New Math vs Old Math: Understanding the Difference
reviewed by Mary Grace Carlos
Updated on October 20, 2025
Learning is changing, and so are schools and education practices. Math class doesn’t look the same as it did decades ago. The new math teaching method aims to help kids learn, but leaves parents puzzled and occupied. In this new math vs old math review, I break down these two concepts, underline differences, and show why new math is here to stay.
What is new math vs old math?
Old math is concerned with traditional ways of learning mathematics, relying on memorizing formulas and procedures, while new math, associated with Common Core, focuses more on understanding concepts behind the math, using multiple math strategies to solve problems.
Both old and new math strategies aim to help students give the right answers, but follow different paths to get there.
New math vs old math: A brief overview
Old math |
New math |
|
| Primary approach | Kids follow a set of formulas and standard algorithms | Use multiple strategies and reasoning |
| Focus on | How to solve (procedural fluency) | Why it works (conceptual understanding) |
| Tools and methods | Memorization, drills, paper-and-pencil calculations | Visual models and breaking numbers apart |
| Pros | Efficiency, strong knowledge of basics, and straightforwardness. | Makes kids understand concepts, flexibility, variety of strategies, and consistency. |
| Cons | Focus on drills and a lack of math understanding, little flexibility, anxiety, and disengagement. | Learning curve, complexity, and time, poor basic skill development |
What is new math?
New math is an approach to math education that puts understanding and investigation at the center of kids’ learning. Instead of memorization and following a formula, children aim to explore why the answer solves the question.
Importantly, the new math approach became popular in elementary schools after 2010, upon the adoption of the Common Core standards initiative.
Note: The roots of the term trace back to the 1950s, when the concept was first introduced and aimed to teach kids to apply math in relation to real-world problems.
The primary principle behind the new math method is encouraging students to break down problems into simpler parts. It allows learners to solve them step by step.
New math method pros
- Real understanding. As kids learn meaning, not just procedure, they may apply math to real-world problems and tasks.
- Variety of strategies. Upon using new math strategies, they will know different ways to solve problems, supporting flexible thinking and problem-solving.
- Consistency and shared values. New math curricula are consistent among many schools thanks to the Common Core approach, which is helpful for their future studies and integration.
New math method challenges
- Learning curve. If you compare old math vs new math, the differences are vivid. Moreover, parents may find them confusing, while teachers struggle to adapt.
- Time and complexity. Methods and approaches may take more time to understand or explain compared to simple memorization. This new math can feel slow, especially for parents.
- Poor basic skills development. The focus on ideas and principles instead of repetitive practices means a kid spends less time on drill basics. In particular, a kid would know what subtraction is, but can fail to be really good at it.
With new math explained, it’s clear why parents turn to math tutors or math learning websites like Brighterly to bridge the gaps. Brighterly math and reading platform takes the best parts of the new math method to make learning clear and practical for every child.
It’s not just a tool. It’s a school-supplemental K-12 platform focused on building math foundations via interaction. How? Through personalized 1:1 math classes that follow US state standards.
Thus, it’s a great way for you to help your kid catch up, stay on track, or simply learn math with confidence.
What is old math?
Old math relates to the traditional ways of learning that imply rote memorization of formulas, rules, and procedures when solving problems or getting an answer. In other words, it uses rote learning, the approach many of us remember from school.
It assumes a kid follows one set way to approach each type of math problem until they can do it automatically. Here, the main goal is to get the correct answer via one standard method.

Old math benefits
Sure, old math has its benefits:
- Efficiency. As standard algorithms are quick to learn, with enough practice, children can calculate quickly.
- Knowledge of basics. Repetition and drills, let’s say times tables, build a strong math foundation. That’s why you can recall some basic math procedures without revising.
- Simplicity. Using one method makes it easy for kids and teachers, as everyone focuses on it.
Old math challenges
- Lack of understanding. Simple rote learning does little to show kids why they learn math in schools. It negatively affects their comprehension and, in turn, motivation.
