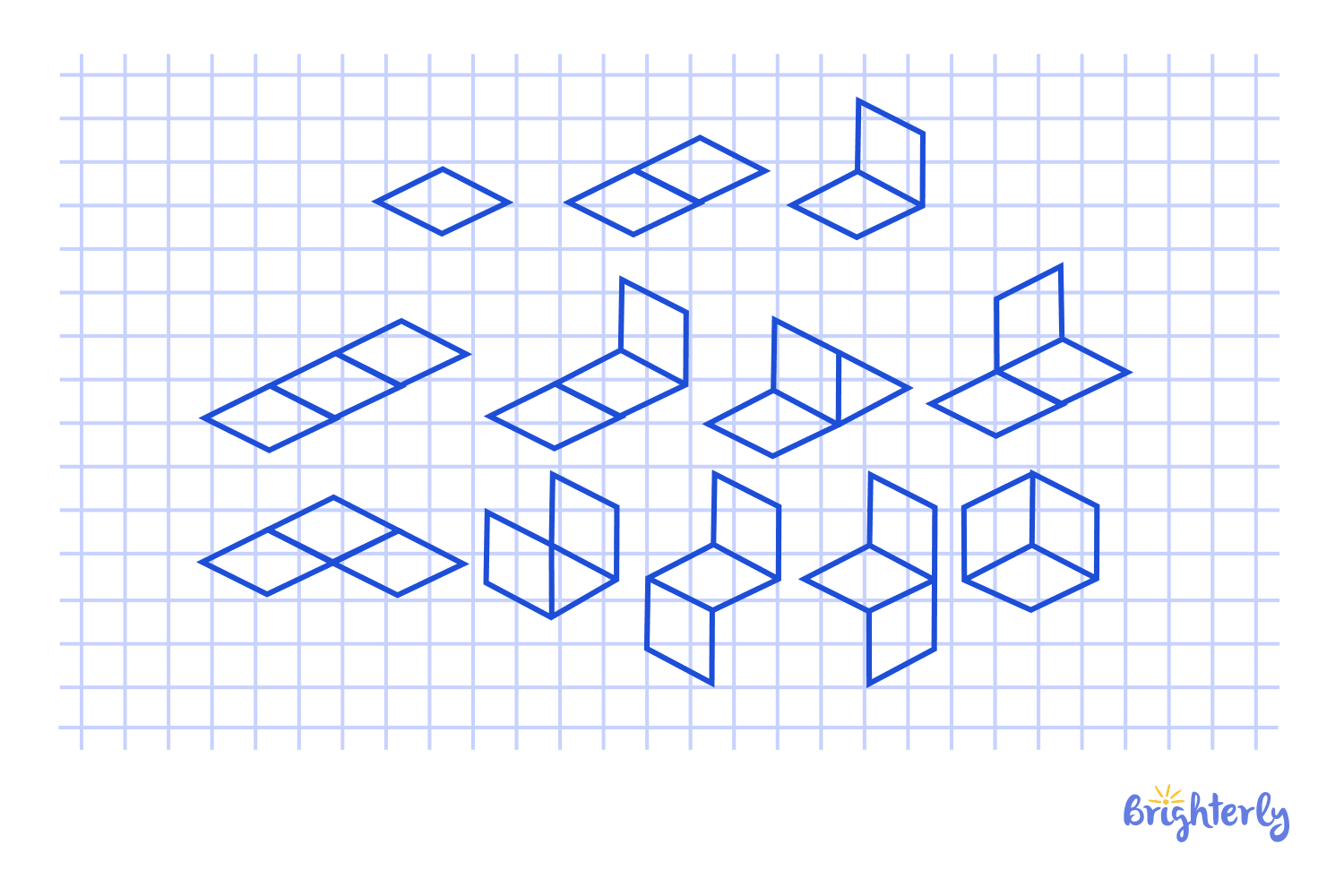
Polyomino
Polyominoes are flat shapes formed by joining many unit squares edge-to-edge. Among the different types are dominoes (2 squares), trominoes (3), and pentominoes (5). Polyomino geometric shapes examples use of these pieces in puzzles and tiling problems is widespread.
Sphericon
Sphericons are unique 3D solids with a single continuous surface and two semicircular edges. A geometric shape with a rolling surface touches the ground at every point – a surprising characteristic.
![]()
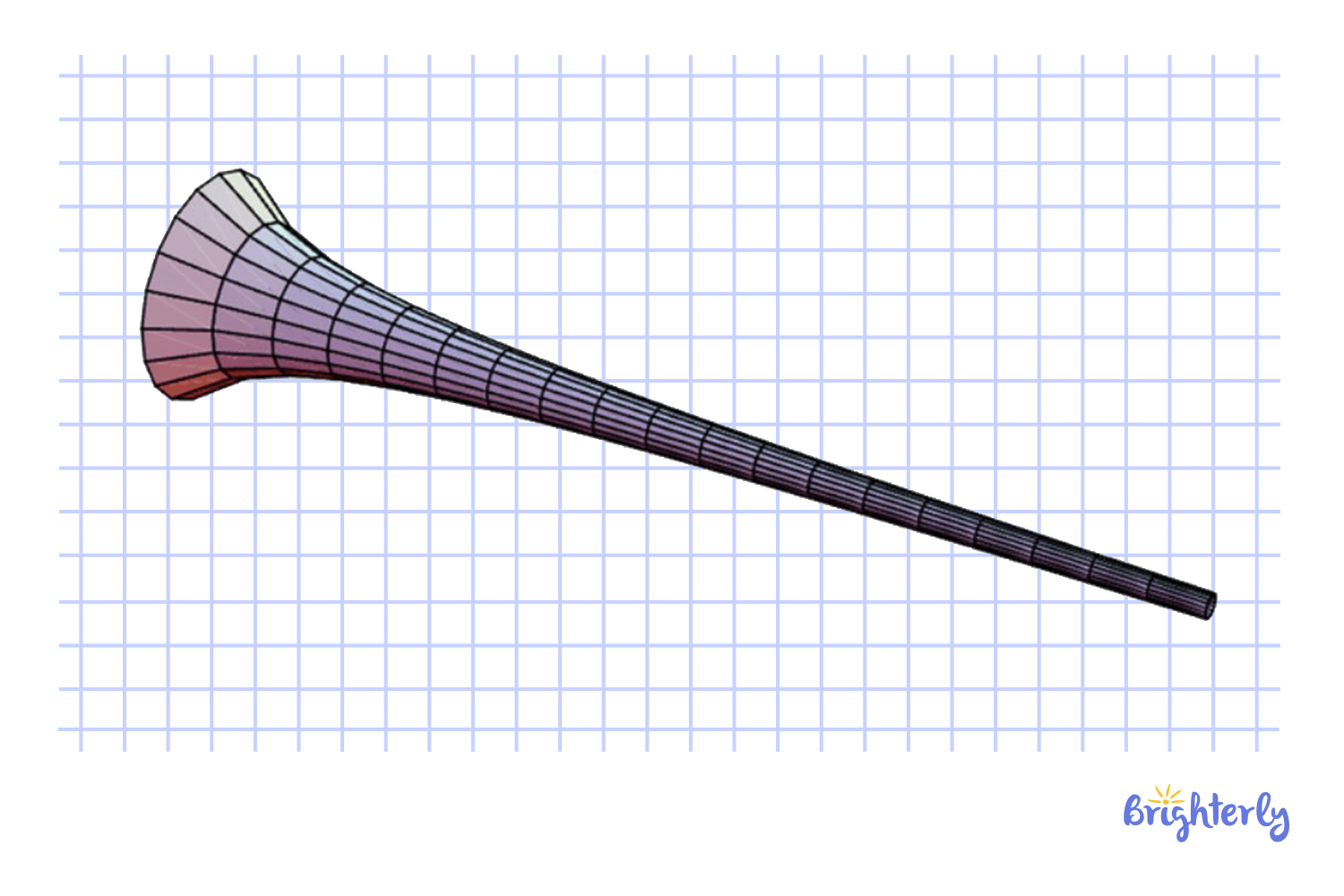
Gabriel’s Horn (Torricelli’s Trumpet)
The Gabriel’s horn is a geometric figure whose surface area is infinite, but its volume is finite. It is famous for its application to calculus and mathematical paradoxes. “The Paradox of the Painter”
The “painter’s paradox” illustrates this counterintuitive property:
- The inside of the horn can only be filled with a finite amount of paint (since it has a finite volume).
