Multiplication – Definition, Examples, Practice Problems, FAQs
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on December 19, 2024
Learning multiplication should not be confused with learning multiplication tables alone.
We discuss the multiplication definition with examples, why we use it, and how to master this arithmetic operation.
Let’s first dive into how multiplication is explained.
Introduction to multiplication
Multiplication is a basic arithmetic operation used to find the repeated addition of a number without a lengthy procedure.
Addition is helpful when it comes to finding the sum of two or more different numbers such as 5 + 4 = 9.
However, to find the sum of a single number with itself multiple times such as 5 + 5 + 5 + 5, addition can be a lengthy process.
Multiplication, on the other hand, is easier. All we have to do is multiply 5 by 4 which results in 20.
Multiplication Definition in Math
The multiplication definition can be looked at as the process of adding a number to itself repeatedly. It is the repeated addition of a number and the number of times is determined by the other number.
The result of a multiplication problem is called a product.
Multiplication examples
Here are some multiplication examples:
- Imagine you had 2 boxes of chocolate with 12 chocolates inside each. We can know the total number of chocolates by simply multiplying 2 by 12 which results in 24. This is an easier way to calculate the total instead of counting the contents of each box.
- In a class of 15 students, each student has 3 items of stationery. To know the total number of items in the class, we multiply 15 by 3. The result is 45.
Multiplication Signs
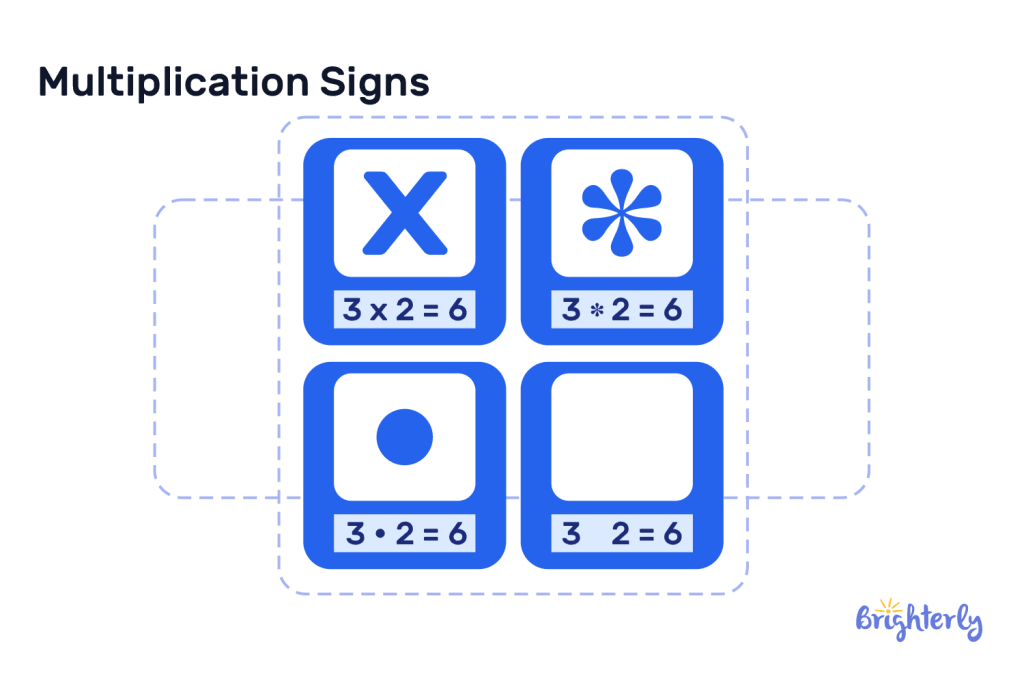
Multiplication Symbol
Multiplication in math can be represented with any of the following symbols:
- “ x ” (this resembles the letter x or a slightly bent plus sign)
- “ * ” (this is the asterisk sign. It is commonly used in computer programming)
- “ • ” (this is a dot. It is mostly used in more advanced mathematics and algebra)
All of these symbols represent the same arithmetic operation of multiplication. However, the most widely used symbol for multiplication is “ x ”.
Multiplication Formula
The formula for multiplication is:
Multiplicand x multiplier = product.