- Little or no flexibility. Relying on one single formula can easily make kids stuck. If a student forgets a step or formula, they will miss a piece and offer a wrong answer to the problem. It can bring disengagement to the math class.
- Math anxiety. On top of it, learners may find math boring or even intimidating. Forgetting a rule brings the risk of failure. At the same time, rote learning with no context makes learning feel like a dry and nonsensical activity. Therefore, old math can be a source of frustration and anxiety.
New math vs old math example: Will one be enough?
A good way to compare traditional math vs Common Core approaches is to analyze how each of them solves the same math problem.

Let’s look at some old and new math examples related to addition, subtraction, and multiplication:
Old math vs new math addition
Here’s an example of the primary math practice: addition.
How would a kid add 48 to 27?
Under old math, it works this way:
- First, a kid writes the numbers one under the other and adds column by column.
- Then, they would add the ones: 8+7=15. From there, they write down the last digit 5 and carry the 1 to the tens.
- Next, they add the tens: 4+2+1 (they carry one from the previous step)=7.
- Finally, they get 75.
What does the new math teaching method bring? Well, it approaches the 48+27 problem in a more conceptual way:
- First, a kid will break numbers into place values. It means the number 48 becomes 40 and 8, while 27 becomes 20 and 7.
- Next, a kid would add the tens (40+20=60) and add the ones (8+7=15).
- After that, your kid would add the results (60+15) and get the answer, which is 75.
Comparing old math vs new math addition, you can see how a teacher would introduce a place value concept at a younger age.
Old math vs new math subtraction
Now, let’s see how a kid would be taught subtraction.
How do they solve 52-19?
If using old math, your kid will use a traditional borrowing method:
- First, they put a column in numbers, 52 over 19.
- Next, since 2 is less than 9, they would borrow 1 from 5 to make 12 in the ones place.
- Then, they subtract 9 from 12 and get 3.
- Now, they switch to tens. As they borrowed 1 from 5, it’s now 4. So, they subtract 1 from 4. 4-1=3.
- In the end, the answer they get is 33.
In comparison, a new way of teaching math would encourage a student to think of subtraction as finding the difference. It will ask, “To get 52, what do I add to 19?”. Seems a bit odd, right?
Yet, a kid would use addition to solve a subtraction problem:
- A kid would add 1 to 19 to get 20, then add 32 to get 52.
- Next, they will add 1 to 32 and get 33 in total.
- So, 52-19=33 but via addition.
What do these new math method examples tell us? Those friendly numbers, like 20, simplify thinking. Besides, it shows that subtraction is an inversion of addition and adds to better math understanding.
Note: Such an approach helps them to apply math in the real world and supports the ability to solve math word problems.
New math vs old math multiplication
What about multiplication, a pretty common practice for 4 grade kids?
Solve 27×12.
Under an old math problem, a child may use a long multiplication algorithm.
For it, they will:
- First, multiply 27 by 2. The result is 54.
- Next, multiply 27 by 10. The result is 270, as you essentially add a zero.
- Finally, add the results of these two parts: 54+270=324. So, when a kid multiples 27 by 12, they get 324.
How does a new math multiplication work? One of the options is to use the area method, also called the box method. Under it, a kid will need to:
- First, split 27 into 20 and 7, then split 12 into 10 and 2.
- After it, a kid will need to multiply 20 by 10 (get 200), then 20 by 2 (get 40).
- Next, they would multiply 7 by 10 (get 70) and 7 by 2 (get 14).
- Finally, add these partial products: 200+40+70+14. The result is 324.
Overall, old math and new math strategies produce the same results. The difference is that new math takes a conceptual approach. So, a kid knows more about place value and distributive properties.
You can see such a contrast between methods in almost all math topics. Old math users would use long division and fraction multiplication, while new math users would resort to visual models and use a set of strategies.
How does new math work?
New math works by making a student an active problem solver who knows how to use different strategies to approach math problems. It focuses on conceptual understanding, real-world application, and breaking complex questions into smaller parts.

A new way of teaching basic math won’t revolve around one drill to do a calculation; it will encourage learners to explore numbers in depth.
Some of the strategies that new math tutors may include:
- Using physical objects and visual aids, like blocks or a number line, or drawing pictures to represent a problem.
- Framing math problems into real contexts (let’s say splitting a pizza or measuring distance).
- Offering multiple strategies, as there is no “correct” one.
- Asking to explain the mathematical reasoning behind solutions with words or drawings
Note: New math in schools won’t focus solely on concepts; it includes homework, practice, drills, and memorization as well. Yet, understanding the topic always comes first, and then kids use math worksheets to practice at home.
In the end, new math helps develop an intuitive sense of the numbers and their relationships that students use over time.
Note: If you are looking for some tips to help your kid with math, check out How to improve math skills guide.
How is math taught now?
Today, new math in schools is taught under Common Core principles or a similar state curriculum, depending on how districts adopt standards. It’s designed so that concepts build on each other each year, while math students move from basic arithmetic to more advanced math smoothly.
How is the new way of teaching math organized?
- New math revolves more around exploration and debates. The role of a teacher is to guide a group discussion, correct mistakes, and highlight the reasoning that fits best.
- A teacher is more likely to present a problem and ask a student to solve it.
- In a class, children may work in groups with manipulatives, including blocks and beads, to find an answer to math problems via different solution methods.
- The same goes for assignments, math worksheets, and math tests that may require solving a problem in two ways, and after it, supporting it with an explanation for the choice of strategy.
That way, the new math method teaches through collaboration and support instead of the drills common for a traditional math class. Moreover, it is quite flexible, whereas teachers would adapt lessons and include specific math goals for IEP, or Individualized Education Programs.
So, math is taught with a blend of activities for comprehension, real-world scenario solving, and practice to support students in being fluent in calculations and problem solving.
However, as the concepts have been a source of debate, some new math vs old math Reddit reviews emphasize that collaboration won’t work for all, making students fall behind.
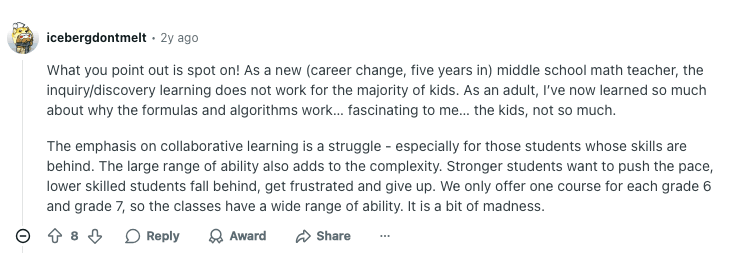
There, a balanced approach, with enough practice and attention, may help a kid catch up. Brighterly math and reading platform offers 1:1 tutoring, where its teachers create an individual math program for your kid.
Brighterly makes new math for kids fun and clear, so that children can use it at school and at home.
What is the difference between new and old math?
The difference between old math and new math lies in their approach and philosophy. Both want the kids to know how to produce answers to math problems, but old math is more about learning procedure, while new math leans toward understanding the concepts.
Old math prioritizes speed and memorization within a system built on algorithms and repetition. There, it’s better to use one way for certain math problems. New math is different in this regard, as it wants to show multiple ways to find solutions and improve understanding of how concepts can help solve problems applied to real life.
New math vs old math: Conclusion
Education keeps changing, and so does the way students learn math. As this new math vs old math review shows, there are advantages and disadvantages of both methods.
The new way of learning mathematics will certainly stay, as it brings more than fast results coming from drills. It builds lasting understanding and supports the application of math in the real world. Moreover, new math helps kids to be confident, not confused.
If you want your kid to learn math in more engaging way, book free math lesson now, and see how Brighterly’s personalized 1:1 classes work.