Polygon – Shape, Types, Formulas, Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on October 28, 2024
Identifying and knowing different shapes is crucial for the development of every child, not just in math, but for navigating through the real world. This article by Brighterly dives into the polygon definition and examples to help learners understand these types of shapes.
What is a Polygon?
A Polygon is a 2-dimensional flat shape, connected by straight lines without any openings or curved sides.
But what does polygon mean?
The word polygon is derived from two Greek words; “poly” and “gon” with “poly” meaning many and “gon” meaning angles.
Therefore polygons have many angles. As a matter of fact, polygons can only have three or more angles.
Polygon definition
In math and standard geometry, we define polygons as any plane and closed shape made of straight connected lines.
What does a polygon look like?
A polygon looks like a notebook, a door, or a slice of pizza. The following are some of the characteristics that can help us identify the polygon:
- It must have at least 3 sides
- It is a two-dimensional shape, i.e, it only has length and width
- It has no open spaces or curved edges
- It is made up of straight lines and sides, i.e, it is a plane shape
Examples of polygons
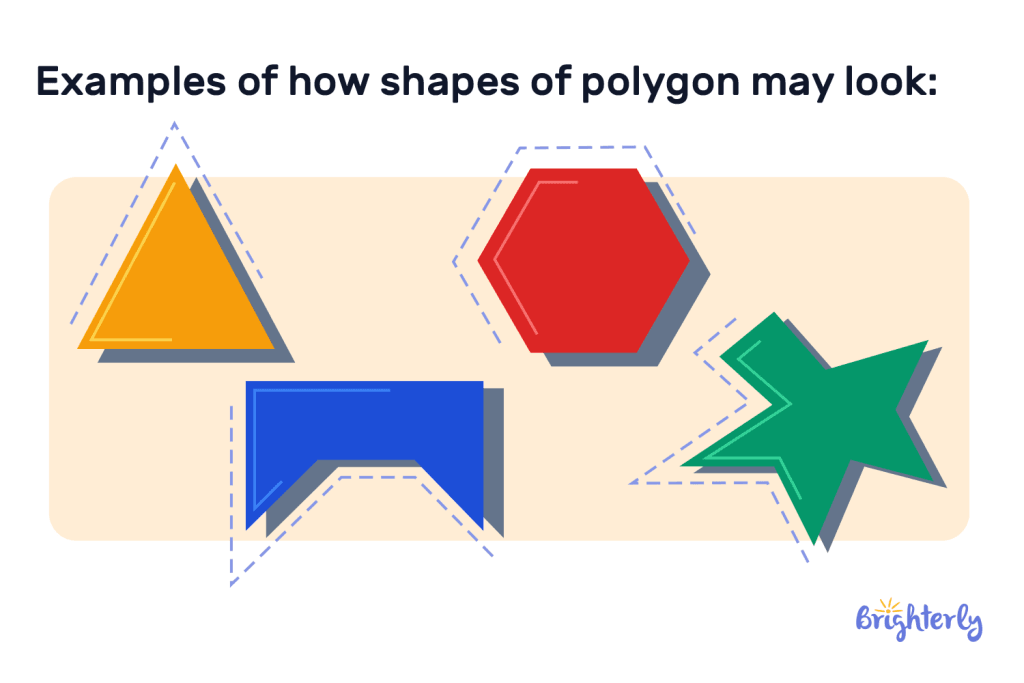
Following the examples we have listed above, here are some examples of how shapes of polygon may look:
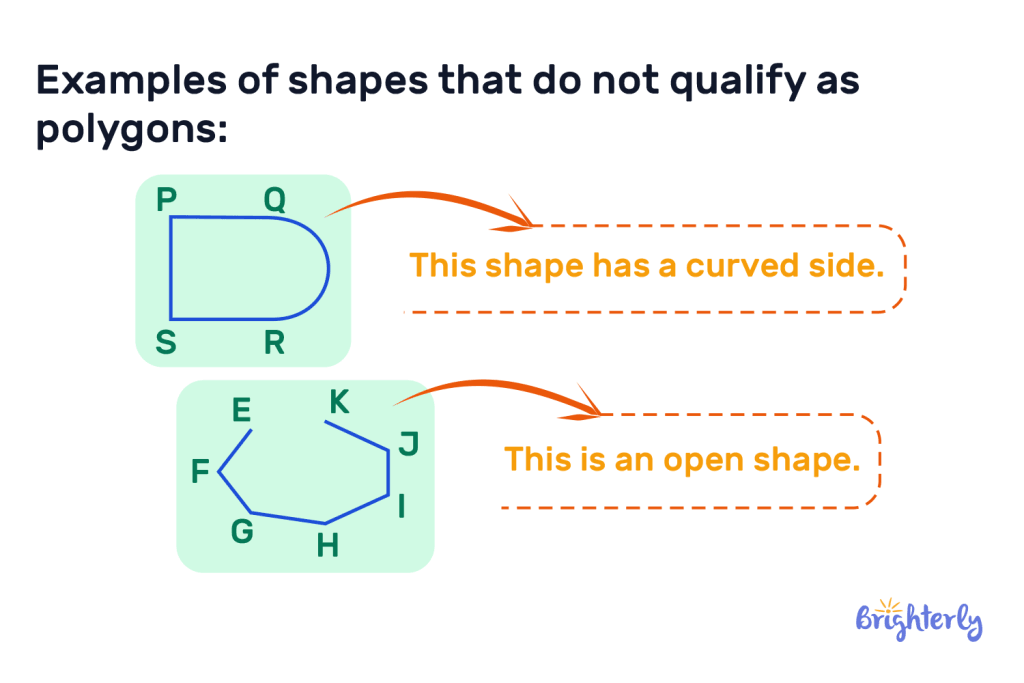
Also, here are some examples of shapes that do not qualify as polygons:
Polygon: Chart
As long as a shape possesses the characteristics we mentioned above, it qualifies as a polygon and one of these characteristics is that a polygon must have at least three sides. This means a polygon may have 3,4,5, or more sides. The below polygon classification chart consists of polygon examples and what they are called according to the number of sides it has:
| Number of sides on the shape | Name of Polygon |
| 3 | Trigon or Triangle |
| 4 | Tetragon or Quadilateral |
| 5 | Pentagon |
| 6 | Hexagon |
| 7 | Heptagon |
| 8 | Octagon |
| 9 | Nonagon |
| 10 | Decagon |