The multiplication terms: multiplicand and multiplier are the parts of multiplication and can also be known as factors. The multiplicand is the first number and the multiplier is the second number. The result of multiplication is the product.
Properties of Multiplication
Multiplication, like the other arithmetic operations, also has some properties that guide the way we use it for solving mathematical problems:
Closure Property of Multiplication
According to this property, the product of two similar numbers will be a similar number. For example, 3 x 2 = 6. These numbers are similar because they are all positive integers. If we multiply fractions, the result will be a fraction too, same as decimals.
Commutative Property of Multiplication
Per this property, we can switch the order in which we arrange the multiplicand and the multiplier without altering the result. For instance, 3 x 4 = 12, and 4 x 3 = 12.
Associative Property of Multiplication
This property states that when we group two or more numbers to multiply by another number, the result is the same if we change the grouping.
For example, 4 x (5 x 6) is the same as 5 x (6 x 4). The result in both equations is 120.
Distributive Property of Multiplication
The distributive property states that we may simplify a multiplication problem that involves grouping addition or subtraction by multiplying each number separately before we add or subtract.
For instance: 3 x (2 + 7) can be solved as:
(3 x 2) + (3 x 7)
= (6) + (21)
= 27.
Identity Property of Multiplication
1 is the identity number in multiplication, and thus, the property states that multiplying any number by 1 leaves the number unchanged.
For example, 568 x 1 = 568
Zero Property of Multiplication
The zero property of multiplication states that any number multiplied by 0 will always be 0.
For example, 1,000,000 x 0 = 0 and 1 x 0 = 0
Multiplying Integers
Integers are whole numbers that are either zero, positive, or negative.
The rules for multiplying integers are:
- + x + = + (positive multiplied by positive is positive). E.g., 2 x 7 = 14
- – x – = + (negative multiplied by negative is positive). E.g., –3 x –5 = 15
- + x – = – (positive multiplied by negative is negative). E.g., 6 x –5 = –30
These rules must be followed when multiplying integers to avoid mistakes.
Multiplying Fractions
To multiply fractions, we multiply both parts of the fractions by their respective parts. This means we multiply the numerator of the multiplicand by the numerator of the multiplier and do the same for the denominators as well.
For example, for 3/6 x ⅖, we first solve 3 x 2 = 6. Then, we multiply 6 by 5 which is 30. The product is thus, 6/30. We can also simplify it to ⅕.
Multiplying Decimals
We multiply decimals the same way we multiply whole numbers.
For example, 3.5 x 6.13 will be multiplied like 35 x 613 which is 21455.
We determine the location of the decimal point by counting the decimal places in each number and adding them.
This means because 3.5 has one decimal place and 6.13 has two decimal places, 21455 will have three decimal places.
Therefore 21455 becomes 21.455.
Multiplying Numbers with Powers
There are different ways to multiply numbers with powers. If the exponents are different but the bases are the same, we add the exponents but leave the bases as is. For example 32 x 35 = 37. All we did here is add the exponents (2 + 5).
However, if the bases are different but the exponents are the same, we multiply the bases but leave the exponents. For example 54 + 44 = 5 x 4 = 204.
Tips to Master Multiplication
Multiplication is direct. This means multiplication mastery requires regular practice including studying the multiplication table. Start with smaller and memorable multiples of numbers, like 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, etc., and work your way up.
Here are some other tips to help you master multiplication:
- Learn with visual tools like the number line and multiplication chart.
- Apply multiplication to everyday activities to make the learning process more engaging.
