ADHD and Spelling: Common Challenges and Ways to Help
reviewed by Laila A. Lico
Updated on February 1, 2026
ADHD and spelling challenges co-occur. If parents and teachers only knew how often! Then they wouldn’t ask why a bright, curious child still struggles to write words correctly.
This article is my attempt to explain why spelling can be so hard for children with ADHD and help them thrive. This isn’t advice that is too good to be true, but exact strategies that come from working closely with students, families, learning specialists, and the result of thorough research.
Does ADHD affect spelling?
The answer to the question, ‘Does ADHD affect spelling and reading?’ will be yes, definitely. A bushel of studies strongly suggests that ADHD children have greater difficulties in writing compared to other abilities and make more spelling errors than typically developing children, not only under dictation, but also in a copy task.
ADHD spelling mistakes happen because of problems with attention, working memory, and learning process organization, all of which are critical for writing and reading words accurately.
Do people with ADHD struggle with words?
People with ADHD do struggle with words, but the cause of this struggle isn’t rooted in language itself. When I watch a child with ADHD and spelling difficulties, what I see isn’t confusion about language. Typically, kids with ADHD know words and read them aloud correctly. They can hear sounds in a word and recognize the correct spelling when they see it. Yet writing those words accurately can get tricky. Why is it so?
Let me put it metaphorically to explain what is happening with a child with ADHD spelling. Imagine a brain running on a highway with too many exits and not enough signs. It simply can’t quickly figure out which exit is the right one or how to choose it.
In my experience, a child with ADHD can stare at a familiar word and still spell it incorrectly because so many processes must occur simultaneously. Thus, spelling is a complex multi-sensory process. It requires holding the sounds of a word in working memory, remembering the correct letter order, applying rules (e.g., when to use ie vs ei), and checking over work, and all of these while staying focused!
That’s a tall order for most students, and even more so when attention and organization are under strain. With attention pulling in different directions and working memory overloaded, the brain drops pieces of information along the way.
Besides, students with spelling learning disability related to ADHD face the sheer number of deep rabbit holes they can fall down in a single spelling task. It can be any distraction, for instance, a noise in the room, a thought about an upcoming fun activity, a message from a friend, or the impulse to rush ahead; anything can affect spelling and make the difference between correct and incorrect.
Not always can people with dysfunctional spelling and ADHD cope with this problem alone. Sometimes they need urgent help.
ADHD spelling strategies that help
- Spelling help from professionals
- Multi-sensory spelling practice
- Breaking words into smaller parts
- Spelling through reading practice
- Slow writing practice
Surveys and experimental studies indicate that when learning is adapted to how ADHD brains work, some spelling strategies can seriously strengthen this skill. For example, when self-monitoring, structured practice, and multi-sensory intervention are applied, spelling accuracy and on-task behavior do improve.
Note: In a study where students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder were taught self-monitoring strategies, both their time on task and their spelling accuracy increased compared with baseline levels.
Get spelling help from professionals
Individualized learning support is probably the most effective way to give a child with ADHD and spelling challenges a chance. Now, it’s easy. Parents don’t need to ask their neighbors’ advice to find an experienced learning professional. All you need to do is choose one from a specialized platform, as the Brighterly math and reading platform, for example.
Brighterly reading tutors know how to help an ADHD child with spelling and offer focused sessions broken into smaller chunks. Convenient online lessons integrate spelling practice and writing skills without overwhelming the child. Crucially, the personalized lessons are designed purposefully to reduce fatigue and improve attention control, and you can see the results soon.
Students with ADHD spelling experience difficulties with processing symbols because of the lack of concentration and inability to organize and manage the learning process by themselves. They need a teacher who understands their problem and uses gentle repetition to weave together phonics, memory, and writing.
Brighterly lessons are built with these specifics in mind and help students with ADHD and spelling trouble get a handle on spelling patterns in a more organized way using an interactive approach and printable reading worksheets for kids.
These worksheets guide a child through one small spelling task at a time, keeping attention on the word rather than drifting to everything else in the room.
Use multisensory spelling practice
Multisensory learning means engaging more than one sense at a time: say the word aloud, trace letters, clap syllables, or build words from tiles to help words “stick.”

Multisensory teaching is a real remedy for younger school-aged children who need different ways to process sounds and letter patterns. Parents can try this strategy at home. For example, you can ask your child to say a word out loud, tap each syllable on the table, and then build it with letter tiles before writing it down.
Break words into smaller parts
This is probably the easiest way if you don’t know how to help ADHD child with spelling. Long words are intimidating for them, so teaching children to break words into syllables, prefixes, or sound chunks reduces cognitive load.
You can apply one of the spelling strategies at home in the following ways:
- You can write a long word on paper, cover part of it with your hand, and reveal one syllable at a time as your child spells it out loud.
- Another strategy is to draw short lines under the word to mark sound chunks, then spell each part separately before putting the whole word back together.
Note: For further strategies, you can check comprehensive ADHD and Writing article.
Practice spelling through reading
Reading and spelling have a connection; it’s understood. Naturally, when children read regularly, they absorb spelling patterns and rules. As I mentioned previously, reading worksheets for kids and guided reading sessions strengthen word recognition and spelling accuracy better than any other method.
Parents notice a striking change from the older versions of their child’s writing once reading becomes part of the daily routine.
Note: You can find more information on the topic in the ADHD and Reading article.
Try slow writing to cure ADHD spelling
Children make quite a lot of spelling mistakes because they rush. What can be of real help in this case is slower writing, a habit of self-checking, and breaks between. These are the three worthy methods to catch errors before they pile up.
Last but not least, this is a great strategy to regulate emotions when they are too intense. The less frustration kids feel, the more overall learning outcomes there will be in the long run.
Why do people with ADHD have difficulty spelling?
People with ADHD have difficulty spelling because of how their brains work. Children with ADHD are just as capable as their peers; however, their brains process information differently, and the symptoms include:
- Kids can’t sustain focus and skip letters or sounds;
- Working memory is in deficit, which means trouble holding sounds and rules in mind;
- Spelling doesn’t become automatic, requiring constant effort;
- Kids show impulsivity and write too quickly without reviewing their work.
These challenges explain why ADHD-related spelling problems often appear inconsistent. On good days, spelling looks fine. On harder days, errors multiply. You can see it vividly during tests or long assignments, when the ADHD brain is too excited and works faster than the hands.
Common ADHD spelling mistakes
- Leaving out letters or syllables
- Mixing up similar sounds (b/d, p/b, f/v)
- Writing letters in the wrong order
- Inconsistent spelling of the same word
- Trouble applying spelling rules.

These errors can occur in both boys and girls, though symptoms may appear differently.
Note: If you want to dive deeper into the topic of ADHD spelling, don’t miss out on the How to help kids with spelling article.
How does dyslexia affect spelling compared to ADHD?
Dyslexia affects spelling because of difficulties processing speech sounds, while ADHD affects spelling mainly due to inattention, rushing, and working memory challenges.
In other words, “Does dyslexia affect spelling the same way ADHD does?” – the answer to this question is that both children with dyslexia and children with ADHD may struggle with spelling. Yet the root causes and patterns of those struggles are distinct.
Dyslexia is a language-based spelling learning disability
Dyslexia deals with phonological processing. Thus, their brain has trouble linking sounds (phonemes) with letters (graphemes), affecting the reading effectiveness as early as preschool. The signs of dyslexia spelling include (but aren’t limited to):
- spell words phonetically (writing how they sound rather than how they are)
- reverse or confuse letters (like felt instead of left)
- misremember the sequence of letters and not associate letters with sounds.
If comparing kids with dyslexia to those without learning disorders, children with dyslexia make more errors across reading and spelling tasks. Usually, they show deeper language processing issues, even compared with kids with ADHD and spelling difficulties.
ADHD: spelling difficulties from executive and memory challenges
In contrast, my experience with students who have ADHD spelling shows a different pattern. These kids understand the sounds of words and the spelling rules in theory, but have a harder time applying that knowledge in writing.
They have the pieces of the puzzle, but don’t know how to put them together under cognitive strain. So, numerous mistakes don’t come from phonological deficits like in dyslexia, but from such factors as:
- attention lapses (skipping parts of words because focus drifts)
- trouble holding letter sounds and rules in mind while writing
- difficulty with planning, monitoring, and checking work.
I’ve seen students with ADHD and spelling problems who know how to spell a word aloud and still write it wrong. It’s all because their memory “dropped it” mid-process, or they got distracted before checking their work.
Here are some simple examples of how spelling difficulties can look in children with dyslexia and ADHD.
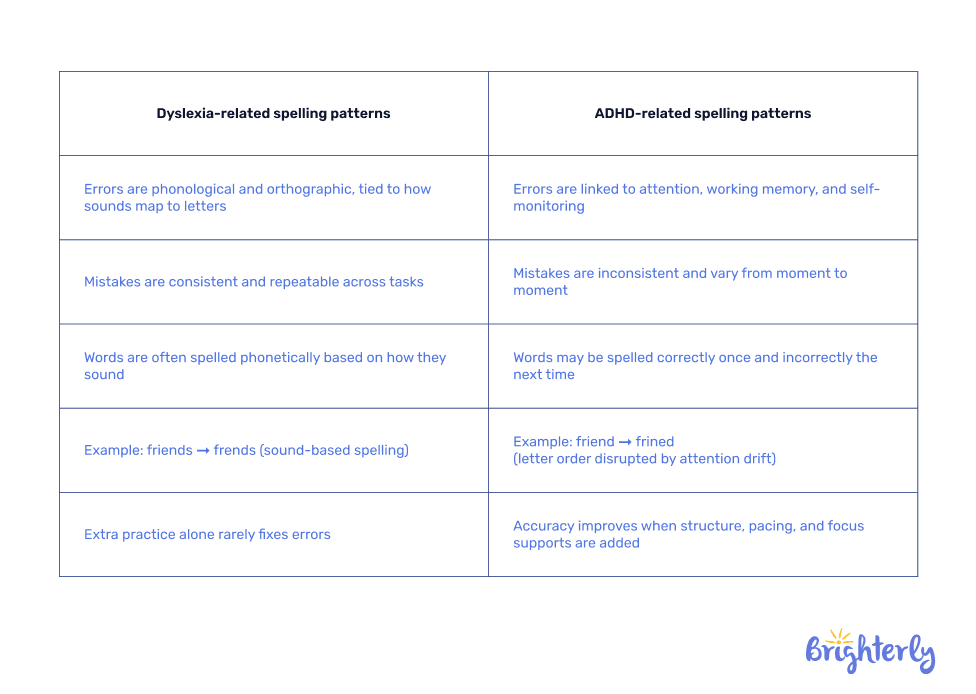
These patterns aren’t random and reflect underlying cognitive profiles, so educators can choose appropriate interventions when needed.
What if a child has both ADHD and dyslexia?
When both conditions are present, the child struggles with both the phonological challenges of dyslexia and the executive/memory ADHD spelling challenges. In those situations, a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work.
If that’s the case, some of the best strategies you can use include multi-sensory instruction and structured practice. Overall, you should adopt a more personal approach to teaching that addresses both the language-based and attention/memory components of spelling.
Conclusion
Luckily, ADHD doesn’t define a child’s ability or future. Patience and timely support are key when you want to help children improve spelling skills and gain confidence. With small steps, you can achieve real progress through professional help, multisensory learning, guided reading, and other proven ADHD spelling strategies.
For those who need extra support, e-learning resources like the Brighterly math and reading platform offer 1:1 personalized lessons. You can book free reading lesson and test it out right away.