Number Properties – Definition, Types, Chart
reviewed by Mary Grace Carlos
Updated on January 8, 2026
Whether your child is just starting with basic addition or has moved to more complex algebraic equations, number properties is one of the most important topics they can learn, as they are what govern how math works. Think of them as the “grammar” of math, which makes sure that no matter how you move numbers or group them, the logic stays consistent. And knowing these properties of numbers will not only help your child find the right answer, but also do that in a more efficient way.
To help your child make sense of different number properties in math, we’ve prepared this comprehensive guide, where we will look into key properties, a formula chart, fun facts, examples, and more.
About number properties
The number properties are the fundamental arithmetic rules, using which we define how numbers (and letters representing numbers) interact with each other when we add, subtract, multiply, and divide. Without this, trying to solve even the simplest problems in math would be a chaotic trial-and-error. Instead, these properties of math and numbers help us to simplify expressions and solve for variables in a logically sound way.
What are number properties?
To put simply, the number properties in math are the rules that define how numbers interact together during mathematical operations (from simple additions to more complex equations). They make sure that no matter how you arrange the numbers, the logic and the results remain consistent.
Below, we will explore what are all the properties in math, as well as some number properties examples.
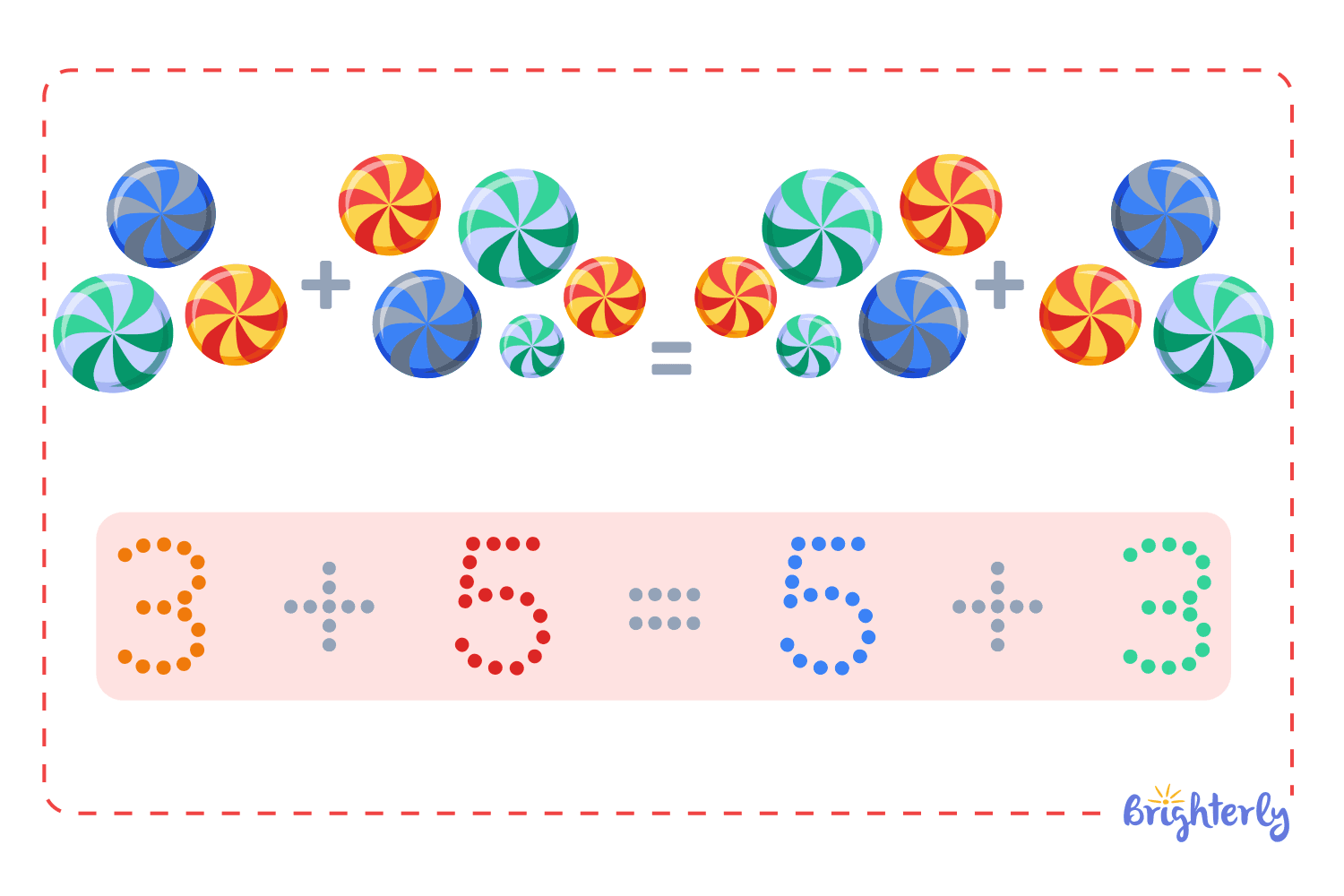
Commutative property
The word commutative originates from “commute”, which means to move or exchange, and it encapsulates the principle of this property perfectly. The property states that the order of numbers does not change the final result when you are adding or multiplying.
Let’s look at the example of numbers 3 and 9. When adding 3 + 9, the answer is 12, right? Now, if we flip the numbers and 9 + 3, we will still get 12. The same is true for multiplication, as 5 x 4 = 20, and 4 x 5 = 20 too.
Associative property
The next one in the list of types of properties in math is the associative property. As in the previous case, the name of the property gives it away. According to this property, the way you group (or associate) numbers when using parentheses doesn’t affect the outcome when adding or multiplying.
Let’s look at math property examples of the associative property. In the addition example below, no matter how we group 6, 7, and 8, the answer will always be 21:
- (6 + 7) + 8 = 21
- 6 + (7 + 8) = 21
The same is true for multiplication, because no matter how we group them when multiplying 6, 7, and 8, the answer will always be 336.
Distributive property
Another one of the number properties in math is the distributive property, and it’s a very interesting one! This property states that if a number is multiplied by the sum of two numbers, the answer will be the same if you multiply the number by each of the two numbers and make an addition. This may sound a bit confusing, but it’s quite simple. Let’s look at an example of this property.
- 3 + 4 = 7
- 5(7) = (5 x 3) + (5 x 4) = 35
This property is especially often used in algebra, and your child will come across it a lot, especially when they need to simplify equations.
Identity property
The last property is the identity property. This one doesn’t have a single formal definition, because there are two sub-types here, but overall, the name refers to the “identity” of the number (its value) remaining unchanged after operations. There are two types of operations under this number property:
- Adding 0 to or subtracting 0 from the number keeps the value the same
- Multiplying or dividing a number by 1 doesn’t affect its value
Let’s look at an example. In the case of multiplication and addition, 0 doesn’t add or take away from the number, leaving it exactly the same as it was before the operation.
- 8 + 0 = 8
- 8 – 0 = 8
In the case of multiplication and division, using 1 for the operations doesn’t change the number’s value.
- 16 x 1 = 16, as in the number 16 already contains 1 number 16
- 16 / 1 = 16, as there are 16 units of one in the number 16
Distributive property of multiplication over addition
The distributive property of multiplication over addition is just another way to describe the distributive property of numbers. So, if your kid comes across this term, they shouldn’t be confused. In fact, this title is a bit more descriptive, as it tells them exactly what the property does: it distributes multiplication over addition.
The main idea of this number property is that if you multiply a sum by a number, it would be the same if you multiplied each individual number in that sum by the multiplier and then added the results together.
Understanding this property will be a lifesaver for your child once they start algebra. While adding 10 + 2 to get 12 is easy, when they have variables like x in parentheses, addition becomes a bit trickier. In cases like this, this property helps simplify expressions like 5(x + 4), even though we cannot add x + 4 to get a single answer. In this case, we can “hand out” the multiplier 5 to both numbers, getting a 5x + 20, which is much easier to solve.
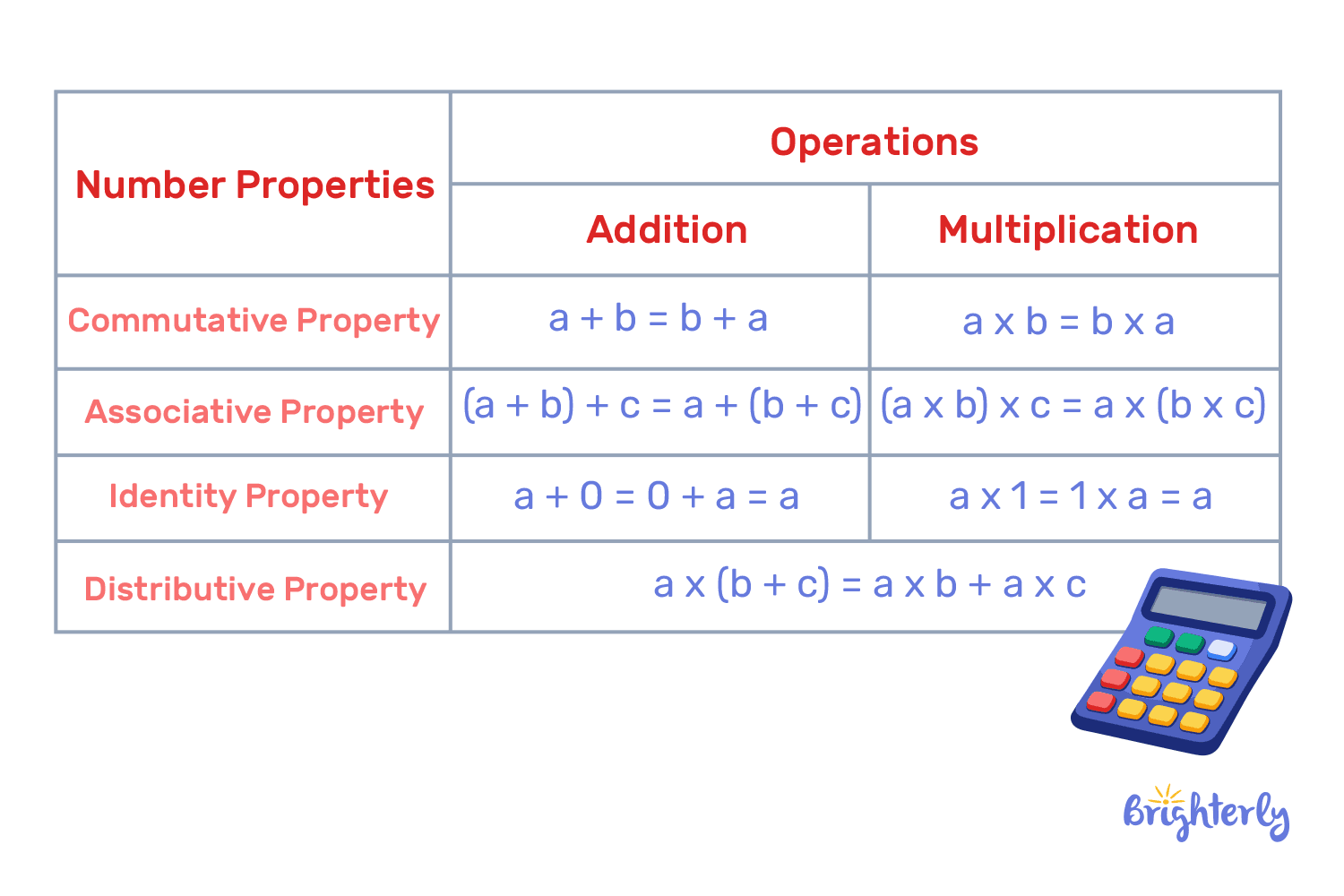
Formula chart of basic number properties
As with almost every other concept in math, all properties of math have their formulas, which can help students memorize them more easily.
Commutative property
- a + b = b + a
- c x d = d x c
This property states that the value of the answer doesn’t change if you flip the order of the added or multiplied numbers.
Associative property
- Addition: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
- Multiplication: (a × b) × c = a × (b × c)
In the case of addition and multiplication, how the numbers are grouped in parentheses doesn’t affect the final value.
Distributive property
- a x (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
When you multiply a number across a sum, you will get the same outcome if you multiply the same number by each part of the sum.
Identity property
- Addition/subtraction: a + 0 = a, a – 0 = a
- Multiplication/division: a x 1 = a, a / 1 = a
This property states that the value of a number doesn’t change when 0 is added or subtracted, or when the number is multiplied or divided by 1.
Solved examples of number properties
Here are some more solved exercises to give you a better idea of what are the 4 properties of math with examples and how they look in practice:
1. Simplify the expression 18 + 47 + 2 using the commutative property of numbers and find the answers.
Solution: We know that changing the order of the numbers won’t affect the outcome, so we can simplify the expression as 47 + 18 + 2, 18 + 2 + 47, 2 + 18 + 47, etc. We can also use the sum of two numbers, like 20 + 47 or 18 + 49, to get the answer.
Answer:
| 18 + 47 + 2 = 67 |
2. Which property can we use to solve 7(20+3)?
Solution: We need to use the distributive property, which applies when multiplying by addition. Here, we need to distribute 7 to both numbers, and then find the sum, like so (7 x 20) + (7 x 3) = 140 + 21 = 161
Answer:
| Distributive property, 7(20+3) = 161 |
3. Simplify (14 x 5) x 2 with the relevant property.
Solution: Here, as you can remember from the properties of numbers with examples we looked into, we need to use the associative property, which states that the way the numbers are grouped doesn’t affect the result in the case of addition and multiplication.
Using this property, we can regroup the expression to make finding the answer easier. One way to do it is by regrouping it to 14 x (5 x 2). 5 x 2 = 10, and multiplying by 10 is easier than multiplying by 14. So, (14 x 5) x 2 = 14 x (5 x 2) = 14 x 10 = 140
Answer:
| Associative property, (14 x 5) x 2 = 140 |
Practice problems of number properties
- Simplify using the commutative property:
25 + 89 + 75 = ?
16 + 14 + 27 = ?
- Apply the distributive property:
6(10 + 4) = ?
12(5 + 3) = ?
- Group to simplify using the associative property:
(17 x 4) x 24 = ?
5 x (5 x 6) = ?
- Check the identity of the number:
526 + 0 = ?
14 – 0 = ?
148 x 1 = ?
1974 / 1 = ?
Fun number properties facts!
Did you know that all math properties, while they seem dry at first sight, have many cool quirks?
- 0 is a powerful number, as it can fully delete another number when multiplied by it. When you multiply a number by 0, the answer will always be zero. This is known as the zero property of multiplication.
- The identity properties are unique to their operations, with 0 only applying to addition and subtraction, and 1 only applying to multiplication and division.
- The distributive property is a well-known trick among people who solve large problems in their heads, often subconsciously, as it makes the process easier. For example, 12 x 15 = (12 x 10) + (12 x 5) = 120 + 60 = 180
Pretty fun, isn’t it? This is definitely not an exhaustive list of number properties in math, but it can give a glimpse into how interesting the topic actually is.
Conclusion
Number properties might seem like just a list of rules to memorize, but they are actually the secret shortcuts that can make math easier and much more fun for your child. By understanding properties math definition and examples, your child can learn how to move numbers around like pieces of a puzzle to find the simplest path towards the right answer.
We hope this article was a useful resource to learn about math properties and examples, and that your child will be more confident when tackling numbers and operations going forward.
Frequently asked questions about number properties
What are the 4 properties of math with examples?
The main properties of math are:
- Commutative (3 + 2 = 2 + 3)
- Associative (1 + 2) + 3 = 1 + (2 +3)
- Distributive 2(3 + 4) = 2×3 + 2×4 = 6 + 8
- Identity (5 + 0 = 5, 5×1 = 5)
What is a number property?
Number properties in math are rules that apply to a set of operations and govern how we perform those operations. These laws define how numbers interact so that our calculations are organized and accurate, regardless of how the numbers are grouped.
Why are number properties important in mathematics?
Number properties are among the core concepts of mathematics because they enable us to perform operations correctly, simplify equations, and solve for unknown variables. For students, these rules provide a logical framework that they can use to approach algebraic expressions in a more structured way.
Do number properties apply to all mathematical operations?
As we’ve seen in the examples of math properties earlier, each number property applies to specific operations. For example, the commutative property applies only to addition and multiplication, while the identity property applies only to adding/subtracting 0 and multiplying/dividing by 1.
What is the difference between the distributive property and the distributive property of multiplication over addition?
There is no functional difference, as these are simply the terms we use to describe the property. The distributive property of multiplication over addition is the full formal, and more descriptive, name, while the distributive property is simply the shorter and commonly used version.
Number properties: Worksheets
The free printable worksheets below can help you put your newly acquired knowledge into practice. All come filled with engaging exercises related to number properties and fun puzzles.