Reviewed by Rachelle Bencio Yu
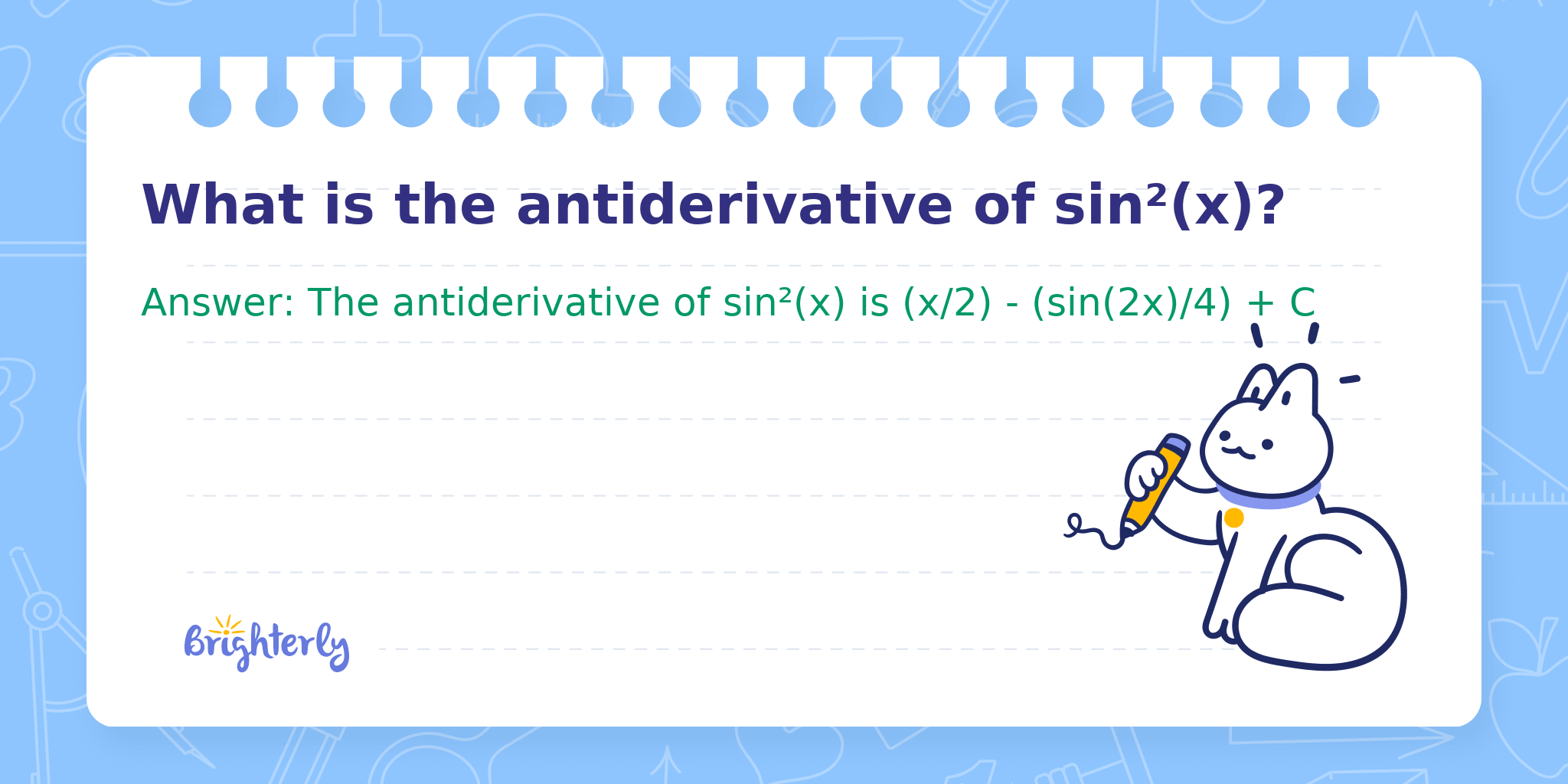
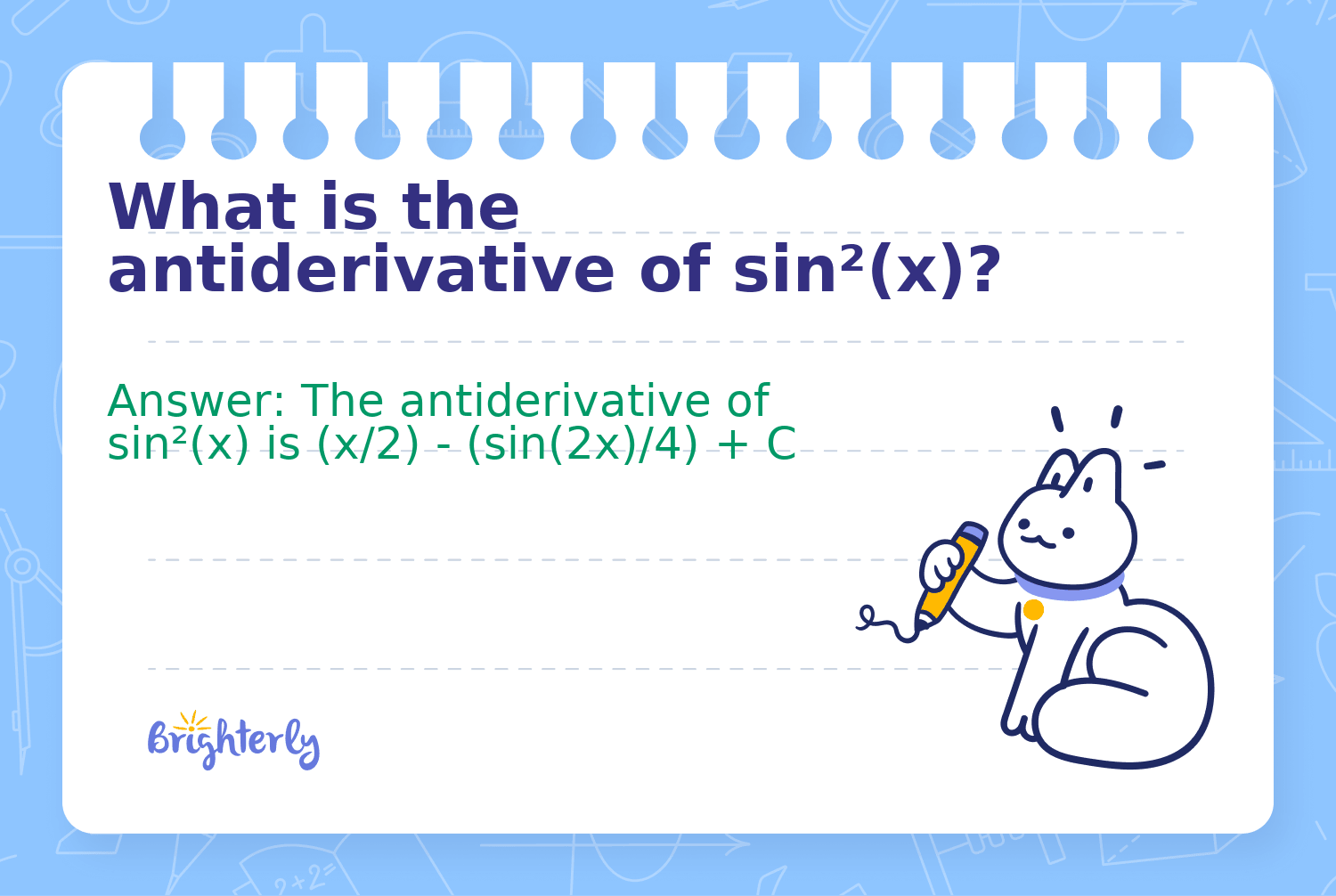
What is the antiderivative of sin²(x)?
Answer: The antiderivative of sin²(x) is (x/2) - (sin(2x)/4) + C
Finding the antiderivative of sin²(x) involves integrating a trigonometric function squared, which is common in calculus. This calculation uses identities and integration techniques to break the function into a more manageable form. Understanding this process is essential for solving problems involving the area under trigonometric curves.
Methods
Math Tutor Explanation Using the Power-Reduction Identity
The power-reduction identity allows us to transform sin²(x) into a sum of trigonometric functions that are easier to integrate.
Step 1: Step 1: Rewrite sin²(x) as (1 - cos(2x))/2 using the power-reduction identity
Step 2: Step 2: Integrate (1/2) - (1/2)cos(2x) with respect to x
Math Tutor Explanation Using Substitution
Alternatively, the substitution method can be used after expressing sin²(x) in terms of cos(2x).
Step 1: Step 1: Set u = 2x so that du = 2 dx
Step 2: Step 2: Substitute and adjust the limits or differentials as needed
Step 1:
Step 2:
Math Tutor suggests: Explore More Integrals and Trigonometric Calculus
Deepen your understanding of integrals and trigonometric functions with these related calculus questions.
FAQ on Integrating Squared Trig Functions
Why do we use the power-reduction identity when integrating sin²(x)?
The power-reduction identity makes the integral easier by expressing sin²(x) as a sum of functions that are straightforward to integrate.
Can the antiderivative of sin²(x) be written differently?
Yes, though (x/2) - (sin(2x)/4) + C is the most common form, equivalent expressions may arise from different algebraic manipulations.
What is the antiderivative of sin²(ax)?
It is (x/2) - (sin(2ax)/(4a)) + C, adjusting for the coefficient inside the sine function.
What does the 'C' mean in the antiderivative?
C is the constant of integration, accounting for any constant value that could be added and still satisfy the indefinite integral.
How can I check if my integration of sin²(x) is correct?
Differentiate your result; you should recover the original function sin²(x).