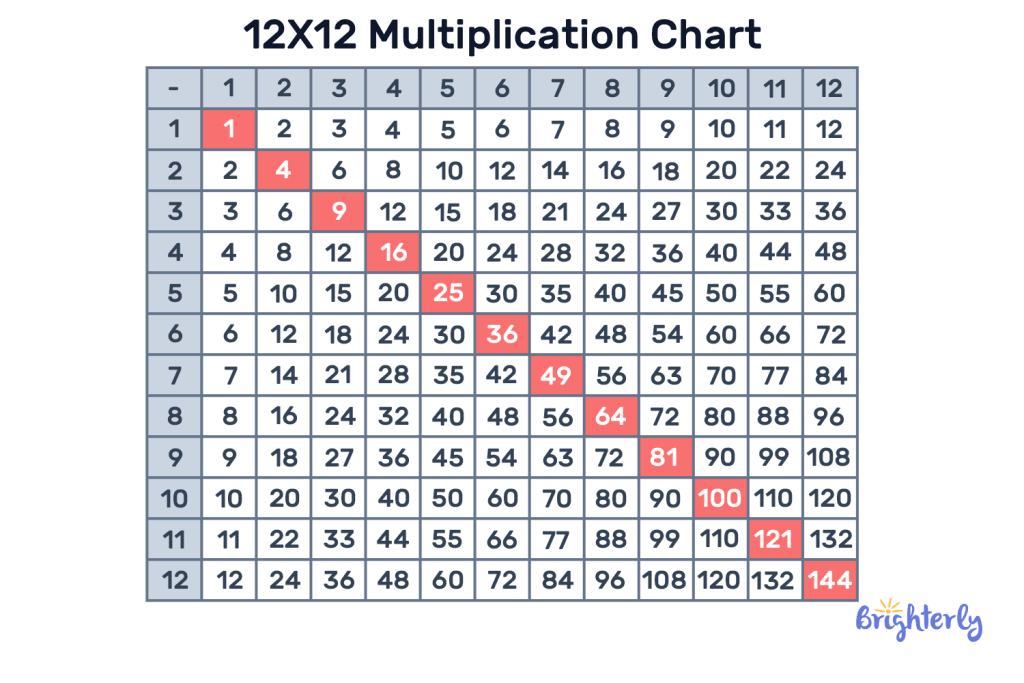
Multiplication Table
The multiplication table comprises the multiples of each number. It can also be used for basic math multiplication without calculation.
The first row is made up of numbers 1 to 12 or more and the columns of each number are the multiplications of those numbers. The first column also contains numbers 1 to 12 or more, depending on the table’s length. The multiples of each number here are the rows they are located.
We can multiply numbers with the table by looking for the multiplicand on the first row and the multiplier on the first column, then finding which cell their rows and columns intersect.
Multiplication Tricks
Multiplication has some cool tricks that can make calculations faster. They include:
- To multiply by 2, simply add the number by itself.
- Instead of multiplying a number by 9, we can multiply it by 10 and then subtract the original number. For instance 9 x 4 = 10 x 4 = 40 – 4 = 36.
How to Solve Multiplication Problems?
Here are helpful multiplication steps to solve math problems:
- Read and understand the problem
- Confirm if multiplication is the most appropriate operation
- Identify the parts of a multiplication problem involved
- Proceed to multiply.
- Verify that the result applies to the question’s context.
Multiplication Without Regrouping
We may solve the multiplication for multi-digit numbers by arranging them in a vertical order. When this happens, we may need to regroup or carry over. Let’s first discuss how to multiply without regrouping in this method:
- Arrange the digits of the multiplicand on the digit(s) of the multiplier vertically with the correct order of place values. This means the ones should be on top of each other, the tens, hundreds, and so on.
- Begin multiplication from the rightmost numbers.
- For example:
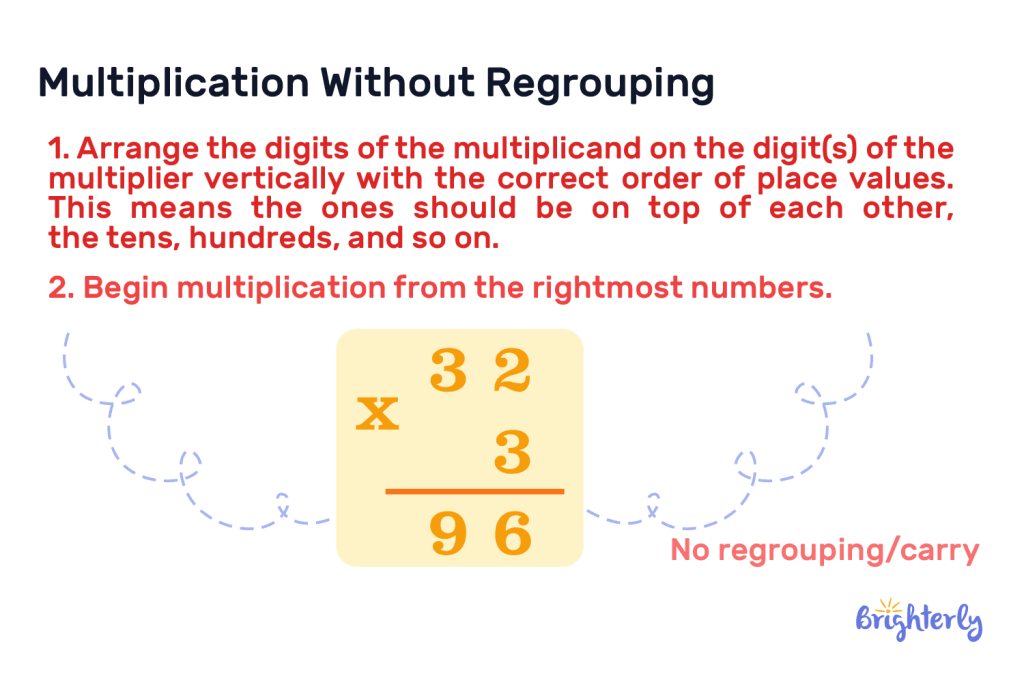
In this example, we multiply 3 by 2 which is 6, then we multiply 3 by 3 which is 9. Therefore 32 x 3 = 96.
Multiplication With Regrouping
When multiplying in the vertical order, the product of the digits may result in a 2-digit figure. When this happens, we carry over the larger digit to the next number. We multiply the second number and add the digit we carried over to the product.
In this example, we multiply 3 by 67:
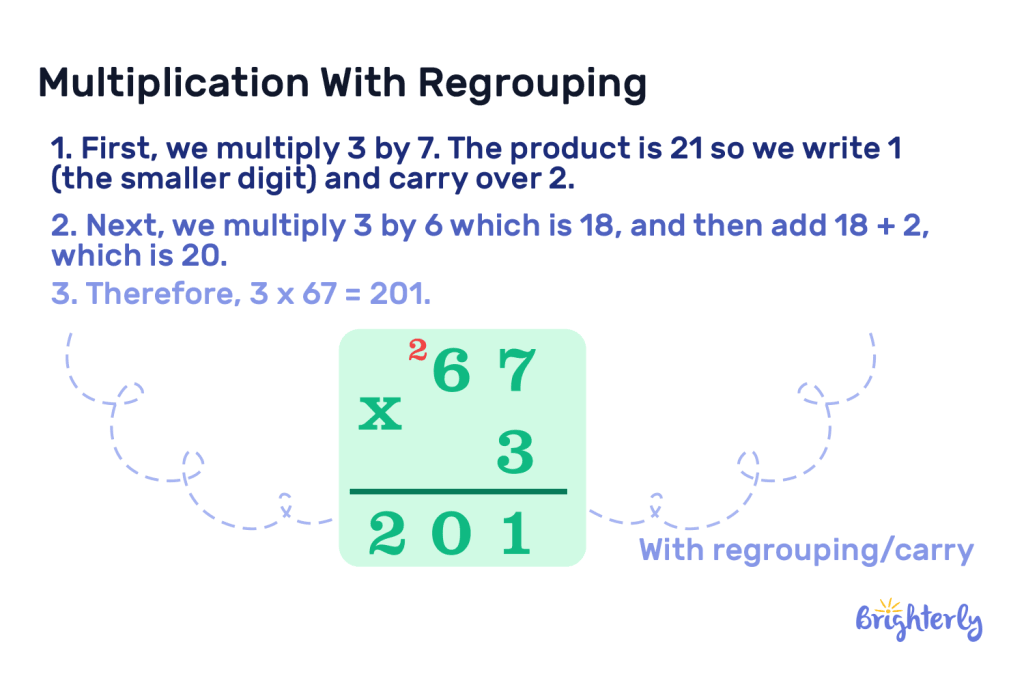
- First, we multiply 3 by 7. The product is 21 so we write 1 (the smaller digit) and carry over 2.
- Next, we multiply 3 by 6 which is 18, and then add 18 + 2, which is 20.
- Therefore, 3 x 67 = 201.