- Despite this, there would be infinity of paint required to cover the outer surface of the horn (since its surface area is infinite).
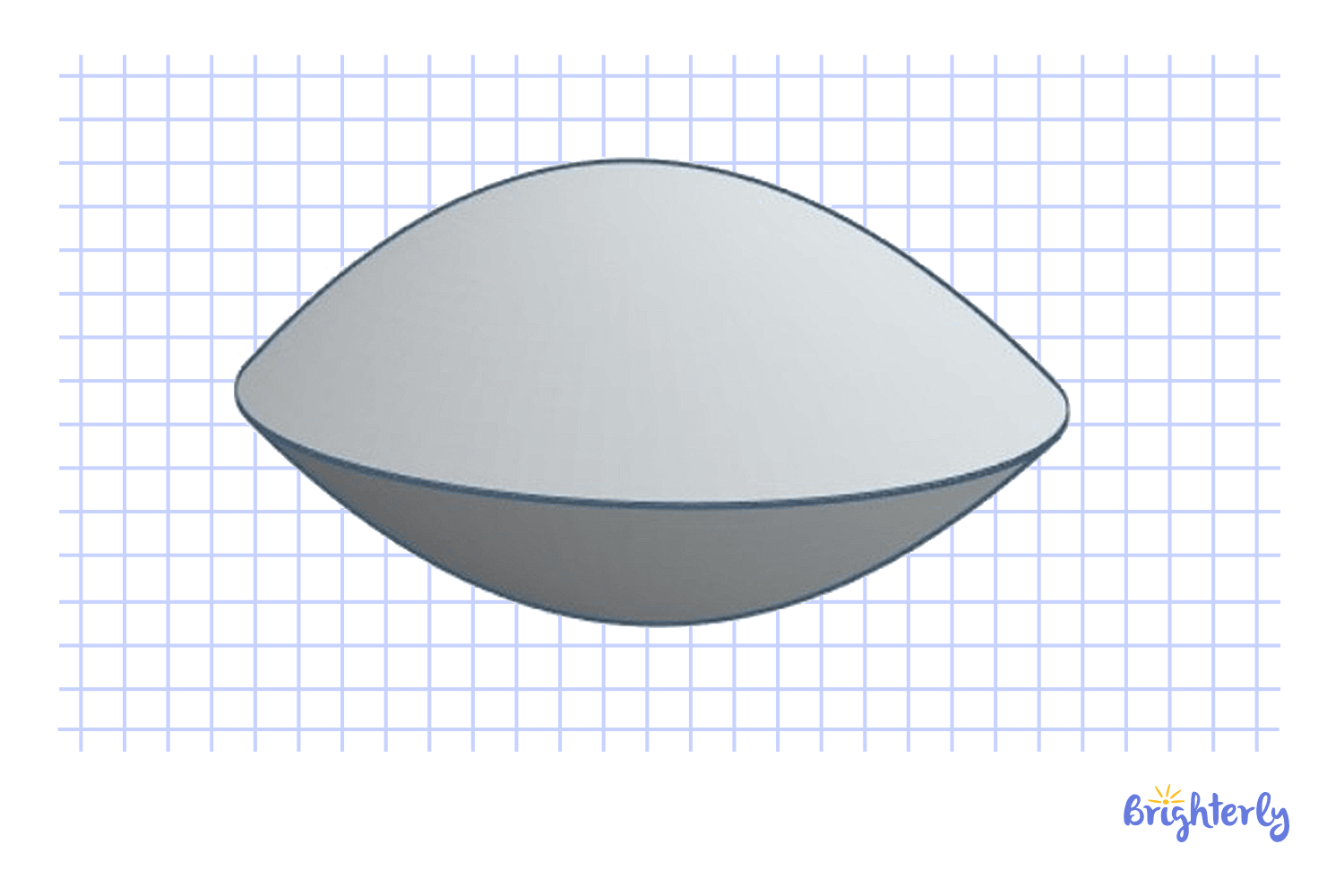
Lentoid
Lentoids are lens-shaped 3D bodies that appear like circles from one perspective, and like convex lenses from another. It is used in geometry as well as biology and jewelry descriptions.
Real-life applications of geometric shapes
Geometric shapes are not just abstract math concepts — they appear everywhere in everyday life. Architects and engineers use triangles, rectangles, and cylinders to design strong buildings, bridges, and tunnels. Circles and spheres are essential in wheels, balls, gears, and pipes because they allow smooth motion and even distribution of force.
In technology and design, screens, books, and tables are often rectangular, while cubes and prisms are common in packaging and storage. Nature also follows geometric patterns: honeycombs form hexagons for efficiency, planets resemble spheres, and snowflakes show symmetrical polygon shapes. Learning geometric shapes helps children better understand the world around them and see how math connects to real objects and practical problem-solving.
Solved examples on geometry shapes
Example 1: How many faces does a rectangular prism have?
Solution: A rectangular prism has six faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices.
Example 2: What do you call a triangle with one right angle?
Solution: A triangle with one right angle is called a right-angled triangle.
Example 3: Do cones belong to an open geometry shapes or a closed shapes?
Solution: A cone is a closed shape because its base and curved surface enclose space.
Example 4: How many sides does a heptagon have?
Solution: A heptagon has seven sides and seven angles.
Example 5: What type of polygon has all sides and angles equal and has eight sides?
Solution: A polygon with eight equal sides and angles is called a regular octagon.
Practice problems on geometric shapes
- A rectangle has:
- 4 equal sides
- 2 pairs of equal sides
- none of these
- 3 pairs of equal sides
- The line passing through the center of a circle connecting two points of it is called:
- diameter
- radius
- chord
- circumference
- Among all the types of shapes in geometry, a cylinder is a:
- one-dimensional shape
- two-dimensional shape
- three-dimensional shape
- none of this
- A pentagon with all sides and angles is called:
- open pentagon
- hexagon
- closed pentagon
- regular pentagon
Frequently Asked Questions on Geometric Shape
What are geometric shapes?
Geometric shapes are figures formed by points, lines, curves, or surfaces. They can be two-dimensional, like squares and circles, or three-dimensional, like cubes and spheres, each having defined properties such as sides, angles, and symmetry.
How did geometric shapes get discovered?
The shapes geometry were studied by ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Greeks. Over time, mathematicians formalized their properties and classification. Today, we have them leading to modern geometry as a mathematical discipline.
What are some geometric shapes?
Common geometric shapes include triangles, squares, rectangles, circles, cubes, spheres, cones, and others. There are also unusual forms like sphericons and Reuleaux triangles.
How many geometric shapes are there?
There is no fixed number of geometric shapes. Basic geometric shapes, 2D and 3D, are well-known, but mathematically, shapes are infinite, including polygons, polyhedra, curved shapes, and complex forms used in higher mathematics and design.
Geometric shapes worksheets
Here you can find free online shape worksheets (basic to advanced) that help with identifying shapes, understanding sides and symmetry, recognizing geometric properties: