Common Core Math Standards
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on October 23, 2025
After decades of solving math problems a certain way, educators start to prefer teaching Common Core math. Although it may seem complex to some parents, the importance of this approach in the US can hardly be diminished. But what is Core math in essence? And what are its benefits? Let’s demystify.
Key points
- Common Core math focuses on coherence, depth, and rigor, helping kids understand the “why” behind math rather than just memorizing rules.
- This approach builds critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application skills.
- Some parents and students find it challenging at first because it requires conceptual understanding rather than rote learning.
- With personalized tutoring, Common Core-aligned worksheets, and customized learning plans, Brighterly helps kids master math with confidence.
What’s Common Core math?
The Common Core math standards define coherence, focus, and rigor as three main focal points for education. Under this system, children should cover fewer topics but study them in depth.
Instead of choosing the first and easiest solution, Common Core mathematics pushes kids to question the “why” behind each equation. For example, after solving a task, the kids don’t just move on to the next question; they have to figure out why the solution they picked worked in the first place.
So, the answer to “Why choose mathematical practices in the Common Core style?” is simple: these standards help kids build critical thinking and analytical skills!
Why mastering Common Core math problems can be hard
Despite many benefits, some children and parents find Common Core practices complex, as understanding the concepts instead of simple memorization can be really more complicated at the first stages. But this approach is beneficial in the long run.
Here’s what Geillan Aly, founder and CEO of Compassionate Math, has to say about how to teach Common Core math so it really works for both parents and kids:
“Parents commonly feel uncomfortable with Common Core math. But the main reason for this is that our generation was taught using algorithms and rules without providing meaning.”
As a parent, if you want to help your child with their math, ask them to explain what they understand. Have them show you what they learned and what method they used. This way, you’ll be able to figure out the idea they need help with.
How does Common Core math work?
Common Core math takes a narrower approach to subject concepts than traditional math. In this progressive strategy, each new lesson is built on past knowledge with a strong emphasis on real-world problems and cases. This way, kids can apply their wisdom practically.
How to do mathematics Common Core with Brighterly
Brighterly math and reading platform team believes in the power of Core standards in math and their ability to change how well children succeed in the subject and their future careers. To achieve this aim, Brighterly experts have built a system where kids can get proper tutoring support with Common Core math resources tailored to their needs.
Benefits of mastering Common Core math standards with Brighterly
Professional tutoring help
For math tutors at Brighterly, teaching to help kids understand is their philosophy. This approach, combined with the careful Common Core math tutor selection and personalized 1:1 lessons, creates a friendly and cooperative atmosphere where students can grasp even the most complex ideas.
Personalized Common Core curriculum
At Brighterly, you get a learning plan based on the Common Core math curriculum that is adjusted to your child’s preferences and individuality. In particular, tutors use Common Core math resources, information, and techniques, yet tailor the pacing and content of the class to create a safe and comfortable environment for your kid.
Common Core-aligned worksheets
Among various learning materials on the platform, students can practice both math and reading topics in dedicated Common Core worksheets. These free printable materials are designed to bring confidence in math and reading by being fully aligned with Common Core standards.
Additionally, you can browse diagnostic tests and math worksheets for kids to find exercises that train the basic understanding of addition, division, measurements, geometry, algebra, and many other areas. All these materials are also available on the Brighterly website for free!
How many states still use Common Core math?
The American Common Core math practice standards were developed in 2010 and have been adopted in 30 US states. 15 other states either revised, repealed, or replaced these standards with their own, and 4 states never adopted them. One state partially adopted Common Core for English Language Arts only.
Adopted |
Adopted with changes |
Never adopted |
Partially adopted |
| California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Maine, Maryland, Michigan, Mississippi, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Dakota, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin, Wyoming | Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Missouri, New York, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Carolina, West Virginia | Alaska, Nebraska, Texas, Virginia | Minnesota |
Source: World Population Review
Common Core math for grades 1-5
Common Core math lessons for grades 1-5 cover the basic operations and algebraic thinking, numbers and operations in Base 10, measurement and data, and geometry. The details for each grade are in the table below.
| Grade | Key skills and focus areas |
| Grade 1 |
|
| Grade 2 |
|
| Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
|
| Grade 5 |
|
Common Core math for grades 6-8
Common Core math practices for kids in grades 6-8 aim at building a solid foundation in several main domains that help them prepare for high school math and real-world problem solving. Below is a detailed grade-by-grade overview of these domains.
| Grade | Key skills and focus areas |
| Grade 6 |
|
| Grade 7 |
|
| Grade 8 |
|
Common Core math for grades 9-12
The Common Core math standards for grades 9-12 focus on deepening students’ understanding and skills like problem-solving and reasoning. They are essential to successfully graduate from school and enter college, as well as for further professional development. See more details below.
| Domain | Description | Examples |
| Number & Quantity | Understand complex numbers, vector quantities, and related operations. | Find conjugates of complex numbers, add or subtract vectors. |
| Algebra | Create, interpret, and manipulate equations, expressions, and inequalities; solve systems. | Factor quadratics, solve rational and radical equations, and solve systems of equations. |
| Functions | Understand, evaluate, and analyze functions, including sequences and function notation. | Interpret function notation, graph, and compare functions. |
| Geometry | Work with transformations, matrices, and geometric representations, including vectors. | Use 2×2 matrices for transformations, and represent complex numbers geometrically. |
| Statistics & Probability | Analyze data, calculate probabilities, and make inferences. | Analyze and interpret data reports to make assumptions or basic predictions |
Common Core mathematics standards
In this section, Common Core math is explained with more details and real-life examples to show where this knowledge can be used apart from a math class.
Teaching to understand problems
Problem-solving is one of the key Common Core math examples. Think about the case when your child first encounters a topic. What do they do then? Right, they move to solve the problems attached. After all, it’s what they got their marks for.
This approach is a huge concern. According to all Common Core standards, math students should first understand the topic and have its clear explanation in their heads and only then move to solving related tasks. Why does it matter?
- Children can hardly remember and reproduce the information they mindlessly memorized even a year ago.
- Without proper understanding, kids can hardly build on what they’ve learned and adopt more complicated topics. Thus, they are less likely to succeed in the subject in the long run.
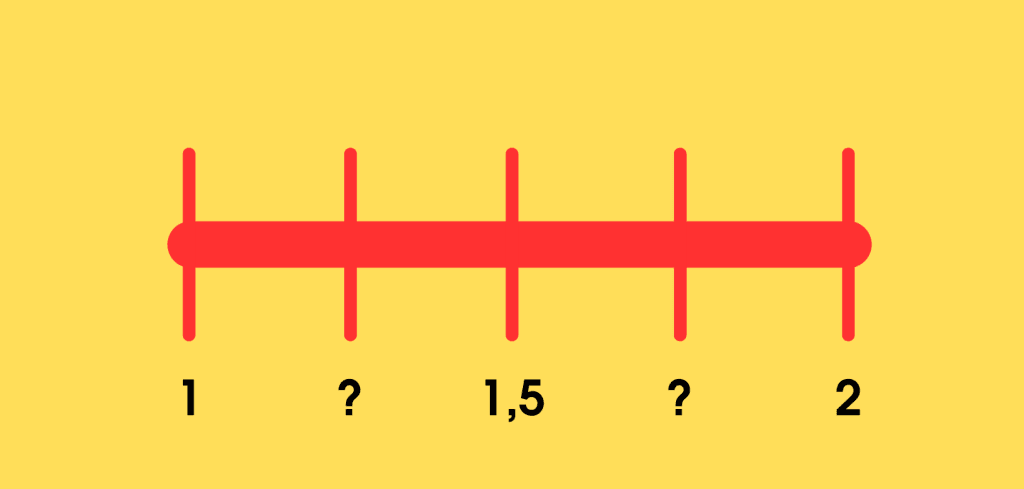
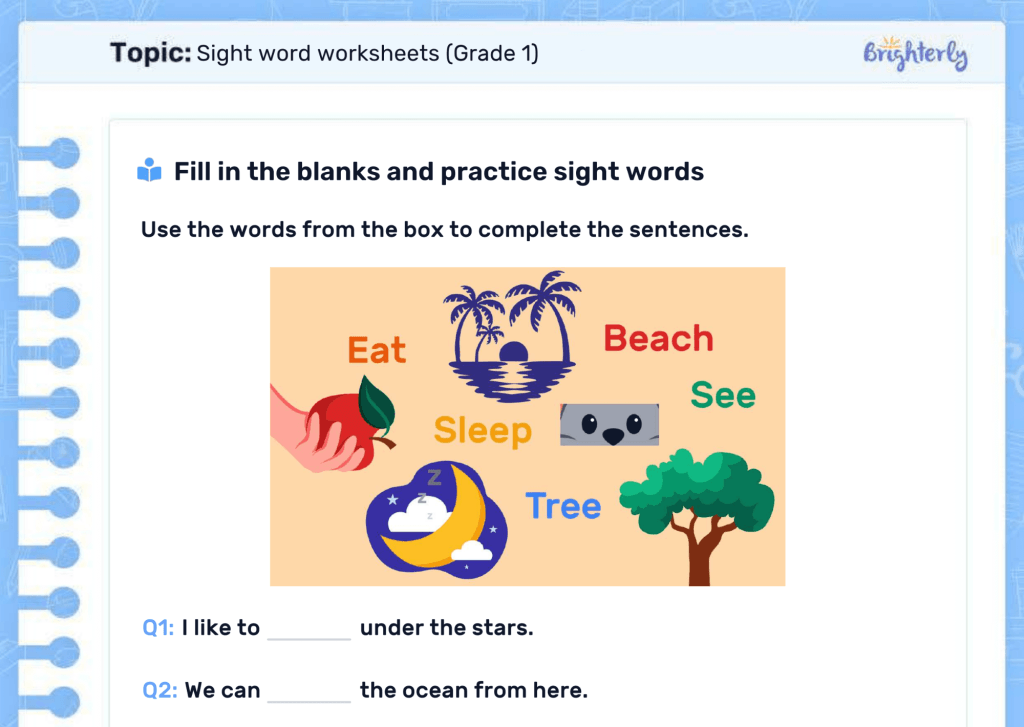
Above, you can see one typical example of Common Core math problems for 4th to 6th math classes. It teaches kids a few things:
- Conceptual understanding relations between numbers (which is a solid knowledge base to use in future studies);
- The actual subject — learning to define and write decimals.
Thinking quantitatively and abstractly
This means that children should make sense of quantities and use them when solving problems. So, actually, the point entails two Common Core standards for math:
- think outside of the given situation and learn to represent it symbolically or decontextualize
- and, also learn to find the context or contextualize.
Let’s take this task as an example:
A bakery sells muffins in boxes of 6. Each box costs $12.50. If Mary wants to buy 18 muffins, how much would she need to pay?
Contextually, children should step away from the problem and get a kind of parachute view of it. First, they should understand that the price listed — $12.50 — is given per box (which contains 6 muffins). So, the right solution is to calculate how many boxes we need related to the number of muffins in one box.
The decontextualization works the opposite way. Children shouldn’t be distracted by an abstract task description (all the muffins affair meant). Instead, they should learn to define an equation hidden behind the story: 6x = 18 muffins. The cost per box is $12.50, so the total sum Mary must spend is 12.50x.
Constructing and critiquing viable arguments
Common Core mathematics standards demand that kids use previously learned information to build on and explore their ideas. They should make guesses, produce fresh ideas along with their current knowledge, be able to explain their point to other students, and delve into why some things work and others don’t.
The youngest learners usually try to explain concepts with elementary tools like drawings, diagrams, and actions. As they grow, they start analyzing how their ideas work in different situations.
Modeling with mathematics
Each student has a different learning style, but one thing is clear for any of them — having a real-world example in mind is the best way to memorize something and better apply it in the future. Knowing that 1000 meters equals 1 km is not enough. Kids should understand what those things mean when on a journey. According to the math standards in Common Core, this applies to all concept types.
Delving further, the teacher will likely start explaining the topic by describing the distances children often have to cover. For example, they can try to describe the length of a schoolyard or ask kids to define the way they travel from home to school.
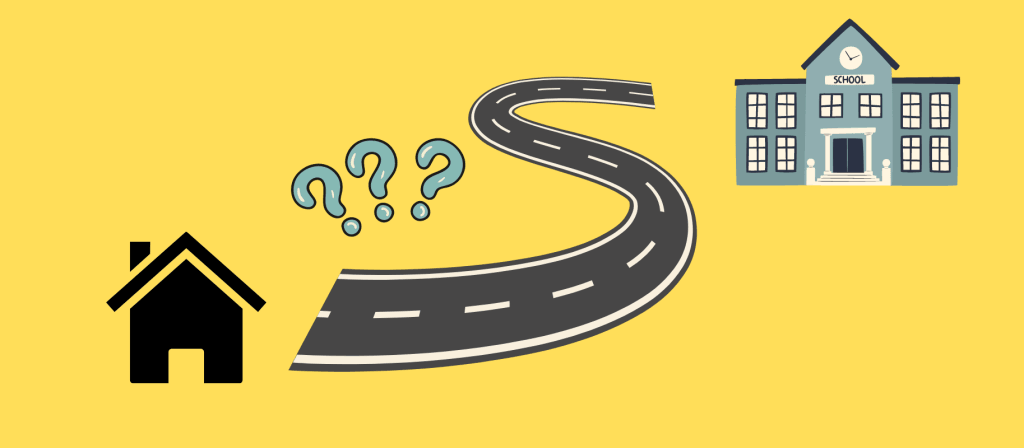
This Common Core math example also helps kids develop spatial awareness, visualization, and imagination. Knowing the basics of geometry and arithmetic will help them plan routes and understand more complex 3D shapes. With visualization skills, it’ll be easier for a student to scale models, understand the proportions, and navigate maps.
Modeling is also used in the graphic design department and digital arts, which are naturally more creative areas.
Using the appropriate tools
Hundreds of tools help solve Common Core math problems or apply solutions to real-life situations. However, the number of existing tools supersedes the number of students who know how to use them.

Ok, so during regular math classes, teachers just say which tools to use. But what if kids learn to find those tools on their own? For instance, teachers can ask them to compile a list of resources needed to work with some math topic. This works for elementary to middle school. As for senior learners, they may be asked to find the best resources on a topic beyond classroom materials (like books or websites).
Building precision
As one of Common Core learning standards, math precision is about learning to communicate explicitly and clearly with others. Students should be able to provide definitions and reasonings for the concepts they learn to show they really understand them.
In the early stages of education, children can build precision by explaining what they think about a symbol or math problem to their peers. Their attempts may seem humble and distorted at first, but they will improve as children mature. In high school, they learn to provide complex definitions and support a discussion on advanced concepts that require much reasoning from their side.
Building dialogs is another powerful technique. One student asks for the meaning of a concept they don’t understand, and classmates try to explain Common Core math things to them — that’s how it works.
Thinking structurally
Structural thinking is the key Common Core math method. While traditional math approaches usually provided isolated explanations, Common Core encourages finding unique links between new skills and knowledge with those formerly obtained.
By learning and recalling previous topics, students are more likely to recognize patterns and break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. This simple twist makes the whole process more consistent and efficient.
Structural thinking also promotes using repeated reasoning from past problems in the current ones. This teaches students to adapt and adjust their solutions based on the discovered similarities. Also, it helps strengthen past knowledge and make it a solid basis for the newly obtained skills, define similar patterns, and adjust specific algorithms to solve problems more efficiently.
Learning to find regularity
The simplest answer to what is the point of Common Core math transition is that it helps find regularity in problems. With this approach, students learn to find repeated patterns or similar algorithms, thus solving problems more easily. These standards also help see complex problems as a set of smaller steps they can resolve one by one.
For instance, kids learn that multiplication is a simplified form of repeated addition, or that the formula (x – 1)*(x + 1) can be shortened into x^2 – 1. This can make math less stressful and more enjoyable for them.
Benefits of Common Core math
For those wondering why Common Core math is more practical and efficient than traditional ways, here’s a table showing the key differences between these two concepts.
Common Core math |
Traditional math |
|
| Approach | Stresses reasoning and conceptual understanding | Focuses on memorization, procedural steps, and getting correct answers |
| Problem solving | Promotes multiple problem-solving methods | Typically offers one standard method or algorithm for solving a problem |
| Focus | Provides fewer topics yet taught in detail for deeper fluency | Covers a wider range of topics, but in less depth |
| Critical thinking | Emphasizes critical thinking, reasoning, and explanation | Focuses more on getting the right answer rather than explaining the solution |
| Real-world application | Incorporates math into real-world scenarios for practical problem-solving | Puts more focus on abstract problems |
| Use of visuals and models | Implements visual aids and decomposition for deeper understanding | Focuses more on memorization of formulas and algorithms instead of visualization |
| Communication | Encourages discussion and explanation | Doesn’t focus on the discussion, pays more attention to the correct answers and calculations |
| Assessment | Assesses deeper understanding, application, and reasoning skills | Assesses the ability to recall the right formulas and accurately integrate required methods |
Conclusion
Simply put, Common Core math meaning is to help students understand the “why” behind math. Its standards help students flexibly apply the discovered concepts in real life and find different ways of solving problems, while traditional math principles focus more on procedural accuracy and memorization.
Here are the exact benefits of Common Core math vs traditional math examples:
- Common Core standards focus on a deeper understanding of the given topic rather than just memorizing formulas and rules to solve problems.
- Students profess flexibility in problem-solving, finding multiple ways of resolving problems instead of just one standardized algorithm.
- Common Core promotes critical thinking by not just finding but also explaining solutions, constructing arguments, and reasoning instead of focusing on the right answer.
- Real-world problems are part of the Common Core approach that makes math more applicable in everyday life.
- Common Core standards are based on progressive concept building, based on connecting new and prior knowledge.
If you’ve made a decision to start learning Common Core math or improve your current progress under its standards, there is nothing better than hiring a private tutor for this aim. And the great news is that Brighterly Common Core tutors can work with your child for one lesson completely free of charge!
Just book free lesson now and get the action plan to boost math confidence for your kid.