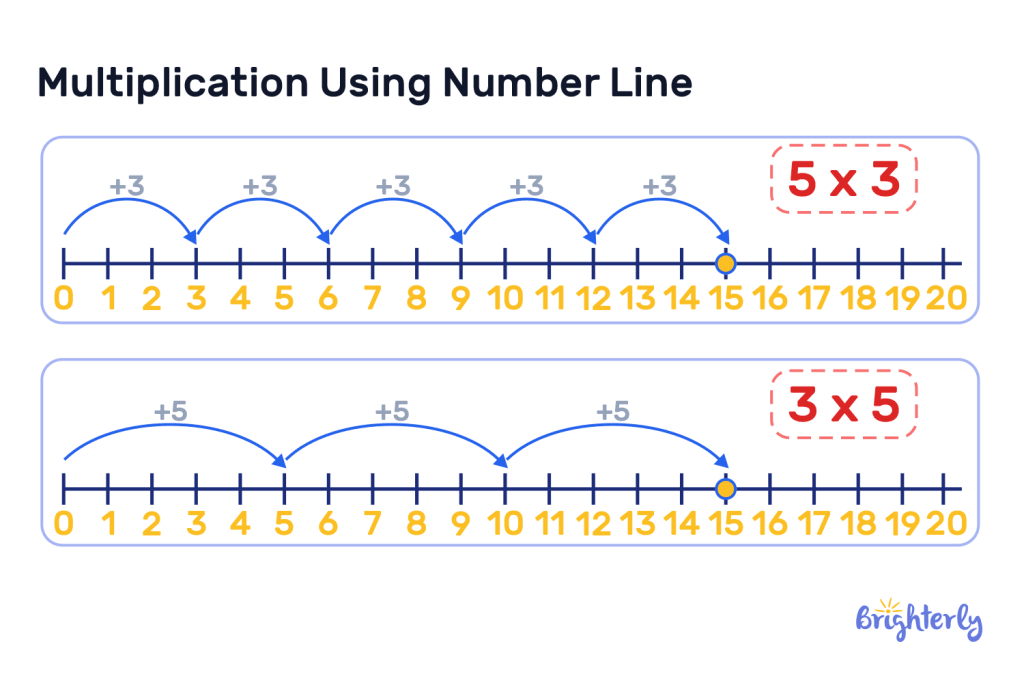
Multiplication Using Number Line
We can multiply with a number line by starting from 0, then moving towards the right in jumps of the multiplicand in the number of times as the multiplier.
An example of multiplication with a number line is if we were to multiply 5 by 3 using a number line, we start from 0 and then move towards the right in jumps of 5, 3 times. We land on 15 which is the product.
Word Problems on Multiplication
Word problems for multiplication usually involve practical scenarios that may require using multiplication to solve. For example, what is the total number of floor tiles in a room when each row has 6 tiles and each column has 7 tiles?
We solve this with multiplication: 6 x 7 = 42.
There are 42 tiles in the room.
Solved Examples On Multiplication
Solved math problem 1
What is the product of 42 x 4?
Solution
4 2
x 4
168
| 42 x 4 = 168. |
Solved math problem 2
How do we multiply 4.2 by 5.4
Solution
We multiply decimals the same way we multiply regular whole numbers. Therefore 4.2 x 5.4 becomes 42 x 54 = 2268.
| Since both numbers have 1 decimal place, the answer should have 2 decimal places, so 2268 becomes 22.68 |
Practice Problems On Multiplication
Multiplication: worksheets
Practice and learn more about multiplication through our free worksheets:
- Multiplication worksheets
- Multiplication word problem worksheets
- Distributive property of multiplication worksheets
Frequently Asked Questions On Multiplication
What is multiplication in mathematics?
Multiplication is the combination of two or more numbers. We may find the multiplication of a number by repeatedly adding it by itself as many times as the other number.
What are the properties of multiplication?
The properties of multiplication are Commutative Property, Associative Property, Distributive Property, Identity Property, and Zero Property.
How can I master multiplication?
Master multiplication by practicing regularly, learning with visual tools, and relating the problems to real-life scenarios.
How can I solve multiplication problems?
You can solve multiplication problems by reading and understanding the problem, confirming if multiplication is the appropriate operation, multiplying, and then verifying if the product matches the context of the question.