Fun fact: Upon inspection, you may notice that the prefixes are of Greek origin. For instance, “Tri” means three in Greek, “Tetra” means four, and so on. This is because of the original roots of the word and many mathematical terms in ancient Greece.
Polygon types
There are two (2) types of polygon shapes; regular and irregular.
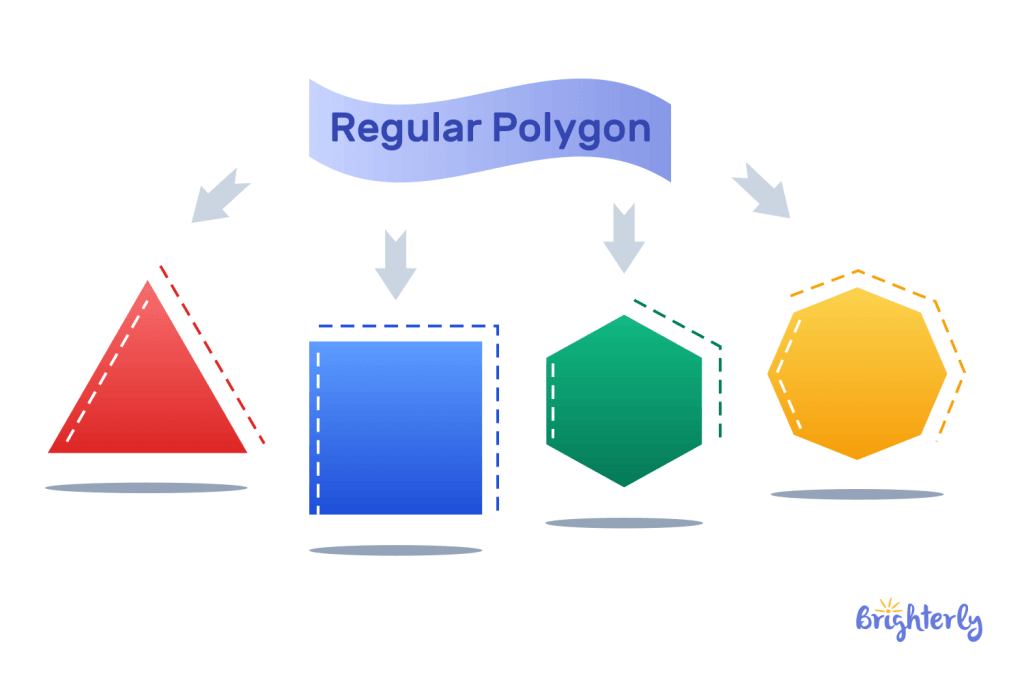
Regular Polygon
A polygon is said to be regular when all the sides and angles are equal. A square is an example of a regular polygon. Here are some other examples of regular polygons:
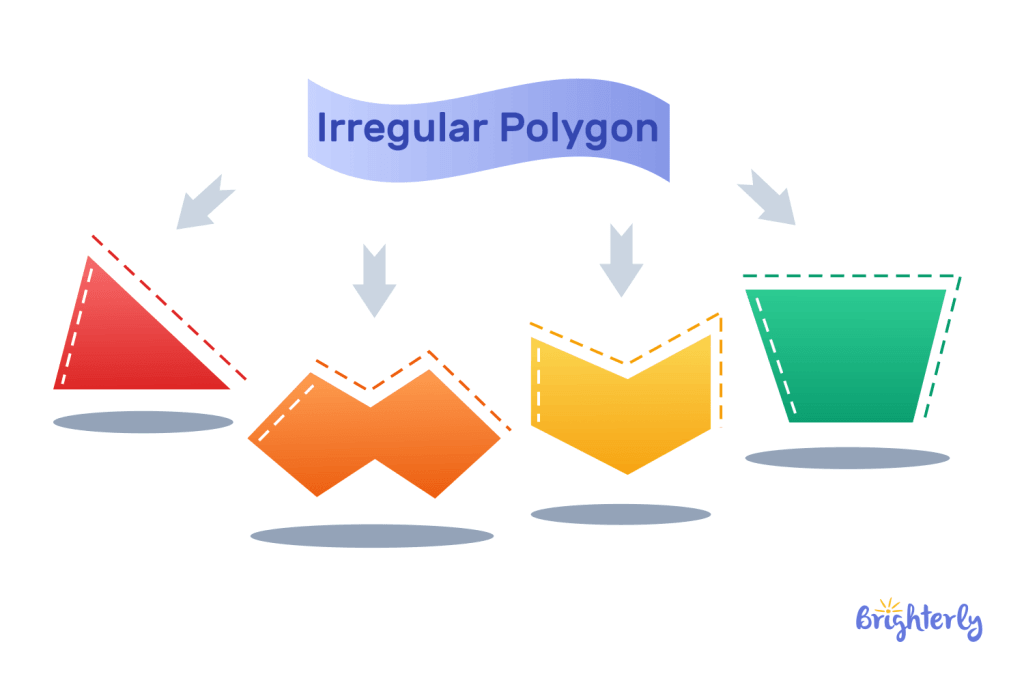
Irregular Polygon
When the sides and angles that make up the shape are unequal, it is an irregular polygon. An obtuse triangle is an example of an irregular polygon.
These are some other examples of irregular polygons:
Polygons can also be classified into different types based on the interior angles: Convex and Concave.
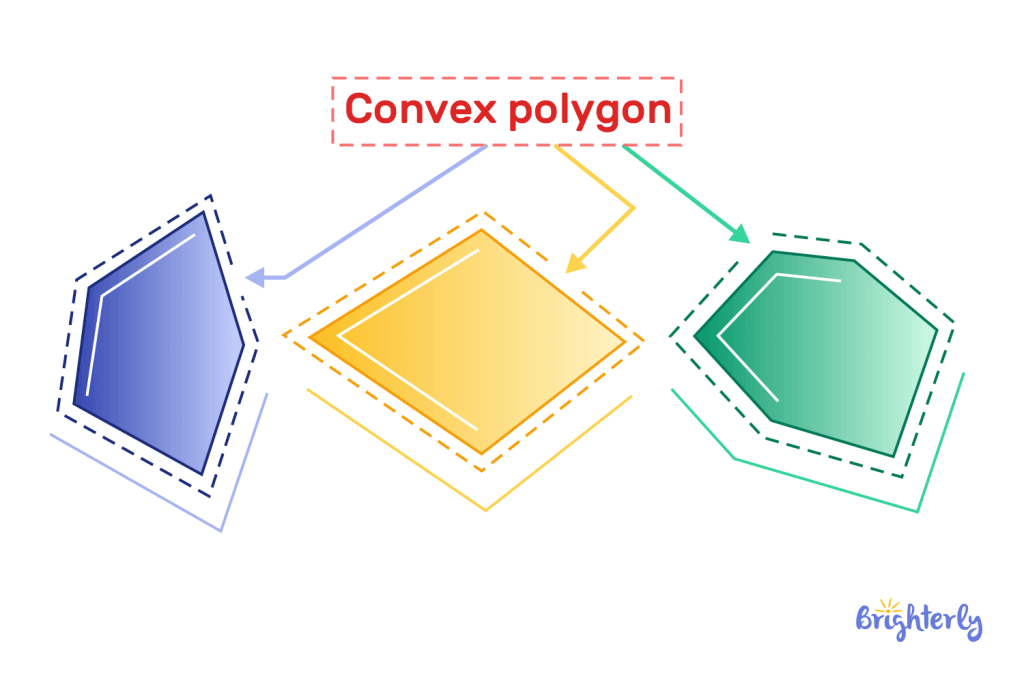
Convex polygon
For this type of polygon, all the interior angles are less than 180° degrees. Convex polygons are also regular polygons.
Here are some examples of how it looks:
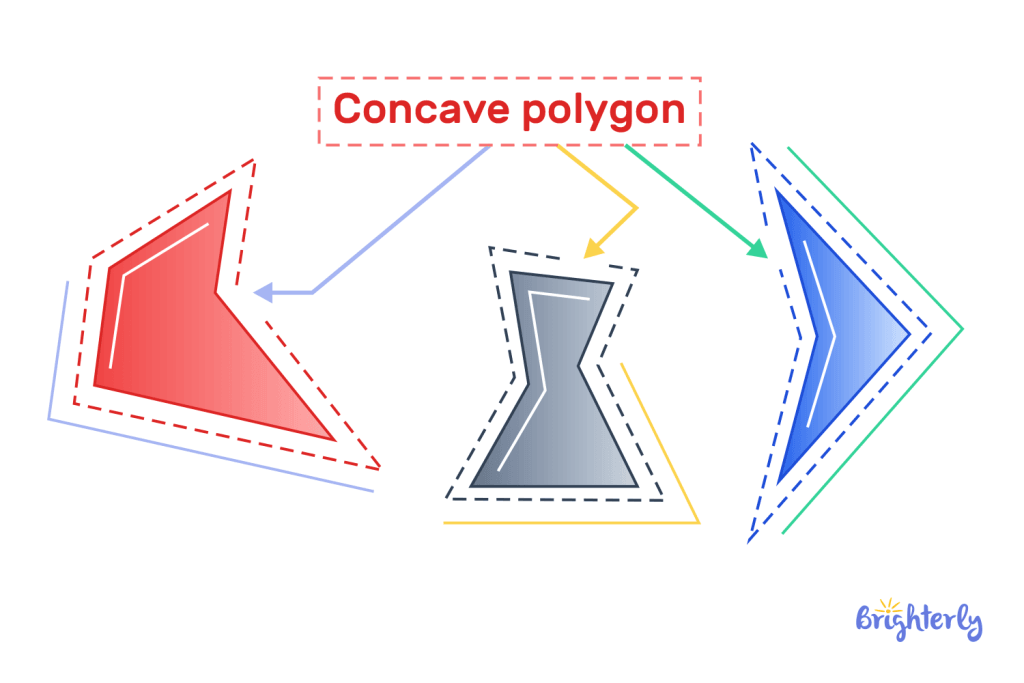
Concave polygon
This type of polygon has one or more interior angles greater than 180° degrees. Concave polygons fall under irregular polygons.
These are some shapes that form the concave polygon:
There are still some other types of polygons such as simple polygons, complex polygons, equiangular polygons, tangential polygons, and so on. But now, let’s stick to the ones we’ve already discussed.
Angles of a polygon
Polygons have two angles:
- Interior angles
- Exterior angles
The interior angles are the angles that may be found inside the polygon at the point where two sides of the shape meet.
The exterior angles, however, are the angles that are formed outside the polygon when one side touches another.
Sum of the interior angles of a polygon
When we want to get the interior angles of a polygon, we observe the number of sides in the polygon, subtract 2 from it, and then multiply it by 180°.
Let’s assume we were given a polygon with 5 sides, here’s how we would solve for the sum of the interior angles:
(5-2) × 180°
= 3 × 180°
= 540°
Thus, we can conclude that a pentagon (polygon with 5 sides) has as 540° as the sum of its interior angles.
Sum of the exterior angles of a polygon
The calculation of the sum of the exterior angles always is 360°. This means if we were to find the exterior angle of a hexagon (polygon with six sides), we would add all the sides, and the result would be 360° — this is the same for both regular and irregular polygons.
The irregular polygon has unique angles and sides, so each angle is different. To find an exterior angle for an irregular polygon, you will have to know the number of sides in the polygon, as well as the values of some of the other exterior angles.
Finally, don’t forget that a regular polygon has equal sides and angles which means each angle will be the same, and to find the exterior angle you only have to divide 360° by the number of sides in the polygon.
Solved Math Tasks: Examples
Solved math problem 1
Examine the given shapes below, which of these three different polygons is a tetragon?
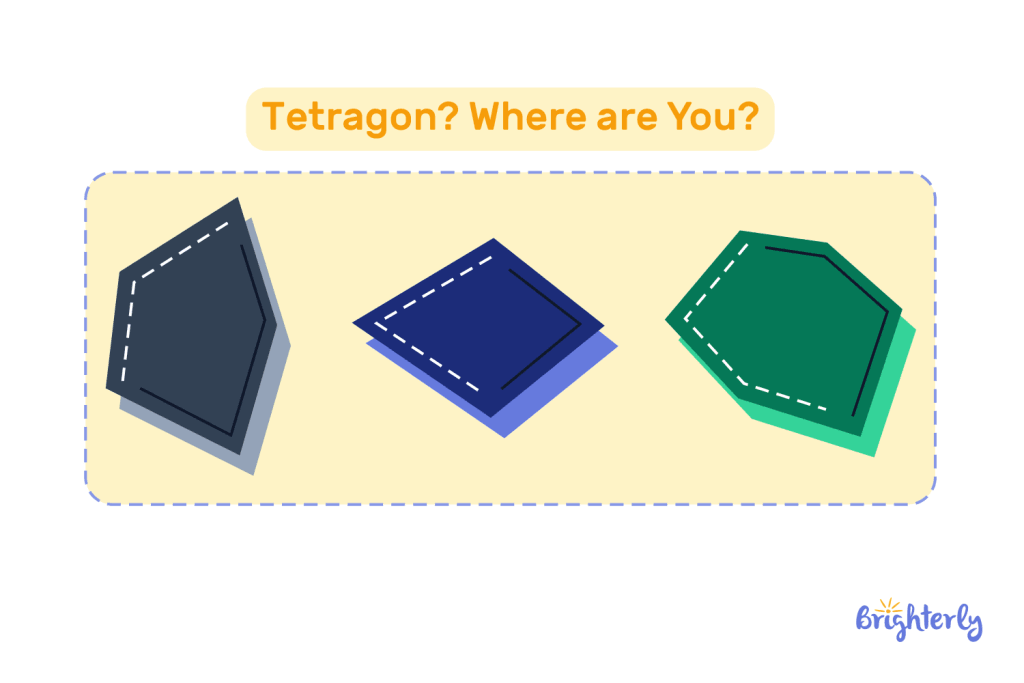
Answer
| A tetragon or a quadrilateral is a type of polygon with four sides. From the images above, the middle polygon is a tetragon. |
Solved math problem 2
What types of pentagons are each of the following:
- A pentagon with 7 sides
- A pentagon with 9 sides
- A pentagon with equal angles and sides
- A pentagon with 3 sides
- A pentagon with 5 sides
- A pentagon with 10 sides
Answer
|
Solved math problem 3
We have been given a polygon with an unspecified number of sides. How do we find the number of sides it has when its interior angles add up to 540°?
Answer
Remember that the sum of the interior angles adds up to 180°, to find the number of sides, we’d follow the formula:
540° = (n–2) × 180°
n–2 = 540/180
n–2 = 3
n = 3 + 2
n = 5
| The polygon with 540° as the sum of its interior angles has 5 sides (a pentagon). |
Solved math problem 4
Find the interior angle of a polygon with 8 sides.
Answer
(8–2) × 180°
=1080°
| An octagon has 1080° as the cumulative interior angle. |
Polygon: Practice Math Problems
Polygon: worksheets
With Brighterly, young students can further their learning about shapes, polygons, math, and geometry through our worksheets. Here are some of them: